Abstract
Aims
To compare in vivo DNA lesions induced during helical and sequential coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) and to evaluate the effect of CT parameters on double-strand break (DSB) levels.
Methods
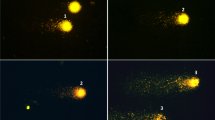
Thirty-six patients were examined with various CT protocols and modes (helical scan, n = 27; sequential scan, n = 9) either using a 64-slice dual-source or a 128-slice CT system. Blood samples were obtained before and 30 min after CT. Lymphocytes were isolated, stained against the phosphorylated histone variant γ-H2AX, and DSBs were visualised by using fluorescence microscopy.
Results
DSB yields 30 min after CTA ranged from 0.04 to 0.71 per cell and showed a significant correlation to DLP (ρ = 0.81, p < 0.00001). Median DSB yield and median DLP were significantly lower after sequential compared to helical CT examinations (0.11 vs. 0.37 DSBs/cell and 249 vs. 958 mGy cm, p < 0.00001). Additional calcium scoring led to an increase in DLP (p = 0.15) and DSB levels (p = 0.04). DSB levels normalised to the DLP showed a significant correlation to the attenuation of the blood (ρ = 0.53, p = 0.01) and a negative correlation to the body mass index of the patients (ρ = −0.37, p = 0.06).
Conclusion
γ-H2AX immunofluorescence microscopy allows one to determine dose-related effects on x-ray-induced DSB levels and to consider individual factors which cannot be monitored by physical dose measurements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hermann F et al (2009) Estimated radiation dose associated with cardiac CT angiography. JAMA 301(5):500–507
Paul JF, Abada HT (2007) Strategies for reduction of radiation dose in cardiac multislice CT. Eur Radiol 17:2028–2037
Achenbach S, Anders K, Kalender WA (2008) Dual-source cardiac computed tomography: image quality and dose considerations. Eur Radiol 18:1188–1198
Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hadamitzky M et al (2006) Radiation dose estimates from cardiac multislice computed tomography in daily practice: impact of different scanning protocols on effective dose estimates. Circulation 113:1305–1310
Leschka S, Scheffel H, Desbiolles L et al (2007) Image quality and reconstruction intervals of dual-source CT coronary angiography: recommendations for ECG-pulsing windowing. Invest Radiol 42:543–549
Herzog BA, Husmann L, Burkhard N et al (2008) Accuracy of low-dose computed tomography coronary angiography using prospective electrocardiogram-triggering: first clinical experience. Eur Heart J 29:3037–3042
Stolzmann P, Leschka S, Scheffel H et al (2008) Dual-source CT in step-and-shoot mode: noninvasive coronary angiography with low radiation dose. Radiology 249:71–80
Earls JP, Berman EL, Urban BA et al (2008) Prospectively gated transverse coronary CT angiography versus retrospectively gated helical technique: improved image quality and reduced radiation dose. Radiology 246:742–753
Hausleiter J, Meyer T (2008) Tips to minimize radiation exposure. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2:325–327
Deak P, van Straten M, Shrimpton PC, Zankl M, Kalender WA (2008) Validation of a Monte Carlo tool for patient-specific dose simulations in multi-slice computed tomography. Eur Radiol 18:759–772
Kalender WA, Schmidt B, Zankl M, Schmidt M (1999) A PC program for estimating organ dose and effective dose values in computed tomography. Eur Radiol 9:555–562
Bauchinger M (1995) Quantification of low-level radiation exposure by conventional chromosome aberration analysis. Mutat Res 339:177–189
Edwards AA, Lindholm C, Darroudi F et al (2005) Review of translocations detected by FISH for retrospective biological dosimetry applications. Radiat Prot Dosim 113:396–402
Lobrich M, Rief N, Kuhne M et al (2005) In vivo formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks after computed tomography examinations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:8984–8989
Rothkamm K, Balroop S, Shekhdar J, Fernie P, Goh V (2007) Leukocyte DNA damage after multi-detector row CT: a quantitative biomarker of low-level radiation exposure. Radiology 242:244–251
Flohr TG, McCollough CH, Bruder H et al (2006) First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol 16:256–268
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM (1998) DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem 273:5858–5868
Rothkamm K, Lobrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:5057–5062
Haberle L, Pfahlberg A, Gefeller O (2009) Assessment of multiple ordinal endpoints. Biom J 51:217–226
Rosenbaum PR (1994) Coherence in observational studies. Biometrics 50:368–374
Kuefner MA, Grudzenski S, Schwab SA et al (2009) DNA double-strand breaks and their repair in blood lymphocytes of patients undergoing angiographic procedures. Invest Radiol 44:440–446
Gutstein A, Dey D, Cheng V et al (2008) Algorithm for radiation dose reduction with helical dual source coronary computed tomography angiography in clinical practice. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2:311–322
Hermann F, Martinoff S, Meyer T et al (2008) Reduction of radiation dose estimates in cardiac 64-slice CT angiography in patients after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Invest Radiol 43:253–260
McCollough CH, Primak AN, Saba O et al (2007) Dose performance of a 64-channel dual-source CT scanner. Radiology 243:775–784
Weustink AC, Mollet NR, Neefjes LA et al (2009) Preserved diagnostic performance of dual-source CT coronary angiography with reduced radiation exposure and cancer risk. Radiology 252:53–60
Grudzenski S, Kuefner MA, Heckmann MB, Uder M, Lobrich M (2009) Contrast medium-enhanced radiation damage caused by CT examinations. Radiology 253:706–714
Norman A, Cochran ST, Sayre JW (2001) Meta-analysis of increases in micronuclei in peripheral blood lymbphocytes after angiography or excretory urography. Radiat Res 155:740–743
Rube CE, Grudzenski S, Kuhne M et al (2008) DNA double-strand break repair of blood lymphocytes and normal tissues analysed in a preclinical mouse model: implications for radiosensitivity testing. Clin Cancer Res 14:6546–6555
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Engert for excellent technical assistance and L. Distel for extraordinary collaboration in the laboratory. We also wish to acknowledge G. Muschiol for his support. This work was partly supported by a grant from “Bundesministerium für Forschung und Bildung”, Bonn, Germany [grant number BMBF 01 EV0708].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuefner, M.A., Grudzenski, S., Hamann, J. et al. Effect of CT scan protocols on x-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in blood lymphocytes of patients undergoing coronary CT angiography. Eur Radiol 20, 2917–2924 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1873-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1873-9