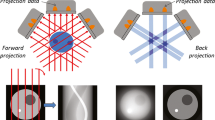
Abstract
Objectives
To explain the technical principles of and differences between commercially available iterative reconstruction (IR) algorithms for computed tomography (CT) in non-mathematical terms for radiologists and clinicians.
Methods
Technical details of the different proprietary IR techniques were distilled from available scientific articles and manufacturers' white papers and were verified by the manufacturers. Clinical results were obtained from a literature search spanning January 2006 to January 2012, including only original research papers concerning IR for CT.
Results
IR for CT iteratively reduces noise and artefacts in either image space or raw data, or both. Reported dose reductions ranged from 23 % to 76 % compared to locally used default filtered back-projection (FBP) settings, with similar noise, artefacts, subjective, and objective image quality.
Conclusion
IR has the potential to allow reducing the radiation dose while preserving image quality. Disadvantages of IR include blotchy image appearance and longer computational time. Future studies need to address differences between IR algorithms for clinical low-dose CT.
Key Points
• Iterative reconstruction technology for CT is presented in non-mathematical terms.
• IR reduces noise and artefacts compared to filtered back-projection.
• IR can improve image quality in routine-dose CT and lower the radiation dose.
• IR's disadvantages include longer computation and blotchy appearance of some images.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIDR 3D:
-
Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction 3D
- ART:
-
Algebraic reconstruction technique
- ASIR:
-
Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise ratio
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTDIvol :
-
Volume Computed Tomography Dose Index
- DLP:
-
Dose-length product
- FBP:
-
Filtered back-projection
- IRIS:
-
Iterative Reconstruction in Image Space
- MBIR:
-
Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction
- SAFIRE:
-
Sinogram-Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
References
Xu J, Mahesh M, Tsui BM (2009) Is iterative reconstruction ready for MDCT? J Am Coll Radiol 6:274–276
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography—an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 357:2277–2284
Smith-Bindman R (2010) Is computed tomography safe? N Engl J Med 363:1–4
Hall EJ, Brenner DJ (2008) Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Br J Radiol 81:362–378
Smith-Bindman R, Miglioretti DL, Johnson E et al (2012) Use of diagnostic imaging studies and associated radiation exposure for patients enrolled in large integrated health care systems, 1996-2010. JAMA 307:2400–2409
Bogdanich W (2011) Radiation Boom. The New York Times. Available via http://topics.nytimes.com/top/news/us/series/radiation_boom/index.html. Accessed Nov 2012
Lee TY, Chhem RK (2010) Impact of new technologies on dose reduction in CT. Eur J Radiol 76:28–35
Hentel KD, Sharma R, Wladyka C, Min RJ (2011) Appropriate use of CT in the emergency department. Emerg Med 1:6–13
Macias CG, Sahouria JJ (2011) The appropriate use of CT: quality improvement and clinical decision-making in pediatric emergency medicine. Pediatr Radiol 41(Suppl 2):498–504
Taylor AJ, Cerqueira M, Hodgson JM et al (2010) ACCF/SCCT/ACR/AHA/ASE/ASNC/NASCI/SCAI/SCMR 2010 Appropriate Use Criteria for Cardiac Computed Tomography. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Circulation 122:e525-e555
Kerl JM, Bauer RW, Maurer TB et al (2011) Dose levels at coronary CT angiography—a comparison of dual energy, dual source and 16-slice CT. Eur Radiol 21:530–537
Fleischmann D, Boas FE (2011) Computed tomography—old ideas and new technology. Eur Radiol 21:510–517
Pan X, Sidky EY, Vannier M (2009) Why do commercial CT scanners still employ traditional, filtered back-projection for image reconstruction? Inverse Probl 25:1230009
Nelson RC, Feuerlein S, Boll DT (2011) New iterative reconstruction techniques for cardiovascular computed tomography: how do they work, and what are the advantages and disadvantages? J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 5:286–292
Funama Y, Taguchi K, Utsunomiya D et al (2011) Combination of a low-tube-voltage technique with hybrid iterative reconstruction (iDose) algorithm at coronary computed tomographic angiography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:480–485
Gervaise A, Osemont B, Lecocq S et al (2012) CT image quality improvement using adaptive iterative dose reduction with wide-volume acquisition on 320-detector CT. Eur Radiol 22:295–301
Korn A, Fenchel M, Bender B et al (2011) Iterative reconstruction in head CT: image quality of routine and low-dose protocols in comparison with standard filtered back-projection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:218–224
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Digumarthy SR et al (2010) Radiation dose reduction with chest computed tomography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique: initial experience. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:40–45
Winklehner A, Karlo C, Puippe G et al (2011) Raw data-based iterative reconstruction in body CTA: evaluation of radiation dose saving potential. Eur Radiol 21:2521–2526
Sato J, Akahane M, Inano S et al (2011) Effect of radiation dose and adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction on image quality of pulmonary computed tomography. Jpn J Radiol 30:146–153
Moscariello A, Takx RA, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Coronary CT angiography: image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and potential for radiation dose reduction using a novel iterative image reconstruction technique-comparison with traditional filtered back projection. Eur Radiol 21:2130–2138
Singh S, Kalra MK, Gilman MD et al (2011) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique for radiation dose reduction in chest CT: a pilot study. Radiology 259:565–573
Pontana F, Duhamel A, Pagniez J et al (2011) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (part 2): image quality of low-dose CT examinations in 80 patients. Eur Radiol 21:636–643
Leipsic J, Labounty TM, Heilbron B et al (2010) Estimated radiation dose reduction using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction in coronary CT angiography: the ERASIR study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:655–660
Yanagawa M, Honda O, Kikuyama A et al (2012) Pulmonary nodules: Effect of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) technique on performance of a computer-aided detection (CAD) system-Comparison of performance between different-dose CT scans. Eur J Radiol 81:2877–2886
Leipsic J, Heilbron BG, Hague C (2012) Iterative reconstruction for coronary CT angiography: finding its way. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28:613–620
Grant K, Flohr T (2010) Iterative Reconstruction in Image Space (IRIS). Siemens Medical Solutions Whitepaper. Available via http://www.medical.siemens.com/siemens/en_US/gg_ct_FBAs/files/Case_Studies/IRIS_Whitepaper.pdf. Accessed Nov 2012
Grant K, Raupach R (2012) SAFIRE: Sinogram Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction. Siemens Medical Solutions Whitepaper. Available via http://www.medical.siemens.com/siemens/en_US/gg_ct_FBAs/files/Definition_AS/Safire.pdf. Accessed Nov 2012
Irwan B, Nakanishi S, Blum A (2012) AIDR 3D - reduces dose and simultaneously improves image quality. Toshiba Medical Systems Whitepaper. Available via http://www.toshiba-medical.eu/upload/TMSE_CT/White%20Papers/White%20Papers/Toshiba_White%20paper%20CT_nov11.pdf?epslanguage=en. Accessed Nov 2012
Noel PB, Fingerle AA, Renger B, Munzel D, Rummeny EJ, Dobritz M (2011) Initial performance characterization of a clinical noise-suppressing reconstruction algorithm for MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:1404–1409
Scibelli A (2011) iDose4 iterative reconstruction technique. Philips Healthcare Whitepaper. Available via https://www.healthcare.philips.com/pwc_hc/main/shared/Assets/Documents/ct/idose_white_paper_452296267841.pdf. Accessed Nov 2012
Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W (2009) Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:764–771
Thibault JB, Sauer KD, Bouman CA, Hsieh J (2007) A three-dimensional statistical approach to improved image quality for multislice helical CT. Med Phys 34:4526–4544
Silva AC, Lawder HJ, Hara A, Kujak J, Pavlicek W (2010) Innovations in CT dose reduction strategy: application of the adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction algorithm. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:191–199
Sagara Y, Hara AK, Pavlicek W, Silva AC, Paden RG, Wu Q (2010) Abdominal CT: comparison of low-dose CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction and routine-dose CT with filtered back projection in 53 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:713–719
GE Healthcare (2011) Computed tomography: ASiR* High Image Quality and Low Dose: Forget compromise. Available via http://www.gehealthcare.com/euen/ct/products/Asir/. Accessed Nov 2012.
Thibault JB (2010) Veo: CT model-based iterative reconstruction. GE Healthcare Whitepaper. Available via http://www.gehealthcare.com/dose/pdfs/Veo_white_paper.pdf. Accessed Nov 2012
Scheffel H, Stolzmann P, Schlett CL et al (2011) Coronary artery plaques: cardiac CT with model-based and adaptive-statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Eur J Radiol 81:e363–e369
Bittencourt MS, Schmidt B, Seltmann M et al (2011) Iterative reconstruction in image space (IRIS) in cardiac computed tomography: initial experience. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27:1081–1087
Bulla S, Blanke P, Hassepass F et al (2012) Reducing the radiation dose for low-dose CT of the paranasal sinuses using iterative reconstruction: feasibility and image quality. Eur J Radiol 81:2246–2250
Ghetti C, Ortenzia O, Serreli G (2011) CT iterative reconstruction in image space: a phantom study. Phys Med 28:161–165
Hu XH, Ding XF, Wu RZ, Zhang MM (2011) Radiation dose of non-enhanced chest CT can be reduced 40 % by using iterative reconstruction in image space. Clin Radiol 66:1023–1029
Lee SJ, Park SH, Kim AY et al (2011) A prospective comparison of standard-dose CT enterography and 50 % reduced-dose CT enterography with and without noise reduction for evaluating Crohn disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:50–57
May MS, Wust W, Brand M et al (2011) Dose reduction in abdominal computed tomography: intraindividual comparison of image quality of full-dose standard and half-dose iterative reconstructions with dual-source computed tomography. Invest Radiol 46:465–470
Park EA, Lee W, Kim KW et al (2012) Iterative reconstruction of dual-source coronary CT angiography: assessment of image quality and radiation dose. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28:1775–1786
Pontana F, Pagniez J, Flohr T et al (2011) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (Part 1): evaluation of image noise reduction in 32 patients. Eur Radiol 21:627–635
Renker M, Ramachandra A, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Iterative image reconstruction techniques: applications for cardiac CT. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 5:225–230
Renker M, Nance JW Jr, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography: comparison of iterative and filtered back projection image reconstruction. Radiology 260:390–399
Schindera ST, Diedrichsen L, Muller HC et al (2011) Iterative reconstruction algorithm for abdominal multidetector CT at different tube voltages: assessment of diagnostic accuracy, image quality, and radiation dose in a phantom study. Radiology 260:454–462
European Guidelines on Quality Criteria for Computed Tomography (1999) Report EUR 16262. Brussels, Belgium: European Commission
Mayo JR, Aldrich J, Muller NL (2003) Radiation exposure at chest CT: a statement of the Fleischner Society. Radiology 228:15–21
Cornfeld D, Israel G, Detroy E, Bokhari J, Mojibian H (2011) Impact of Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction (ASIR) on radiation dose and image quality in aortic dissection studies: a qualitative and quantitative analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:W336–W340
Flicek KT, Hara AK, Silva AC, Wu Q, Peter MB, Johnson CD (2010) Reducing the radiation dose for CT colonography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: a pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:126–131
Gosling O, Loader R, Venables P et al (2010) A comparison of radiation doses between state-of-the-art multislice CT coronary angiography with iterative reconstruction, multislice CT coronary angiography with standard filtered back-projection and invasive diagnostic coronary angiography. Heart 96:922–926
Honda O, Yanagawa M, Inoue A et al (2011) Image quality of multiplanar reconstruction of pulmonary CT scans using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. Br J Radiol 84:335–341
Kambadakone AR, Chaudhary NA, Desai GS, Nguyen DD, Kulkarni NM, Sahani DV (2011) Low-dose MDCT and CT enterography of patients with Crohn disease: feasibility of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:W743–W752
Kilic K, Erbas G, Guryildirim M, Arac M, Ilgit E, Coskun B (2011) Lowering the dose in head CT using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1578–1582
Leipsic J, Labounty TM, Heilbron B et al (2010) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: assessment of image noise and image quality in coronary CT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:649–654
Leipsic J, Nguyen G, Brown J, Sin D, Mayo JR (2010) A prospective evaluation of dose reduction and image quality in chest CT using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:1095–1099
Marin D, Nelson RC, Schindera ST et al (2010) Low-tube-voltage, high-tube-current multidetector abdominal CT: improved image quality and decreased radiation dose with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction algorithm—initial clinical experience. Radiology 254:145–153
Martinsen AC, Saether HK, Hol PK, Olsen DR, Skaane P (2011) Iterative reconstruction reduces abdominal CT dose. Eur J Radiol 81:1483–1487
Matsuda I, Hanaoka S, Akahane M et al (2010) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction for volume-rendered computed tomography portovenography: improvement of image quality. Jpn J Radiol 28:700–706
Mieville FA, Gudinchet F, Rizzo E et al (2011) Paediatric cardiac CT examinations: impact of the iterative reconstruction method ASIR on image quality—preliminary findings. Pediatr Radiol 41:1154–1164
Min JK, Swaminathan RV, Vass M, Gallagher S, Weinsaft JW (2009) High-definition multidetector computed tomography for evaluation of coronary artery stents: comparison to standard-definition 64-detector row computed tomography. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 3:246–251
Mitsumori LM, Shuman WP, Busey JM, Kolokythas O, Koprowicz KM (2012) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction versus filtered back projection in the same patient: 64 channel liver CT image quality and patient radiation dose. Eur Radiol 22:138–143
Mueck FG, Korner M, Scherr MK et al (2011) Upgrade to Iterative Image Reconstruction (IR) in abdominal MDCT imaging: a clinical study for detailed parameter optimization beyond vendor recommendations using the Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction Environment (ASIR). Rofo 184:229–238
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Ackman JB et al (2010) Diffuse lung disease: CT of the chest with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Radiology 256:261–269
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Kambadakone AK et al (2010) Reducing abdominal CT radiation dose with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Invest Radiol 45:202–210
Rapalino O, Kamalian S, Payabvash S et al (2012) Cranial CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: improved image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:609–615
Singh S, Kalra MK, Hsieh J et al (2010) Abdominal CT: comparison of adaptive statistical iterative and filtered back projection reconstruction techniques. Radiology 257:373–383
Vorona GA, Ceschin RC, Clayton BL, Sutcavage T, Tadros SS, Panigrahy A (2011) Reducing abdominal CT radiation dose with the adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique in children: a feasibility study. Pediatr Radiol 41:1174–1182
Yanagawa M, Honda O, Yoshida S et al (2010) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique for pulmonary CT: image quality of the cadaveric lung on standard- and reduced-dose CT. Acad Radiol 17:1259–1266
Habets J, Symersky P, de Mol BA, Mali WP, Leiner T, Budde RP (2012) A novel iterative reconstruction algorithm allows reduced dose multidetector-row CT imaging of mechanical prosthetic heart valves. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28:1567–1575
Utsunomiya D, Weigold WG, Weissman G, Taylor AJ (2012) Effect of hybrid iterative reconstruction technique on quantitative and qualitative image analysis at 256-slice prospective gating cardiac CT. Eur Radiol 22:1287–1294
Beister M, Kolditz D, Kalender WA (2012) Iterative reconstruction methods in X-ray CT. Phys Med 28:94–108
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Roy Irwan, PhD (Toshiba Medical Systems), Alain Vlassenbroek, PhD (Philips Healthcare), Raymond Ubaghs (GE Healthcare), and Michiel de Bruijn (Siemens Medical Solutions) for reviewing the IR algorithm paragraphs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willemink, M.J., de Jong, P.A., Leiner, T. et al. Iterative reconstruction techniques for computed tomography Part 1: Technical principles. Eur Radiol 23, 1623–1631 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2765-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2765-y