Abstract
Purpose
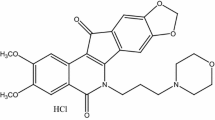
Irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) is a potent topoisomerase I inhibitor and is established and used widely as an antitumor agent. However, it sometimes causes severe side effects such as myelosuppression and diarrhea. These dose-limiting toxicities prevent the adoption of CPT-11 in aggressive chemotherapy. Thus we sought to determine in a rat model whether extending the period of infusion of CPT-11 would ameliorate the adverse reactions.
Methods
CPT-11 was administered intravenously (i.v.) to rats at a dose of 60 mg/kg per day for four consecutive days as a bolus injection or as 3-, 8- or 24-h infusions, and then blood cell counts and the incidence of acute and delayed-onset diarrhea were monitored.
Results
Serious acute and delayed-onset diarrhea and marked decreases in the number of neutrophils and lymphocytes were observed in the bolus injection group. These symptoms were alleviated in the infusion groups with the degree of alleviation dependent on infusion time. In the bolus injection group, mucosal impairment of the cecal epithelium including wall thickening, edema, a decrease in the number and size of crypts, and the formation of a pseudomembrane-like substance was observed, whereas these changes were less severe in the infusion groups. Areas under the plasma concentration-time curves (AUCpla) of CPT-11 and its metabolite, 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), differed little among the bolus injection group, and the 3-h and 8-h infusion groups. However, the AUCpla values of CPT-11 and SN-38 were significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in the 24-h infusion group. The maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of CPT-11 decreased with increasing infusion time, but those of SN-38 did not.
Conclusions
It was confirmed that the side effects of CPT-11 were alleviated by extending the infusion time. The pharmacokinetic parameters suggested that the Cmax of CPT-11 is closely related to the incidence and severity of adverse reactions such as myelosuppression and acute and delayed-onset diarrhea.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUCcec :
-
Area under the cecal tissue concentration-time curve
- AUCmar :
-
Area under the bone marrow tissue concentration-time curve
- AUCpla :
-
Area under the plasma concentration-time curve
- Cmax :
-
Maximum concentration
- CLtot :
-
Total clearance
- CPT:
-
Camptothecin
- CPT-11:
-
Irinotecan hydrochloride [7-ethyl-10-(4-(piperidino)-1-piperidino)carbonyloxycamptothecin]
- G-CSF:
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- i.v.:
-
Intravenous(ly)
- MRT:
-
Mean residence time
- SN-38:
-
7-Ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin
- SN-38G:
-
SN-38 glucuronide
- T1/2 :
-
Half-life
- UGT:
-
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
References
Abigerges D, Armand JP, Chabot GG, Da Costa L, Fadel E, Cote C, Hérait P, Gandia D (1994) Irinotecan (CPT-11) high-dose escalation using intensive high-dose loperamide to control diarrhea. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:446
Ando M, Eguchi K, Shinnkai T, Tamura T, Ohe Y, Yamamoto M, Kurata T, Kasai T, Ohmatsu H, Kubota K, Sekine I, Hojo N, Matsumoto T, Kodama T, Kakinuma R, Saijo N (1997) Phase I study of sequentially administered topoisomerase I inhibitor (irinotecan) and topoisomerase II inhibitor (etoposide) for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 76:1494
Ando M, Ando Y, Sekido Y, Ando M, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y (2002) Genetic polymorphisms of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 gene and irinotecan toxicity in Japanese cancer patients. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:591
Ando Y, Saka H, Ando M, Sawa T, Muro K, Ueoka H, Yokoyama A, Saitoh S, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y (2000) Polymorphisms of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene and irinotecan toxicity: a pharmacogenetics analysis. Cancer Res 60:6921
Beubler E, Bukhave K, Madsen JR (1986) Significance of calcium for the prostaglandin E2-mediated secretory response to 5-hydroxytryptamine in the small intestine of rat in vivo. Gastroenterology 90:1972
Burakoff R, Percy WH (1992) Studies in vivo and in vitro on effects of PGE2 on colonic motility in rabbits. Am J Physiol 262:G23
Carven PA, Derubertis FR (1983) Patterns of prostaglandin synthesis and degradation in isolated superficial and proliferative colonic epithelial cells compared to residual colon. Prostaglandin 26:583
Crane CH, Janjan NA, Mason K, Milas L (2002) Preoperative chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer: emerging treatment strategies. Oncology 16:39
Del-Bino G, Lassota P, Darzynkiewicz Z (1991) The S-phase cytotoxicity of camptothecin. Exp Cell Res 193:27
De Jonge MJA, Sparreboom A, Planting AST, Van der Berg MEL, De Boer-Dennert MM, Ter Steeg J, Jacques C, Verweij J (2000) Phase I study of 3-week schedule of irinotecan combined with cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 18:187
Egusa Y, Fujiwara Y, Syaharuddin E, Sumiyoshi H, Isobe T, Yamakido M (1998) Mobilization of peripheral blood stem cells in patients with advanced thoracic malignancies after irinotecan (CPT-11) administration. Anticancer Res 18:481
Fukuoka M, Niitani H, Suzuki A, Motomiya M, Hasegawa K, Nishiwaki Y, Kuriyama T, Ariyoshi Y, Negoro S, Masuda N, Nakajima S, Taguchi T (1992) A phase II study of CPT-11, a new derivative of camptothecin, for previously untreated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 10:16
Furuta T, Yokokura T (1990) Effect of administration schedules on the antitumor activity of CPT-11, a camptothecin derivative (in Japanese). Jpn J Cancer Chemother 17:121
Furuta T, Yokokura T, Mutai M (1988) Antitumor activity of CPT-11 against rat Walker 256 carcinoma (in Japanese). Jpn J Cancer Chemother 15:2757
Gandia D, Abigerges D, Armand JP, Chabot GG, Da Costa L, De Forni M (1993) CPT-11-induced cholinergic effects in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 11:196
Gerrits CJ, de Jonge MJ, Schellens JH, Stoter G, Verweij J (1997) Topoisomerase I inhibitors: the relevance of prolonged exposure for present clinical development. Br J Cancer 76:952
Goncalves E, Da Costa L, Abigerges D, Armand JP (1995) A new enkephalinase inhibitor as an alternative to loperamide in the prevention of diarrhea induced by CPT-11. J Clin Oncol 13:2144
Gupta E, Lestingi TM, Mick R, Ramirez J, Vokes EE, Ratain MJ (1994) Metabolic fate of irinotecan in humans: correlation of glucuronidation with diarrhea. Cancer Res 54:3723
Gupta E, Wang X, Ramirez J, Ratain MJ (1997) Modulation of glucuronidation of SN-38, the active metabolite of irinotecan, by valproic acid and phenobarbital. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 39:440
Hecht JR (1998) Gastrointestinal toxicity of irinotecan. Oncology 12:72
Herben VMM, Schellens JHM, Swart M, Gruia G, Vernillet L, Beijnen JH (1999) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan administered as a low-dose, continuous intravenous infusion over 14 days in patients with malignant solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 17:1897
Kase Y, Hayakawa T, Aburada M, Komatsu Y, Kamataki T (1997) Preventive effects of Hange-shashin-to on irinotecan hydrochloride-caused diarrhea and its relevance to the colonic prostaglandin E2 and water absorption in the rat. Jpn J Pharmacol 75:407
Kawato Y, Tsumori T, Akahane K, Sekiguchi M, Sato K (1990) Inhibitory effect of CPT-11, a derivative of camptothecin, on acetylcholinesterase, and its binding ability to acetylcholine receptors (in Japanese). Clin Rep 24:7407
Kawato Y, Aonuma M, Hirota Y, Kuga H, Sato K (1991) Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumor effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res 51:4187
Kehrer DFS, Sparreboom A, Verweij J, de Bruijn P, Nierop CA, van der Schraaf J, Ruijgrok EJ, de Jonge JA (2001) Modulation of irinotecan-induced diarrhea by cotreatment with neomycin in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 7:1136
Kojima A, Shinkai T, Saijo N (1993) Cytogenetic effects of CPT-11 and its active metabolite, SN-38 on human lymphocytes. Jpn J Clin Oncol 23:116
Kudoh S, Fukuoka M, Matsuda N, Kusunoki Y, Matsui K, Negoro G, Takifuji N, Nakagawa K, Hirashima T, Tamanoi M, Nitta T, Yana H, Takada M (1993) Relationship between CPT-11 pharmacokinetics and diarrhea in the combination chemotherapy of irinotecan (CPT-11) and cisplatin (CDDP). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 12:141
Kunimoto T, Nitta K, Tanaka T, Uehara M, Baba H, Takeuchi M, Yokokura T, Sawada S, Miyasaka T, Mutai M (1987) Antitumor activity of 7-ethyl-10-(4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino)carbonyloxycamptothecin, a novel water-soluble derivative of camptothecin, against murine tumors. Cancer Res 46:5944
Kurita A, Kaneda N (1999) High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of the camptothecin derivative irinotecan hydrochloride, CPT-11, and its metabolites SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide in rat plasma with a fully automated on-line solid phase extraction system, PROSPEKT. J Chromatogr B 724:335
Kurita A, Kado S, Kaneda N, Onoue M, Hashimoto S, Yokokura T (2000) Modified irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) administration schedule improves induction of delayed-onset diarrhea in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 46:211
Luria RC, Rimon G, Moran A (1993) PGE2 inhibits Na+-K+-ATPase activity and ouabain binding in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol 264:F61
Ma KM, Zamboni WC, Radomski KM, Furman WL, Santana VM, Houghton PJ, Hanna SK, Smith AK, Stewart CF (2000) Pharmacokinetics of irinotecan and its metabolites SN-38 and APC in children with recurrent solid tumors after protracted low-dose irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res 6:813
Masuda N, Fukuoka M, Kudoh S, Kusunoki Y, Matsui K, Takifuji N, Nakazawa K, Tamanoi M, Nitta T, Hirashima T, Negoro S, Takada M (1993) Phase I and pharmacologic study of irinotecan in combination with cisplatin for advanced lung cancer. Br J Cancer 68:777
Mehta VK, Cho C, Ford JM, Jambalos C, Poen J, Koong A, Lin A, Bastidas JA, Young H, Dunphy EP, Fisher G (2003) Phase II trial of preoperative 3D conformal radiotherapy, protracted venous infusion 5-fluorouracil, and weekly CPT-11, followed by surgery for ultrasound-staged T3 rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 55:132
Mori K, Machida S, Yoshida T, Yoshida M, Kano Y, Tominaga K (1999) A phase II study of irinotecan and infusional cisplatin with recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor support for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43:467
Mori K, Kondo T, Kamiyama Y, Kano Y, Tominaga K (2003) Preventive effect of Kampo medicine (Hangeshasin-to) against irinotecan-induced diarrhea in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 51:403–406
Ohe Y, Sakai Y, Shinkai T, Eguchi K, Tamura T, Kojima A, Kunikane H, Okamoto H, Karato A, Ohmatsu H, Kanzawa F, Saijo N (1993) Phase I study and pharmacokinetics of CPT-11 with 5-day continuous infusion. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:972
Ohno R, Okada K, Masaoka T, Kuramoto A, Arima T, Yoshida Y, Ariyoshi H, Ichimaru M, Sakai Y, Oguro M, Ito Y, Morishima Y, Yokomaru S, Ohta K (1990) An early phase II study of CPT-11: a new derivative of camptothecin, for the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 8:1907
Pro B, Lozano R, Ajani JA (2001) Therapeutic response to octreotide in patients with refractory CPT-11 induced diarrhea. Invest New Drugs 19:341
Rothenberg ML, Kuhn JG, Burris HA III, Morales MT, Nelson J, Eckardt JR, Rock MK, Terada K, Von Hoff DD (1992) Phase I and pharmacokinetic trial of CPT-11 in patients with refractory solid tumors. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 11:113
Sakai H, Ciener M, Gartmann N, Takeguchi N (1995) Eicosanoid-mediated Cl− secretion induced by the antitumor drug, irinotecan (CPT-11), in the rat colon. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 351:309
Saliba F, Hagipantelli R, Misset JL, Bastian G, Vassal G, Bonnay M, Herait P, Cote C, Mahjoubi M, Mignard D, Cvitkovic E (1998) Pathophysiology and therapy of irinotecan-induced delayed-onset diarrhea in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a prospective assessment. J Clin Oncol 16:2745
Sasaki Y, Hakusui H, Mizuno S, Morita M, Miya T, Eguchi K, Shinkai T, Tamura T, Ohe Y, Saijo N (1995) A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of CPT-11 and its metabolite SN-38. Jpn J Cancer Res 86:101
Savarese D, Al-Zoubi A, Boucher J (2000) Glutamine for irinotecan diarrhea. J Clin Oncol 18:450
Sharon P, Karmeli F, Ranchmilewitz D (1984) Effect of prostanoids on human intestinal Na-K-ATPase activity. Isr J Med Sci 20:677
Shimada Y, Yoshino M, Wakui A, Nakao I, Futatsuki K, Sakata Y, Kambe M, Taguchi T, Ogawa N (1993) Phase II study of CPT-11, a new camptothecin derivative, in metastatic colorectal cancer. CPT-11 Gastrointestinal Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol 11:909
Shirao K, Shimada Y, Kondo H, Saito D, Yamao T, Ono H, Yokoyama T, Fukuda H, Oka M, Watanabe Y, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Fujii T, Oda Y, Muro K, Yoshida S (1997) Phase I-II study of irinotecan hydrochloride combined with cisplatin in patients with advanced gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol 15:921
Takasuna K, Kasai Y, Kitano Y, Mori K, Kakihata K, Hirohashi M, Nomura M (1995) Study on the mechanisms of diarrhea induced by a new anticancer camptothecin derivative, irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11), in rats (in Japanese). Folia Pharmacol Jpn 50:447
Takasuna K, Kasai Y, Kitano Y, Mori K, Kobayashi R, Hagiwara T, Kakihata K, Hirohashi M, Nomura M, Nagai E, Kamataki T (1995) Protective effects of Kampo medicine and baicalin against intestinal toxicity of a new anticancer camptothecin derivative, irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11), in rats. Jpn J Cancer Res 86:978
Takasuna K, Hasegawa T, Hirohashi M, Kato M, Nomura M, Nagai E, Yokoi T, Kamataki T (1996) Involvement of β-glucuronidase in intestinal microflora in the intestinal toxicity of the antitumor camptothecin derivative irinotecan hydrochloride. Cancer Res 56:3752
Takeda Y, Kobayashi K, Akiyama Y, Soma T, Handa S, Kudoh S, Kudo K (2001) Prevention of irinotecan (CPT-11)-induced diarrhea by oral alkalization combined with control of defecation in cancer patients. Int J Cancer 92:269
Takeuchi S, Dobashi K, Fujimoto S, Tanaka K, Suzuki M, Terashima Y, Hasumi K, Akiya K, Negishi Y, Tamiya T, Tanizawa O, Sugawa T, Umesaki N, Sekiba K, Aono T, Nakano H, Noda K, Shirota M, Yakushiji M, Sugiyama T, Hashimoto M, Yajima A, Takamizawa H, Sonoda T, Takeda Y, Tomoda Y, Ohta M, Ozaki M, Hirabayashi K, Hiura M, Hatae M, Nishigaki K, Taguchi T (1991) A late phase II study of CPT-11 on uterine cervical cancer and ovarian cancer. Research Groups of CPT-11 in Gynecologic Cancers (in Japanese). Jpn J Cancer Chemother 18:1681
Takimoto CH, Morrison G, Harold N, Quinn M, Monahan BP, Band RA, Cottrell J, Guemei A, Llorens V, Hehman H, Ismail AS, Flemming D, Gosky DM, Hirota H, Berger SJ, Berger NA, Chen AP, Shapiro JD, Arbuck SG, Wright J, Hamilton JM, Allegra CJ, Grem JL (2000) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan administered as a 96-hours infusion weekly to adult cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 18:659
Trifan OC, Durham WF, Salazar VS, Horton J, Levine BD, Zweifel BS, Davis TW, Masferrer JL (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with celecoxib enhanced antitumor efficacy and reduces diarrhea side effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res 62:5778
Tsuji T, Kaneda N, Kado K, Yokokura T, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D (1991) CPT-11 converting enzyme from rat serum: purification and some properties. J Pharmacobiodyn 14:341
Videla S, Vilaseca J, Guarner F, Salas A, Treseerra F, Crespo E, Antolín M, Nalagelada JR (1994) Role of intestinal microflora in chronic inflammation and ulceration of the rat colon. Gut 53:1090
Acknowledgements
We thank Tsuneo Matsumoto, Yuriko Nagata and Minoru Andoh for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurita, A., Kado, S., Kaneda, N. et al. Alleviation of side effects induced by irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) in rats by intravenous infusion. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52, 349–360 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0682-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0682-0