Abstract
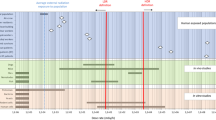
Recently, the risk associated with low doses of ionizing radiation has gained new interest. Here, we analyze and discuss the major differences between two reports recently published on this issue; the report of the French Academy of Sciences and of the French Academy of Medicine published in March 2005, and the BEIR VII—Phase 2 Report of the American National Academy of Sciences published as a preliminary version in July 2005. The conclusion of the French Report is that the linear no-threshold relationship (LNT) may greatly overestimate the carcinogenic effect of low doses (<100 mSv) and even more that of very low doses (<10 mSv), such as those delivered during X-ray examinations. Conversely, the conclusion of the BEIR VII report is that LNT should be used for assessing the detrimental effects of these low and very low doses. The causes of these diverging conclusions should be carefully examined. They seem to be mostly associated with the interpretation of recent biological data. The point of view of the French Report is that these recent data are incompatible with the postulate on which LNT is implicitly based, namely the constancy of the carcinogenic effect per unit dose, irrespective of dose and dose rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joint Report n° 2, Académie Nationale de Médecine, Institut de France—Académie des Sciences (March 30, 2005) Tubiana M, Aurengo A, Averbeck D, Bonnin A, Le Guen B, Masse R, Monier R, Valleron AJ, de Vathaire F. Dose–effect relationships and the estimation of the carcinogenic effects of low doses of ionizing radiation. (http://www.academiemedecine.fr/actualites/rapports.asp) Edition Nucleon (Paris 2005) ISBN 2-84332-018-6
BEIR VII (National Research Council of the National Academies of USA). Health risk from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation. Pre-publication version. July 2005
Tubiana M (2005) Dose–effect relationship and estimation of the carcinogenic effects of low doses of ionizing radiation: The Joint Report of the Académie des Sciences (Paris) and of the Académie Nationale de Médecine. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:317–319
Brenner DJ, Doll R, Goodhead DT, Hall EJ, Land CE, Little JB, Lubin JH, Preston DL, Preston RJ, Puskin JS, Ron E, Sachs RK, Samet JM, Setlow RB, Zaider M (2003) Cancer risk attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: assessing what we really know. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13761–13766
Cardis E, Vrijheid M, Blettner M, Gilbert E, Hakama M, Hill C, Howe G, Kaldor J, Muirhead CR, Schubauer-Berigan M, Yoshimura T, Bermann F, Cowper G, Fix J, Hacker C, Heinmiller B, Marshall M, Thierry-Chef I, Utterback D, Ahn YO, Amoros E, Ashmore P, Auvinen A, Bae JM, Solano JB, Biau A, Combalot E, Deboodt P, Diez Sacristan A, Eklof M, Engels H, Engholm G, Gulis G, Habib R, Holan K, Hyvonen H, Kerekes A, Kurtinaitis J, Malker H, Martuzzi M, Mastauskas A, Monnet A, Moser M, Pearce MS, Richardson DB, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Rogel A, Tardy H, Telle-Lamberton M, Turai I, Usel M, Veress K (2005) Risk of cancer after low doses of ionising radiation: retrospective cohort study in 15 countries. Brit Med J 331:77–83
de Vathaire F (2005) Annexe 4: Les données épidémiologiques. In : Rapport conjoint n° 2 Académie Nationale de Médecine, Institut de France—Académie des Sciences (30 mars 2005) La relation dose–effet et l’estimation des effets cancérogènes des faibles doses de rayonnements ionisants (Edition Nucleon) pp 147–168
Carnes BA, Groer PG, Kotec TJ (1997) Radium dial workers: issues concerning dose response and modeling. Radiat Res 147:707–714
United Nations Scientific Committee on the effects of atomic radiation, sources and effects of ionizing radiation (1994) Publ E.94IX.11. United Nations, New York
Van Kaick G, Wesch H, Luhrs H, Lieberman D, Kaul A (1991) Neoplastic diseases induced by chronic alpha irradiation. Epidemiological, biophysical and clinical results by the German Thoratrast study group. J Radiat Res 32(suppl 2):20–33
Tubiana M. (2003) The carcinogenic effect of low doses: the validity of the linear no-threshold relationship. Int J Low Radiat 1:1–31
Miller RC, Randers-Pehrson G, Geand CR, Hall E, Brenner DJ (1999) The oncogenic transforming potential of the passage of single α particles through mammalian cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:19–22
National Commission Radiological Protection (1990) The relative biological effectiveness of radiation of different quality. Report N° 104, Washington DC
Masse R (1995) RBE for carcinogenesis following exposure to high LET radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 34:223–227
Tanooka H (2001) Threshold dose-response in radiation carcinogenesis: an approach from chronic beta-irradiation experiments and a review of non tumour doses. Int J Radiat Biol 77:541–551
Duport P (2003) A database of cancer induction by low dose radiation in mammals: overview and initial observations. Int J Low Radiat 1:120–131
Averbeck D, Testard I, Boucher D (2006) Changing views on ionizing radiation-induced cellular effects. Int J Low Radiation 3, n° 2
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Ünsal-Kaçmaz K, Linn S (2004) Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem 73:39–85
Shiloh Y (2003) ATM and related protein kinases: safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer 3:155–168
Collis SJ, Schwaninger JM, Ntambi AJ, Keller TW, Nelson WG, Dillehay LE, Deweese TL (2004) Evasion of early cellular response mechanisms following low level radiation induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem 279:49624–49632
Dikomey E, Brammer I (2000) Relationship between cellular radiosensitivity and non-repaired double-strand breaks studied for different growth states, dose rates and plating conditions in a normal fibroblast line. Int J Radiat Biol 76:773–781
Christmann M, Tomicic MT, Roos WP, Kaina B (2003) Mechanisms of human DNA repair: an update. Toxicology 193:3–34
Hoeijmakers JH (2001) Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature 411:366–374
Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K, Lieber MR (2002) Hairpin opening and overhang processing by an Artemis/DNA-dependent protein kinase complex in non homologous end-joining and V(D)J recombination. Cell 108:781–794
Vilenchik MM., Knudson AG (2000) Inverse radiation dose-rate effects on somatic and germ-line mutations and DNA damage rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5381–5386
Vilenchik MM, Knudson AG (2003) Endogenous DNA double-strand breaks: production, fidelity of repair, and induction of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12871–12876
Chalmers A, Johnston P, Woodcock M, Joiner M, Marples B (2004) PARP-1, PARP-2, and the cellular response to low doses of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:410–419
Marples B, Wouters BG, Collis SJ, Chalmers AJ, Joiner MC (2004) Low-dose hyper-radiosensitivity: a consequence of ineffective cell cycle arrest of radiation-damaged G2-phase cells. Radiat Res 161:247–255
Fernet M, Ponette V, Deniaud-Alexandre E, Menissier-De Murcia J, De Murcia G, Giocanti N, Megnin-Chanet F, Favaudon V (2000) Poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase, a major determinant of early cell response X ionising radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:73–84
Ponette V, Le Pechoux C, Deniaud-Alexandre E, Fernet M, Giocanti N, Tourbez H, Favaudon V (2000) Hyperfast early cell response to ionising radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol 72:1233–1243
Rigaud O, Moustacchi E (1996) Radioadaptation for gene mutation and the possible molecular mechanisms of the adaptive response. Mutat Res 358:127–134
Boreham DR, Dolling JA, Maves SR, Siwarungsun N, Mitchel RE (2000) Dose-rate effects for apoptosis and micronucleus formation in gamma-irradiated human lymphocytes. Radiat Res 153:579–586
Guo M, Hay BA (1999) Cell proliferation and apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:745–752
Mirzaie-Joniani H, Eriksson D, Sheikholvaezin A, Johansson A, Lofroth PO, Johansson L, Stigbrand T (2002) Apoptosis induced by low-dose and low-dose-rate radiation. Cancer 94:1210–1214
Ohyama H, Yamada T (1998) Radiation-induced apoptosis: a review. In: Yamada T, Hasimoto Y (eds) Apoptosis, its roles and mechanisms. Business Center for Academic Societies Japan, Tokyo, pp 141–186
Rothkamm K, Löbrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low X-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5057–50562
Löbrich M, Rief N, Kuhne M, Fleckenstein J, Rube C, Uder M (2005) In vivo formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks after computed tomography examinations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8984–8989
Bishay K, Ory K, Olivier MF, Lebeau J, Levalois C, Chevillard S (2001) DNA damage-related RNA expression to assess individual sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Carcinogenesis 22:1179–1183
Amundson SA, Bittner M, Fornace AJ Jr (2003) Functional genomics as a window on radiation stress signalling. Oncogene 22:5828–5833
Amundson SA, RA Lee, CA Koch-Paiz, ML Bittner, P Meltzer, JM Trent, AJ Fornace Jr (2003) Differential responses of stress genes to low dose-rate gamma irradiation. Mol Cancer Res 1:445–452
Amundson SA, Grace MB, McLeland CB, Epperly MW, Yeager A, Zhan Q, Greenberger JS, Fornace AJ Jr (2004) Human in vivo radiation-induced biomarkers: gene expression changes in radiotherapy patients. Cancer Res 64:6368–6371
Amundson SA, Do KT, Vinikoor L, Koch-Paiz CA, Bittner ML, Trent JM, Meltzer P, Fornace AJ Jr (2005) Stress-specific signatures: expression profiling of p53 wild-type and -null human cells. Oncogene 24:4572–4579
Mercier G, Berthault N, Mary J, Peyre J, Antoniadis A, Comet JP, Cornuejols A, Froidevaux C, Dutreix M (2004) Biological detection of low radiation doses by combining results of two microarray analysis methods. Nucleic Acids Res 32:12
Brash DE (1997) Sunlight and the onset of skin cancer. Trends Genet 13:410–414
Radisky DC, Bissell MJ (2004) Cancer. Respect thy neighbor! Science 303:774–775
Bhowmick NA, Chytil A, Plieth D, Gorska AE, Dumont N, Shappell S, Washington MK, Neilson EG, Moses HL (2004) TGF-beta signaling in fibroblasts modulates the oncogenic potential of adjacent epithelia. Science 303:775–777
Burns FJ, Albert RE (1986) Dose response for radiation induced cancer in rat skin. In: FJ Burns, Upton AC, Silini G (eds) Radiation carcinogenesis and DNA alterations. Life Sciences. Plenum Press, New York, pp 51–70
Euvrard S, Kanitakis J, Claudy A (2003) Skin cancers after organ transplantation. N Engl J Med 348:1681–1691
Abelson PH (1994) Risk assessment of low level exposure. Science 265:1507
Feinendegen LE and Neumann RD (2005) Physics must join with biology in better assessing risk from low dose irradiation. Radiation Protection Dosimetry (in press) [Oct 21 Epub ahead of print]
ICRP Draft report of CommitteeI/Task group. Low dose extrapolation of radiation related cancer risk. Dec. 10, 2004
Doll R, Wakeford R (1997) Risk of childhood cancer from fetal irradiation. Br J Radiol 70:130–139
Bithell JF (1993) Statistical issues in assessing the evidence associating obstetric irradiation and childhood malignancy. In: Lengfelder E, Wendhausen H (eds) Neue Bewertung des Strahlenriskos: Niedrigdosis Strahlung und Gesundheit, Munich, pp 53–60
Monson RR, MacMahon B (1984) Prenatal X-ray exposure and cancer in children. In: Boice JD, Fraumeni JF (eds) Radiation carcinogenesis: epidemiology and biological significance. Raven Press, New York, pp 97–105
Delongchamp RR, Mabuchi K, Yoshimoto Y, Preston DL (1997) Cancer mortality among atomic bomb survivors exposed in utero or as young children. Radiat Res 147:385–395
Naumburg E, Belloco R, Cnattingius S, Hall P, Boice J.D, Ekbom A (2001) Intrauterine exposure to diagnostic X rays and risk of childhood leukemia subtypes. Rad Res 156:718–723
Shu XO, Potter JD, Linet MS, Severson RK, Han D, Kersey JH, Neglia JP, Trigg ME, Robison LL (2002) Diagnostic X-Rays and ultrasound exposure and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by immunophenotype. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:177–185
Monchaux G (2004) Risk of fatal versus incidental lung cancer in radon-exposed rats: a reanalysis of French data. Arch Oncol 12:7–12
Rossi HH, Kellerer AM (1972) Radiation carcinogenesis at low doses. Science 175:200–202
Rossi HH (1997) It is time for change. Health Phys Soc Newslett pp 8–9
Rossi HH, Zaider M (1997) Radiogenic lung cancer. The effect of low doses of low LET radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 36:85–88
Boucher D, Hindo J, Averbeck D (2004) Increased repair of gamma-induced DNA double-strand breaks at lower dose-rate in CHO cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 82:125–132
Ames BN, Gold LS (1997) Environmental pollution, pesticides and the prevention of cancer: misconceptions. FASEB J 11:1041–1052
WHO (1957) Questions de santé mentale, posées par l’utilisation de l’énergie nucléaire à des fins pacifiques. (Technical report no. 151) World Health Organization, Geneva
Taylor LS (1980) Some non-scientific influences on radiation protection standards and practice. Health Phys 39:851–874
Pochin EE (1987) Radiation risks in perspective. Br J Radiol 60:42–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tubiana, M., Aurengo, A., Averbeck, D. et al. Recent reports on the effect of low doses of ionizing radiation and its dose–effect relationship. Radiat Environ Biophys 44, 245–251 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-006-0032-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-006-0032-9