Abstract
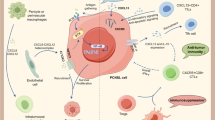
The expression pattern of a subset of chemokines and their corresponding receptors was investigated in primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL). The tumor cells consistently expressed CXCR4, CXCL12, CXCR5, and CXCL13, both at mRNA and protein levels. Cerebral endothelial cells were positive for CXCL12 and CXCL13, while reactive astrocytes and microglial cells expressed CXCL12, CCR5, and CCR6. Inflammatory T cells in PCNSL were characterized by CCR5 and CCR6 positivity. Taken together, our data indicate a cell type-specific repertoire of chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in PCNSL suggesting that chemokine-mediated interactions facilitate crossing of the blood-brain barrier as well as intracerebral dissemination of PCNSL cells. In addition, chemokines expressed by tumor cells may contribute to induction of reactive glial changes and influence the composition of inflammatory infiltrates in PCNSL. Therefore, cell type specific expression of distinct chemokine profiles likely plays a role in the pathogenesis of PCNSL and may contribute to their characteristic histological appearance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleul CC, Fuhlbrigge RC, Casasnovas JM, Aiuti A, Springer TA (1996) A highly efficacious lymphocyte chemoattractant, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). J Exp Med 184:1101–1109
Broxmeyer HE, Kim CH, Cooper SH, Hangoc G, Hromas R, Pelus LM (1999) Effects of CC, CXC, C, and CX3C chemokines on proliferation of myeloid progenitor cells, and insights into SDF-1-induced chemotaxis of progenitors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 872:142–162, discussion 163
Burger JA, Burger M, Kipps TJ (1999) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express functional CXCR4 chemokine receptors that mediate spontaneous migration beneath bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 94:3658–3667
Chunsong H, Yuling H, Li W, Jie X, Gang Z, Qiuping Z, Qingping G, Kejian Z, Li Q, Chang AE, Youxin J, Jinquan T (2006) CXC chemokine ligand 13 and CC chemokine ligand 19 cooperatively render resistance to apoptosis in B cell lineage acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia CD23 + CD5 + B cells. J Immunol 177:6713–6722
Cook DN, Prosser DM, Forster R, Zhang J, Kuklin NA, Abbondanzo SJ, Niu XD, Chen SC, Manfra DJ, Wiekowski MT, Sullivan LM, Smith SR, Greenberg HB, Narula SK, Lipp M, Lira SA (2000) CCR6 mediates dendritic cell localization, lymphocyte homeostasis, and immune responses in mucosal tissue. Immunity 12:495–503
Courts C, Montesinos-Rongen M, Martin-Subero JI, Brunn A, Siemer D, Zuhlke-Jenisch R, Pels H, Jurgens A, Schlegel U, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Schaller C, Reifenberger G, Sabel M, Warnecke-Eberz U, Wiestler OD, Kuppers R, Siebert R, Deckert M (2007) Transcriptional profiling of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway identifies a subgroup of primary lymphoma of the central nervous system with low BCL10 expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:230–237
Cyster JG (1999) Chemokines and the homing of dendritic cells to the T cell areas of lymphoid organs. J Exp Med 189:447–450
Flugel A, Berkowicz T, Ritter T, Labeur M, Jenne DE, Li Z, Ellwart JW, Willem M, Lassmann H, Wekerle H (2001) Migratory activity and functional changes of green fluorescent effector cells before and during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunity 14:547–560
Forster R, Emrich T, Kremmer E, Lipp M (1994) Expression of the G-protein–coupled receptor BLR1 defines mature, recirculating B cells and a subset of T-helper memory cells. Blood 84:830–840
Gatter K, Warnke R (2001) Diffuse large cell lymphomas. Lyon, France, pp 171–174
Greaves DR, Wang W, Dairaghi DJ, Dieu MC, Saint-Vis B, Franz-Bacon K, Rossi D, Caux C, McClanahan T, Gordon S, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ (1997) CCR6, a CC chemokine receptor that interacts with macrophage inflammatory protein 3alpha and is highly expressed in human dendritic cells. J Exp Med 186:837–844
Han Y, He T, Huang DR, Pardo CA, Ransohoff RM (2001) TNF-alpha mediates SDF-1 alpha-induced NF-kappa B activation and cytotoxic effects in primary astrocytes. J Clin Invest 108:425–435
Hieshima K, Imai T, Opdenakker G, Van Damme J, Kusuda J, Tei H, Sakaki Y, Takatsuki K, Miura R, Yoshie O, Nomiyama H (1997) Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine liver and activation-regulated chemokine (LARC) expressed in liver. Chemotactic activity for lymphocytes and gene localization on chromosome 2. J Biol Chem 272:5846–5853
Jahnke K, Coupland SE, Na IK, Loddenkemper C, Keilholz U, Korfel A, Stein H, Thiel E, Scheibenbogen C (2005) Expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR4, CXCR5, and CCR7 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 106:384–385
Jundt F, Anagnostopoulos I, Bommert K, Emmerich F, Muller G, Foss HD, Royer HD, Stein H, Dorken B (1999) Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells induce fibroblasts to secrete eotaxin, a potent chemoattractant for T cells and eosinophils. Blood 94:2065–2071
Klein RS, Rubin JB (2004) Immune and nervous system CXCL12 and CXCR4: parallel roles in patterning and plasticity. Trends Immunol 25:306–314
Krumbholz M, Theil D, Cepok S, Hemmer B, Kivisakk P, Ransohoff RM, Hofbauer M, Farina C, Derfuss T, Hartle C, Newcombe J, Hohlfeld R, Meinl E (2006) Chemokines in multiple sclerosis: CXCL12 and CXCL13 up-regulation is differentially linked to CNS immune cell recruitment. Brain 129:200–211
Lazarini F, Tham TN, Casanova P, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Dubois-Dalcq M (2003) Role of the alpha-chemokine stromal cell-derived factor (SDF-1) in the developing and mature central nervous system. Glia 42:139–148
Luther SA, Lopez T, Bai W, Hanahan D, Cyster JG (2000) BLC expression in pancreatic islets causes B cell recruitment and lymphotoxin-dependent lymphoid neogenesis. Immunity 12:471–481
Mohle R, Bautz F, Rafii S, Moore MA, Brugger W, Kanz L (1998) The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on CD34 + hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 91:4523–4530
Montesinos-Rongen M, Kuppers R, Schluter D, Spieker T, Van Roost D, Schaller C, Reifenberger G, Wiestler OD, Deckert-Schluter M (1999) Primary central nervous system lymphomas are derived from germinal-center B cells and show a preferential usage of the V4–34 gene segment. Am J Pathol 155:2077–2086
Nagasawa T, Kikutani H, Kishimoto T (1994) Molecular cloning and structure of a pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2305–2309
Nagasawa T, Tachibana K, Kishimoto T (1998) A novel CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4: their functions in development, hematopoiesis and HIV infection. Semin Immunol 10:179–185
Ohl L, Bernhardt G, Pabst O, Forster R (2003) Chemokines as organizers of primary and secondary lymphoid organs. Semin Immunol 15:249–255
Palmesino E, Moepps B, Gierschik P, Thelen M (2006) Differences in CXCR4-mediated signaling in B cells. Immunobiology 211:377–389
Paulus W, Jellinger K, Morgello S, Deckert-Schlüter M (2000) Malignant lymphomas. Lyon, France, pp 198–203
Power CA, Church DJ, Meyer A, Alouani S, Proudfoot AE, Clark-Lewis I, Sozzani S, Mantovani A, Wells TN (1997) Cloning and characterization of a specific receptor for the novel CC chemokine MIP-3alpha from lung dendritic cells. J Exp Med 186:825–835
Sallusto F, Mackay CR, Lanzavecchia A (2000) The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 18:593–620
Schlegel U, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Deckert M (2000) Primary CNS lymphoma: clinical presentation, pathological classification, molecular pathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Sci 181:1–12
Smith JR, Braziel RM, Paoletti S, Lipp M, Uguccioni M, Rosenbaum JT (2003) Expression of B-cell-attracting chemokine 1 (CXCL13) by malignant lymphocytes and vascular endothelium in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 101:815–821
Smith JR, Falkenhagen KM, Coupland SE, Chipps TJ, Rosenbaum JT, Braziel RM (2007) Malignant B cells from patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma express stromal cell-derived factor-1. Am J Clin Pathol 127:633–641
Strack A, Asensio VC, Campbell IL, Schluter D, Deckert M (2002) Chemokines are differentially expressed by astrocytes, microglia and inflammatory leukocytes in Toxoplasma encephalitis and critically regulated by interferon-gamma. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 103:458–468
Stumm RK, Rummel J, Junker V, Culmsee C, Pfeiffer M, Krieglstein J, Hollt V, Schulz S (2002) A dual role for the SDF-1/CXCR4 chemokine receptor system in adult brain: isoform-selective regulation of SDF-1 expression modulates CXCR4-dependent neuronal plasticity and cerebral leukocyte recruitment after focal ischemia. J Neurosci 22:5865–5878
Tanabe S, Heesen M, Yoshizawa I, Berman MA, Luo Y, Bleul CC, Springer TA, Okuda K, Gerard N, Dorf ME (1997) Functional expression of the CXC-chemokine receptor-4/fusin on mouse microglial cells and astrocytes. J Immunol 159:905–911
Tanuma N, Sakuma H, Sasaki A, Matsumoto Y (2006) Chemokine expression by astrocytes plays a role in microglia/macrophage activation and subsequent neurodegeneration in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:195–204
Tashiro K, Tada H, Heilker R, Shirozu M, Nakano T, Honjo T (1993) Signal sequence trap: a cloning strategy for secreted proteins and type I membrane proteins. Science 261:600–603
Thompsett AR, Ellison DW, Stevenson FK, Zhu D (1999) V(H) gene sequences from primary central nervous system lymphomas indicate derivation from highly mutated germinal center B cells with ongoing mutational activity. Blood 94:1738–1746
Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Facco M, Carollo D, Miorin M, Tosoni A, Pizzo P, Binotto G, Nicolardi L, Zambello R, Adami F, Agostini C, Semenzato G (2004) Homeostatic chemokines drive migration of malignant B cells in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 104:502–508
Wu L, Paxton WA, Kassam N, Ruffing N, Rottman JB, Sullivan N, Choe H, Sodroski J, Newman W, Koup RA, Mackay CR (1997) CCR5 levels and expression pattern correlate with infectability by macrophage-tropic HIV-1, in vitro. J Exp Med 185:1681–1691
Wu MT, Hwang ST (2002) CXCR5-transduced bone marrow-derived dendritic cells traffic to B cell zones of lymph nodes and modify antigen-specific immune responses. J Immunol 168:5096–5102
Yoshie O, Imai T, Nomiyama H (1997) Novel lymphocyte-specific CC chemokines and their receptors. J Leukoc Biol 62:634–644
Yu P, Wang Y, Chin RK, Martinez-Pomares L, Gordon S, Kosco-Vibois MH, Cyster J, Fu YX (2002) B cells control the migration of a subset of dendritic cells into B cell follicles via CXC chemokine ligand 13 in a lymphotoxin-dependent fashion. J Immunol 168:5117–5123
Acknowledgments
The expert technical assistance of Irmgard Henke and Elena Fischer is gratefully acknowledged. This study was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe/Dr. Mildred Scheel Stiftung für Krebsforschung (grant no: 10-2153-De1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunn, A., Montesinos-Rongen, M., Strack, A. et al. Expression pattern and cellular sources of chemokines in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol 114, 271–276 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0258-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0258-x