Abstract
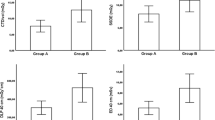
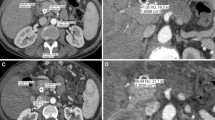
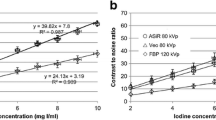
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a contrast material injection protocol with dose and injection rate of contrast material tailored to patient weight (dose tailored to patient weight and fixed injection duration). Hepatic helical CT was performed in 92 patients with chronic liver damage with a dose of 1.4 ml (518 mgI) at a rate of 0.056 ml/s per kilogram body weight of Iopamidol 370. Attenuation values of liver and aorta were measured for calculation of maximum aortic and hepatic enhancement, time to maximum hepatic enhancement, and end of hepatic arterial phase. Correlation coefficients between the injection rate and the four parameters were r=0.008, 0.057, 0.167, and 0.036, and there were no statistically significant correlations between the injection rates and the four parameters. In our injection protocol, uniform temporal scan window may be achieved and the injection rate can be reduced in lighter patients without reducing the degree of enhancement in the aorta and the liver.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonaldi VM, Bret PM, Reinhold C, Atri M (1995) Helical CT of the liver: value of an early hepatic arterial phase. Radiology 197:357
Oliver JH III, Baron RL (1996) Helical biphasic contrast enhanced CT of the liver: technique, indications, interpretations, and pitfalls. Radiology 201:1
Mitsuzaki K, Yamashita Y, Ogata I, Nishiharu T, Urata J, Takahashi M (1996) Multiple-phase helical CT of the liver for detecting small hepatomas in patients with liver cirrhosis: contrast-injection protocol and optimal timing. AJR 167:753
Foley WD, Hoffmann RG, Quiroz FA, Kahn CE, Perret RS (1994) Hepatic helical CT: contrast material injection protocol. Radiology 192:367
Hollete MD, Jeffrey RB Jr, Nino-Murcia M, Jorgensen MJ, Harris DP (1995) Dual-phase helical CT of the liver: value of arterial phase scans in the detection of small (≤1.5 cm) malignant hepatic neoplasms. AJR 164:879
Kopka L, Funke M, Fischer U, Vosshenrich R, Oestmann JW, Grabbe E (1995) Parenchymal liver enhancement with bolus-triggered helical CT: preliminary clinical results. Radiology 195:282
Silverman PM, O'Malley J, Tefft MC, Cooper C, Zeman R (1995) Conspicuity of heptatic metastases on helical CT: effect of different time delays between contrast administration and scanning. AJR 164:619
Heiken JP, Brink JA, McClennan BL, Sagel SS, Crowe TM, Gaines MV (1995) Dynamic incremental CT: effect of volume and concentration of contrast material and patient weight on hepatic enhancement. Radiology 195:353
Brink JA, Heiken JP, Forman HP, Sagel SS, Molina PL, Brown PC (1995) Hepatic spiral CT: reduction of dose of intravenous contrast material. Radiology 197:83
Dean PB, Violante MR, Mahoney JA (1980) Hepatic CT contrast enhancement: effect of dose, duration of infusion, and time elapsed following infusion. Invest Radiol 15:158
Berland LL, Lee JY (1988) Comparison of contrast media injection rates and volumes for hepatic dynamic incremented computed tomography. Invest Radiol 23:918
Harmon BH, Berland LL, Lee JY (1992) Effect of varying rates of low-osmolarity contrast media injection for hepatic CT: correlation with indocyanine green transit time. Radiology 184:379
Heiken JP, Brink JA, McClennan BL, Sagel SS, Forman HP, DiCroce J (1993) Dynamic contrast-enhanced CT of the liver: comparison of contrast medium injection rates and uniphasic and biphasic injection protocols. Radiology 187:327
Garcia PA, Bonaldi VM, Bret PM, Liang L, Reinhold C, Atri M (1996) Effect of rate of contrast medium injection on hepatic enhancement at CT. Radiology 199:185
Bae KT, Heiken JP, Brink JA (1998) Aortic and hepatic peak enhancement at CT: effect of contrast medium injection rate pharmacokinetic analysis and experimental porcine model. Radiology 206:455
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S et al. (1998) Effect of injection rates of contrast material on arterial phase hepatic CT. AJR 171:429
Itoh S, Ikeda M, Achiwa M, Ota T, Satake H, Ishigaki T (2003) Multiphase contrast-enhanced CT of the liver with a multislice CT scanner. Eur Radiol 13:1085
Kopp AF, Heuschmid M, Claussen CD (2002) Multidetector helical CT of the liver for tumor detection and characterization. Eur Radiol 12:745
Sandstede JJ, Tshammler A, Beer M, Vogelsang C, Wittenberg G, Hahn D (2001) Optimization of automatic bolus tracking for timing of the arterial phase of helical liver CT. Eur Radiol 11:1396
Yamashita Y, Komohara Y, Takahashi M, Uchida M, Hayabuchi N, Shimizu T, Narabayashi I (2000) Abdominal helical CT: evaluation of optimal doses of intravenous contrast material. A prospective randomized study. Radiology 216:718
Murakami T, Kim T, Takamura M et al. (2001) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcianoma: detection with double arterial phase multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology 218:763
Foley WD, Mallisee TA, Hohenwalter MD, Wilson CR, Quiroz FA, Taylor AJ (2000) Multiphase hepatic CT with a multirow detector CT scanner. AJR 175:679
Katayama H, Yamaguchi K, Kozuka T, Takashima T, Seez P, Matsuura K (1990) Adverse reactions to ionic and nonionic contrast media. A report from the Japanese committee on the safety of contrast media. Radiology 175:621
Acknowledgement
We thank H. Suzuki for his suggestions in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awai, K., Hori, S. Effect of contrast injection protocol with dose tailored to patient weight and fixed injection duration on aortic and hepatic enhancement at multidetector-row helical CT. Eur Radiol 13, 2155–2160 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1904-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1904-x