Abstract
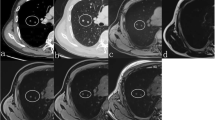
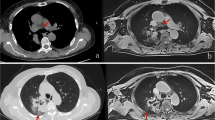
This study aimed at prospectively compared efficacy of non-contrast-enhanced (non-CE) MRI and MDCT for management of pulmonary nodules. A total of 161 patients with 200 nodules underwent MDCT and non-CE MRI (T1WI, T2WI, and STIR) in conjunction with pathological and/or more than 2 years of follow-up examinations. To compare qualitative detection rates between both modalities, all nodules were visually assessed. To compare quantitative and qualitative diagnostic capabilities of MRI, calculation of contrast ratio and visual assessment of probability for malignancy in each nodule were performed. Then, detection rate and diagnostic capability were statistically compared. Although the overall detection rate of each MR sequence (82.5%) was significantly lower than that of MDCT (97.0%, p < 0.05), that of malignant nodules showed no significant difference (p > 0.05). The diagnostic capability of STIR was significantly higher than those of other MR sequences (p < 0.05). Non-CE MR imaging was found to be as useful as MDCT for management of pulmonary nodules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henschke CI, McCauley DI, Yankelevitz DF, Naidich DP, McGuinness G, Miettinen OS, Libby DM, Pasmantier MW, Koizumi J, Altorki NK, Smith JP (1999) Early Lung Cancer Action Project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. Lancet 354:99–105
Swensen SJ, Jett JR, Hartman TE, Midthun DE, Mandrekar SJ, Hillman SL, Sykes AM, Aughenbaugh GL, Bungum AO, Allen KL (2005) CT screening for lung cancer: 5-year prospective experience. Radiology 235:259–265
Garg K, Keith RL, Byers T, Kelly K, Kerzner AL, Lynch DA, Miller YE (2002) Randomized controlled trial with low-dose spiral CT for lung cancer screening: feasibility study and preliminary results. Radiology 225:506–510
MacMahon H, Austin JH, Gamsu G, Herold CJ, Jett JR, Naidich DP, Patz EF Jr, Swensen SJ, Fleischner Society (2005) Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 23:395–400
Swensen SJ (2002) CT screening for lung cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:833–836
Kim JH, Kim HJ, Lee KH, Kim KH, Lee HL (2004) Solitary pulmonary nodules: a comparative study evaluated with contrast-enhanced dynamic MR imaging and CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:766–775
Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Takenaka D, Adachi S, Kono M, Sugimura K (2002) Solitary pulmonary nodules: potential role of dynamic MR imaging in management initial experience. Radiology 224:503–511
Swensen SJ, Viggiano RW, Midthun DE, Müller NL, Sherrick A, Yamashita K, Naidich DP, Patz EF, Hartman TE, Muhm JR, Weaver AL (2000) Lung nodule enhancement at CT: multicenter study. Radiology 214:73–80
Marom EM, Sarvis S, Herndon JE 2nd, Patz EF Jr (2002) T1 lung cancers: sensitivity of diagnosis with fluorodeoxyglucose PET. Radiology 223:453–459
Kim SK, Allen-Auerbach M, Goldin J, Fueger BJ, Dahlbom M, Brown M, Czernin J, Schiepers C (2007) Accuracy of PET/CT in characterization of solitary pulmonary lesions. J Nucl Med 48:214–220
Jeong YJ, Lee KS, Jeong SY, Chung MJ, Shim SS, Kim H, Kwon OJ, Kim S (2005) Solitary pulmonary nodule: characterization with combined wash-in and washout features at dynamic multi-detector row CT. Radiology 237:675–683
Kono R, Fujimoto K, Terasaki H, Müller NL, Kato S, Sadohara J, Hayabuchi N, Takamori S (2007) Dynamic MRI of solitary pulmonary nodules: comparison of enhancement patterns of malignant and benign small peripheral lung lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:26–36
Hashimoto Y, Tsujikawa T, Kondo C, Maki M, Momose M, Nagai A, Ohnuki T, Nishikawa T, Kusakabe K (2006) Accuracy of PET for diagnosis of solid pulmonary lesions with 18F-FDG uptake below the standardized uptake value of 2.5. J Nucl Med 47:426–431
Vogt FM, Herborn CU, Hunold P, Lauenstein TC, Schröder T, Debatin JF, Barkhausen J (2004) HASTE MRI versus chest radiography in the detection of pulmonary nodules: comparison with MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:71–78
Schroeder T, Ruehm SG, Debatin JF, Ladd ME, Barkhausen J, Goehde SC (2005) Detection of pulmonary nodules using a 2D HASTE MR sequence: comparison with MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:979–984
Ohno Y, Sugimura K, Hatabu H (2002) MR imaging of lung cancer. Eur J Radiol 44:172–181
Both M, Schultze J, Reuter M, Bewig B, Hubner R, Bobis I, Noth R, Heller M, Biederer J (2005) Fast T1- and T2-weighted pulmonary MR-imaging in patients with bronchial carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 53:478–488
Kersjes W, Mayer E, Buchenroth M, Schunk K, Fouda N, Cagil H (1997) Diagnosis of pulmonary metastases with turbo-SE MR imaging. Eur Radiol 7:1190–1194
Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Takenaka D, Higashino T, Watanabe H, Ohbayashi C, Yoshimura M, Satouchi M, Nishimura Y, Sugimura K (2004) Metastases in mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: quantitative and qualitative assessment with STIR turbo spin-echo MR imaging. Radiology 231:872–879
Walker R, Kessar P, Blanchard R, Dimasi M, Harper K, DeCarvalho V, Yucel EK, Patriquin L, Eustace S (2000) Turbo STIR magnetic resonance imaging as a whole-body screening tool for metastases in patients with breast carcinoma: preliminary clinical experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:343–350
Yi CA, Jeon TY, Lee KS, Lee JH, Seo JB, Kim YK, Chung MJ (2007) 3-T MRI: usefulness for evaluating primary lung cancer and small nodules in lobes not containing primary tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 18:386–392
Bruegel M, Gaa J, Woertler K, Ganter C, Waldt S, Hillerer C, Rummeny EJ (2007) MRI of the lung: value of different turbo spin-echo, single-shot turbo spin-echo, and 3D gradient-echo pulse sequences for the detection of pulmonary metastases. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:73–81
Romano PS, Mark DH (1992) Patient and hospital characteristics related to in-hospital mortality after lung cancer resection. Chest 101:1332–1337
Ginsberg RJ, Hill LD, Eagan RT, Thomas P, Mountain CF, Deslauriers J, Fry WA, Butz RO, Goldberg M, Waters PF et al (1983) Modern thirty-day operative mortality for surgical resections in lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 86:654–658
Nagasaki F, Flehinger BJ, Martini N (1982) Complications of surgery in the treatment of carcinoma of the lung. Chest 82:25–29
Wiener JI, Chako AC, Merten CW, Gross S, Coffey EL, Stein HL (1986) Breast and axillary tissue MR imaging: correlation of signal intensities and relaxation times with pathologic findings. Radiology 160:299–305
Fossel ET, Brodsky G, deLayre JL, Wilson RE (1983) Nuclear magnetic resonance for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast tissues and axillary lymph nodes. Ann Surg 198:541–545
Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Argersinger RE, Allen-Moore G (1987) A review of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in pathology: are T1 and T2 diagnostic? Med Phys 14:1–37
Shuman WP, Baron RL, Peters MJ, Tazioli PK (1989) Comparison of STIR and spin-echo MR imaging at 1.5 T in 90 lesions of the chest, liver, and pelvis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 152(4):853–859
Fink C, Puderbach M, Biederer J, Fabel M, Dietrich O, Kauczor HU, Reiser MF, Schönberg SO (2007) Lung MRI at 1.5 and 3 Tesla: observer preference study and lesion contrast using five different pulse sequences. Invest Radiol 42(6):377–383
Obuchowski NA, Graham RJ, Baker ME, Powell KA (2001) Ten criteria for effective screening: their application to multislice CT screening for pulmonary and colorectal cancers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:1357–1362
Black WC, Welch HG (1993) Advances in diagnostic imaging and overestimation of disease prevalence and the benefits of therapy. N Engl J Med 328:1237–1243
Black WC, Welch HG (1997) Screening for disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:3–11
Acknowledgement
The authors thanks Munenobu Nogami, M.D., Ph.D. (Division of PET, Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation), Yoshikazu Kotani, M.D. (Division of Cardiovascular and Respiratory Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine), Masahiro Yoshimura, M.D. (Division of Pulmonary Surgery, Hyogo Cancer Center), Takanori Higashino, M.D., Ph.D. (Department of Radiology, Tenri Hospital), Hideaki Kawamitsu, B.S., and Masahiko Fujii, M.D. (Division of Radiology, Kobe University Hospital) for their contribution to this work. This work was supported by Philips Medical Systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Philips Medical Systems and the Knowledge Cluster Initiative of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyama, H., Ohno, Y., Kono, A. et al. Quantitative and qualitative assessment of non-contrast-enhanced pulmonary MR imaging for management of pulmonary nodules in 161 subjects. Eur Radiol 18, 2120–2131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1001-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1001-2