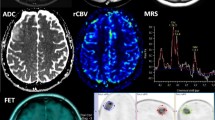
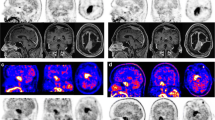
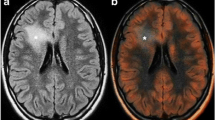
Abstract
Objective
The present article illustrates whether positron-emission tomography (PET) imaging may improve the surgical management of pediatric brain tumors (PBT) at different steps.
Materials and methods
Among 400 consecutive PBT treated between 1995 and 2005 at Erasme Hospital, Brussels, Belgium, we have studied with 18 F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG)–PET and/or L-(methyl-11C)methionine (MET)–PET and integrated PET images in the diagnostic workup of 126 selected cases. The selection criteria were mainly based on the lesion appearance on magnetic resonance (MR) sequences. Cases were selected when MR imaging showed limitations for (1) assessing the evolving nature of an incidental lesion (n = 54), (2) selecting targets for contributive and accurate biopsy (n = 32), and (3) delineating tumor tissue for maximal resection (n = 40). Whenever needed, PET images were integrated in the planning of image-guided surgical procedures (frame-based stereotactic biopsies (SB), frameless navigation-based resections, or leksell gamma knife radiosurgery).
Results
Like in adults, PET imaging really helped the surgical management of the 126 children explored, which represented about 30% of all PBT, especially when the newly diagnosed brain lesion was (1) an incidental finding so that the choice between surgery and conservative MR follow-up was debated, and (2) so infiltrative or ill-defined on MR that the choice between biopsy and resection was hardly discussed. Integrating PET into the diagnostic workup of these two selected groups helped to (1) take a more appropriate decision in incidental lesions by detecting tumor/evolving tissue; (2) better understand complex cases by differentiating indolent and active components of the lesion; (3) improve target selection and diagnostic yield of stereotactic biopsies in gliomas; (4) illustrate the intratumoral histological heterogeneity in gliomas; (5) provide additional prognostic information; (6) reduce the number of trajectories in biopsies performed in eloquent areas such as the brainstem or the pineal region; (7) better delineate ill-defined PBT infiltrative along functional cortex than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); (8) increase significantly, compared to using MRI alone, the number of total tumor resection and the amount of tumor tissue removed in PBT for which a total resection is a key-factor of survival; (9) target the resection on more active areas; (10) improve detection of tumor residues in the operative cavity at the early postoperative stage; (11) facilitate the decision of early second-look surgery for optimizing the radical resection; (12) improve the accuracy of the radiosurgical dosimetry planning.
Conclusions
PET imaging may improve the surgical management of PBT at the diagnostic, surgical, and post-operative steps. Integration of PET in the clinical workup of PBT inaugurates a new approach in which functional data can influence the therapeutic decision process. Although metabolic information from PET are valid and relevant for the clinical purposes, further studies are needed to assess whether PET-guidance may decrease surgical morbidity and increase children survival.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi J, Alavi A, Chawluk J, Kushner M, Powe J, Hickey W, Reivich M (1988) Positron emission tomography in patients with glioma. A predictor of prognosis. Cancer 62:1074–1078
Albright AL (1993) Pediatric brain tumors. CA Cancer J Clin 43:272–288
Albright AL (1996) Diffuse brainstem tumors: when is a biopsy necessary? Pediatr Neurosurg 24:252–255
Bergstrom M, Ericson K, Hagenfeldt L, Mosskin M, von Holst H, Noren G, Eriksson L, Ehrin E, Johnstrom P (1987) PET study of methionine accumulation in glioma and normal brain tissue: competition with branched chain amino acids. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11:208–213
Black PM, Alexander E 3rd, Martin C, Moriarty T, Nabavi A, Wong TZ, Schwartz RB, Jolesz F (1999) Craniotomy for tumor treatment in an intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging unit. Neurosurgery 45:423–431
Black PM (1991) Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 324:1471–1476
Black PM (1991) Brain tumors (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 324:1555–1564
Borgwardt L, Hojgaard L, Carstensen H, Laursen H, Nowak M, Thomsen C, Schmiegelow K (2005) Increased fluorine-18 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG) uptake in childhood CNS tumors is correlated with malignancy grade: a study with FDG positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging coregistration and image fusion. J Clin Oncol 23:3030–3037
Bowers DC, Krause TP, Aronson LJ, Barzi A, Burger PC, Carson BS (2001) Second surgery for recurrent pilocytic astrocytoma in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 34:229–234
Bruggers CS, Friedman HS, Fuller GN, Tien RD, Marks LB, Halperin EC, Hockenberger B, Oakes WJ, Hoffman JM (1993) Comparison of serial PET and MRI scans in a pediatric patient with a brainstem glioma. Med Pediatr Oncol 21:301–306
Chandrasoma PT, Smith MM, Apuzzo MLJ (1989) Stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis of brain masses: comparison of results of biopsy and resected surgical specimen. Neurosurgery 24:160–165
Chen W, Cloughesy T, Kamdar N, Satyamurthy N, Bergsneider M, Liau L, Mischel P, Czernin J, Phelps ME, Silverman DH (2005) Imaging proliferation in brain tumors with 18F-FLT PET: comparison with 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med 46:945–952
Choi SJ, Kim JS, Kim JH, Oh SJ, Lee JG, Kim CJ, Ra YS, Yeo JS, Ryu JS, Moon DH (2005) [18F]3′-deoxy-3′-fluorothymidine PET for the diagnosis and grading of brain tumors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:653–659
Choksey MS, Valentine A, Shawdon H, Freer CER, Lindsay KD (1989) Computed tomography in the diagnosis of malignant brain tumours: do all patients require biopsy? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:821–825
Cohen KJ, Broniscer A, Glod J (2001) Pediatric glial tumors. Curr Treatm Opt Oncol 2:529–536
Croteau D, Scarpace L, Hearshen D, Gutierrez J, Fisher JL, Rock JP, Mikkelsen T (2001) Correlation between magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging and image-guided biopsies: semiquantitative and qualitative histopathological analyses of patients with untreated glioma. Neurosurgery 49:823–829
Derlon JM, Cabal P, Blaizot X, Borha A, Chapon F (2005) Metabolic imaging for supratentorial oligodendrogliomas. Neurochirurgie 51:309–322
De Witte O, Levivier M, Violon P (1996) Prognostic value of positron emission tomography with [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose in the low-grade glioma. Neurosurgery 39:470–476
De Witte O, Levivier M, Violon P (1998) Quantitative imaging study of extent of surgical resection and prognosis of malignant astocytomas. Neurosurgery 43:398–399
De Witte O, Lefranc F, Levivier M (2000) FDG–PET as a prognostic factor in high-grade astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 49:157–163
De Witte O, Goldberg I, Wikler D, Rorive S, Damhaut P, Monclus M, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Goldman S (2001) Positron emission tomography with injection of methionine as a prognostic factor in glioma. J Neurosurg 95:746–750
Di Chiro G (1986) Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumors. A powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool. Invest Radiol 22:360–371
Essig M, Metzner R, Bonsanto M, Hawighorst H, Debus J, Tronnier V (2001) Postoperative fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging of cerebral gliomas: initial results. Eur Radiol 11:2004–2010
Fahlbusch R, Honegger J, Paulus W, Huk W, Buchfelder M (1999) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: experience with 168 patients. J Neurosurg 90:237–250
Feiden W, Steude U, Bise K, Gündisch O (1991) Accuracy of stereotactic brain tumor biopsy: comparison of the histologic findings in biopsy cylinders and resected tumor tissue. Neurosurg Rev 14:51–56
Floeth FW, Stummer W (2005) The value of metabolic imaging in diagnosis and resection of cerebral gliomas. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 1:62–63
Foreman NK, Love S, Gill SS, Coakham HB (1997) Second-look surgery for incompletely resected fourth ventricle ependymomas: technical case report. Neurosurgery 40:856–860
Garty I, Delbeke D, Sandler MP (1989) Correlative pediatric imaging. J Nucl Med 30:15–24
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Herndon JE II, Friedman AH, Cairncross JG, Vick NA, Schold SC Jr (1991) Influence of the type of surgery on the histological diagnosis in patients with anaplastic gliomas. Neurology 41:1741–1744
Goldman S, Levivier M, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Dethy S, Brotchi J, Hildebrand J (1997) Regional methionine and glucose uptake in high grade gliomas: a comparative study on PET-guided stereotactic biopsy. J Nucl Med 38:1–4
Hall WA, Liu H, Martin AJ, Truwit CL (1999) Comparison of stereotactic brain biopsy to interventional magnetic-resonance-imaging-guided brain biopsy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 73:148–153
Hess KR (1999) Extent of resection as a prognostic variable in the treatment of gliomas. J Neurooncol 42:227–231
Hoffman JM, Hanson MW, Friedman HS, Hockenberger BM, Oakes WJ, Halperin EC, Coleman RE (1992) FDG–PET in pediatric posterior fossa brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:62–68
Holthoff VA, Herholz K, Berthold F, Widemann B, Schroder R, Neubauer I (1993) In vivo metabolism of childhood posterior fossa tumors and primitive neuroectodermal tumors before and after treatment. Cancer 72:1394–1403
Kaplan AM, Bandy DJ, Manwaring KH, Chen K, Lawson MA, Moss SD, Duncan JD, Wodrich DL, Schnur JA, Reiman EM (1999) Functional brain mapping using positron emission tomography scanning in preoperative neurosurgical planning for pediatric brain tumors. J Neurosurg 91:797–803
Kaplan AM, Lawson MA, Spataro J, Bandy DJ, Bonstelle CT, Moss SD, Manwaring KH, Reiman EM (1999) Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose and [11C] l-methionine to metabolically characterize dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. J Child Neurol 14:673–677
Kaschten B, Stevenaert A, Sadzot B. (1998) Preoperative evaluation of 54 gliomas by PET with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose and/or carbon-11-methionine. J Nucl Med 39:778–785
Khan RB, Sanford RA, Kun LE, Thompson SJ (2001) Morbidity of second–look surgery in pediatric central nervous system tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:225–229
Levivier M, Goldman S, Bidaut LM, Luxen A, Stanus E, Przedborski S, Balériaux D, Hildebrand J, Brotchi J (1992) Positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic brain biopsy. Neurosurgery 31:792–797
Levivier M, Goldman S, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Baleriaux D, Luxen A, Hildebrand J, Brotchi J (1995) Diagnostic yield of stereotactic brain biopsy guided by positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. J Neurosurg 82:445–452
Levivier M, Wikler D, Goldman S, Pirotte B, Brotchi J (1999) Positron emission tomography in stereotactic conditions as a functional imaging technique for neurosurgical guidance. In: Alexander EB III, Maciunas RM (eds) Advanced neurosurgical navigation. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York, pp 85–99
Levivier M, Wikler D, Goldman S, David P, Metens T, Massager N, Gerosa M, Devriendt D, Desmedt F, Simon S, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J (2000) Integration of the metabolic data of positron emission tomography in the dosimetry planning of radiosurgery with the gamma knife: early experience with brain tumors. J Neurosurg 93:233–238
Levivier M, Massager N, Wikler D, Lorenzoni J, Ruiz S, Devriendt D (2004) Use of stereotactic PET images in dosimetry planning of radiosurgery for brain tumors: clinical experience and proposed classification. J Nucl Med 45:1146–1154
Maehara T, Nariai T, Arai N, Kawai K, Shimizu H, Ishii K, Ishiwata K, Ohno K (2004) Usefulness of [11C]methionine PET in the diagnosis of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 45:41–45
Marec-Berard P, Jouvet A, Thiesse P, Kalifa C, Doz F, Frappaz D (2002) Supratentorial embryonal tumors in children under 5 years of age: an SFOP study of treatment with postoperative chemotherapy alone. Med Pediatr Oncol 38:83–90
Maria BL, Drane WE, Quisling RJ, Hoang KB (1997) Correlation between gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid contrast enhancement and thallium-201 chloride uptake in pediatric brainstem glioma. J Child Neurol 12:341–348
Maria BL, Drane WE, Quisling RG, Ringdahl DM, Mickle JP, Mendenhall NP, Marcus RB Jr, McCollough WM, Hamed LM, Eskin TA (1994) Value of thallium-201 SPECT imaging in childhood brain tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 20:11–18
Massager N, David P, Goldman S, Pirotte B, Wikler D, Salmon I, Nagy N, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2000) Combined MRI- and PET- guided stereotactic biopsy in brainstem mass lesions: diagnostic yield in a series of 30 patients. J Neurosurg 93:951–957
Mineura K, Yasuda T, Kowada M, Sakamoto T, Ogawa T, Shishido F, Uemura K (1985–86) Positron emission tomographic evaluations in the diagnosis and therapy of multifocal glioblastoma. Report of a pediatric case. Pediatr Neurosci 12:208–212
Molenkamp G, Riemann B, Kuwert T, Strater R, Kurlemann G, Schober O, Jurgens H, Wolff JE (1998) Monitoring tumor activity in low grade glioma of childhood. Klin Padiatr 210:239–242
Mosskin M, von Holst H, Bergström M, Collins VP, Eriksson L, Johnström P, Norén G (1987) Positron emission tomography with 11C-methionine and computed tomography of intracranial tumours compared with histopathologic examination of multiple biopsies. Acta Radiol 28:673–681
Oser AB, Moran CJ, Kaufman BA, Park TS (1997) Intracranial tumor in children: MR imaging findings within 24 hours of craniotomy. Radiology 205:807–812
Patronas NJ, Brooks RA, DeLaPaz RL (1983) Glycolytic rate (PET) and contrast enhancement (CT) in human cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 4:533–535
Patronas NJ, Di-Chiro G, Kufta C (1985) Prediction of survival in glioma patients by means of positron emission tomography. J Neurosurg 62:816–822
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Hamacher K, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Muller HW, Zilles K, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2005) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain 128:678–687
Paulino AC, Wen BC, Buatti JM, Hussey DH, Zhen WK, Mayr NA (2002) Intracranial ependymomas: an analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. Am J Clin Oncol 25:117–122
Paulus W, Peiffer J (1989) Intratumoral histologic heterogeneity of gliomas. A quantitative study. Cancer 64:442–447
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Bidaut L, Luxen A, Stanus E, Brucher JM, Baleriaux D, Brotchi J, Levivier M (1995) Use of positron emission tomography (PET) in stereotactic conditions for brain biopsy. Acta Neurochir 134:79–82
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Salzberg S, Wikler D, David P, Vandesteene A, Van Bogaert P, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2003) Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for the planning of stereotactic brain biopsies in children: experience in 9 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 38:146–155
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Lipszyc M (2004) Combined use of [F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose and [C-11]methionine in 45 PET-guided Stereotactic brain biopsies. J Neurosurg 101:476–483
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Vandesteene A (2004) Comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine for PET-guided stereotactic brain biopsy in gliomas. J Nucl Med 45:1293–1298
Pirotte B, Levivier M, Morelli D, Van Bogaert P, Detemmerman D, David P (2005) Positron emission tomography for the early postsurgical evaluation of pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 21:294–300
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Van Bogaert P, David P, Wikler D, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2005) Integration of 11C-methionine-PET and MR imaging for image-guided surgical resection of infiltrative low-grade brain tumors in children. Neurosurgery 57:128–139
Pirotte B, Goldman S, De Witte O, Massager N, Wikler D, Oulad Ben Taib N, Rorive S, Devriendt D, David P, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2006) Integrated PET and MR imaging-guided resection of brain tumors: a report of 103 consecutive procedures. J Neurosurg 104:238–253
Pollack IF (1999) The role of surgery in pediatric gliomas. J Neurooncol 42:271–288
Rosenberg DS, Demarquay G, Jouvet A, Le Bars D, Streichenberger N, Sindou M, Kopp N, Mauguière F, Ryvlin P (2005) [11C]-Methionine PET: dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours compared with other epileptogenic brain neoplasms. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1686–1692
Ruotsalainen U, Suhonen-Polvi H, Eronen E, Kinnala A, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Teras M, Solin O, Wegelius U (1996) Estimated radiation dose to the newborn in FDG–PET studies. J Nucl Med 37:387–393
Scerrati M, Roselli R, Iacoangeli M, Pompucci A, Rossi GF (1996) Prognostic factors in low grade (WHO grade II) gliomas of the cerebral hemispheres: the role of surgery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61:291–296
Shulkin BL (1997) PET applications in pediatrics. Q J Nucl Med 41:281–291
Shulkin BL, Mitchell DS, Ungar DR, Prakash D, Dole MG, Castle VP, Hernandez RJ, Koeppe RA, Hutchinson RJ (1995) Neoplasms in a pediatric population: FDG–PET studies. Radiology 194:495–500
Stummer W, Stocker S, Wagner S, Stepp H, Fritsch C, Goetz C, Goetz AE, Kiefmann R, Reulen HJ (1998) Intraoperative detection of malignant gliomas by 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrin fluorescence. Neurosurgery 42:518–525
Suhonen-Polvi H, Ruotsalainen U, Kinnala A, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Teras M, Makela P, Solin O, Wegelius U (1995) FDG–PET in early infancy: simplified quantification methods to measure cerebral glucose utilization. J Nucl Med 36:1249–1254
Toms SA, Lin WC, Weil RJ, Johnson MD, Jansen ED, Mahadevan-Jansen A (2005) Intraoperative optical spectroscopy identifies infiltrating glioma margins with high sensitivity. Neurosurgery 57:382–391
Utriainen M, Metsahonkala L, Salmi TT, Utriainen T, Kalimo H, Pihko H (2002) Metabolic characterization of childhood brain tumors: comparison of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine positron emission tomography. Cancer 95:1376–1386
Wong TZ, Van der Westhuizen GJ, Coleman RE (2002) Positron emission tomography imaging of brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 12:615–626
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirotte, B., Acerbi, F., Lubansu, A. et al. PET imaging in the surgical management of pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 739–751 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0307-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0307-8