Abstract
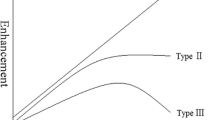
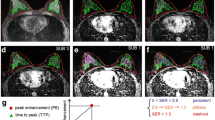
Our aim was to evaluate quantitative parametric analysis for characterization of breast lesions in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) mammography. In 62 patients, contrast-enhanced MR mammography revealed 75 suspicious lesions, of which 18 were benign and 57 were malignant. The quantitative parametric analysis delineates signal intensity changes of contrast-enhanced lesions on a pixel-by-pixel basis. The initial rate of enhancement is coded by color intensity: a slow rate is coded to dark; a fast rate, bright. The postinitial enhancement change is coded by color hue: blue for increasing signal intensity, green for plateau, and red for decrease in signal intensity. Malignant lesions showed a significantly higher number of bright-red (P=0.004) and medium-red (P<0.001) pixels than benign lesions. Benign lesions showed significantly more blue pixels than did malignant lesions (P=0.010). Of the 75 lesions, 72 (96%) showed heterogeneous distribution of pixel color hue. Quantitative parametric analysis of contrast kinetics in lesions can replace the subjective manual region of interest (ROI) method and makes a step toward standardization of MR mammography. It allows quantitative evaluation of different contrast kinetics parameters in contrast-enhanced breast lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heywang SH, Bassermann R, Fenzl G, Nathrat W, Hahn D, Beck R, Krischke I, Eiermann W (1987) MRI of the breast: histopathologic correlation. Eur J Radiol 7:175–182
Fischer U, Kopka L, Brinck U, Korabiowska M, Schauer A, Grabbe E (1997) Prognostic value of contrast-enhanced MR mammography in patients with breast cancer. Eur Radiol 7:1002–1005
Kuhl CK (2000) MRI of breast tumors. Eur Radiol 10:46–58
Kuhl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S, Leutner C, Wardelmann E, Gieseke J, Schild HH (1999) Dynamic breast MR imaging: are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211(1):101–110
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 220(1):13–30
Agoston AT, Daniel BL, Herfkens RJ, Ikeda DM, Birdwell RL, Heiss SG, Sawyer-Glover AM (2001) Intensity-modulated parametric mapping for simultaneous display of rapid dynamic and high-spatial-resolution breast MR imaging data. Radiographics 21(1):217–226
Szabo BK, Wiberg MK, Bone B, Aspelin P (2004) Application of artificial neural networks to the analysis of dynamic MR imaging features of the breast. Eur Radiol 14(7):1217–1225
Oshida K, Nagashima T, Ueda T, Yagata H, Tanabe N, Nakano S, Nikaidou T, Funatsu H, Hashimoto H, Miyazaki M (2005) Pharmacokinetic analysis of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast using dynamic MR mammography. Eur Radiol 15(7):1353–1360
Vomweg TW, Teifke A, Kunz RP, Hintze C, Hlawatsch A, Kern A, Kreitner KF, Thelen M (2004) Combination of low and high resolution sequences in two orientations for dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: more than a compromise. Eur Radiol 14(10):1732–1742
Kuhl CK, Schild HH, Morakkabati N (2005) Dynamic bilateral contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast: trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution. Radiology 236(3):789–800
Baum F, Fischer U, Vosshenrich R, Grabbe E (2002) Classification of hypervascularized lesions in CE MR imaging of the breast. Eur Radiol 12(5):1087–1092
Orel SG (1999) Differentiating benign from malignant enhancing lessions identified at MR imaging of the breast: Are time signal-intensity curves an accurate predictor? Radiology 211:5–7
Gilles R, Guinebretiere JM, Lucidarme O, Cluzel P, Janaud G, Finet JF, Tardivon A, Masselot J, Vanel D (1994) Nonpalpable breast tumors: diagnosis with contrast-enhanced subtraction dynamic MR imaging. Radiology 191(3):625–631
Boetes C, Barentsz JO, Mus RD, van der Sluis RF, van Erning LJ, Hendriks JH, Holland R, Ruys SH (1994) MR characterization of suspicious breast lesions with a gadolinium-enhanced TurboFLASH subtraction technique. Radiology 193(3):777–781
Orel SG, Schnall MD, LiVolsi VA, Troupin RH (1994) Suspicious breast lesions: MR imaging with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiology 190 (2):485–493
Mussurakis S, Buckley DL, Horsman A (1997) Dynamic MRI of invasive breast cancer: assessment of three region-of-interest analysis methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21(3):431–438
Hoffmann U, Brix G, Knopp MV, Hess T, Lorenz WJ (1995) Pharmacokinetic mapping of the breast: a new method for dynamic MR mammography. Magn Reson Med 33(4):506–514
Parker GJ, Suckling J, Tanner SF, Padhani AR, Revell PB, Husband JE, Leach MO (1997) Probing tumor microvascularity by measurement, analysis and display of contrast agent uptake kinetics. J Magn Reson Imaging 7(3):564–674
Degani H, Gusis V, Weinstein D, Fields S, Strano S (1997) Mapping pathophysiological features of breast tumors by MRI at high spatial resolution. Natl Med 3(7):780–782
Furman-Haran E, Grobgeld D, Margalit R, Degani H (1998) Response of MCF7 human breast cancer to tamoxifen: evaluation by the three-time-point, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging method. Clin Cancer Res 4:2299–2304
Furman-Haran E, Grobgeld D, Kelcz F, Degani H (2001) Critical role of spatial resolution in dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:862–867
Tofts PS, Kermode AG (1991) Measurement of the blood-brain barrier permeability and leakage space using dynamic MR imaging 1 Fundamental concepts. Magn Reson Med 17(2):357–367
Tofts PS, Berkowitz B, Schnall MD (1995) Quantitative analysis of dynamic Gd-DTPA enhancement in breast tumors using a permeability model. Magn Reson Med 33(4):564–568
Kelcz F, Furman-Haran E, Grobgeld D, Degani H (2002) Clinical testing of high-spatial-resolution parametric contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1492–1585
Yeh ED, Slanetz PJ, Edmister WB, Talele A, Monticciolo D, Kopans DB (2003) Invasive lobular carcinoma: spectrum of enhancement and morphology on magnetic resonance imaging. Breast J 9(1):13–18
Schelfout K, Van Goethem M, Kersschot E, Verslegers I, Biltjes I, Leyman P, Colpaert C, Thienpont L, Van den Haute J, Gillardin JP, Tjalma W, Buytaert P, De Schepper A (2004) Preoperative breast MRI in patients with invasive lobular breast cancer. Eur Radiol 14(7):1209–1216
Hauth EAM, Stockamp C, Maderwald S, Mühler A, Kimmig R, Jaeger H, Barkhausen J, Forsting M (2006) Evaluation of the three-time-point method for diagnosis of breast lesions in contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Clin Imaging 30(3):160–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauth, E.A.M., Jaeger, H., Maderwald, S. et al. Evaluation of quantitative parametric analysis for characterization of breast lesions in contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Eur Radiol 16, 2834–2841 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0348-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0348-5