Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate safety, efficacy, and symptom-control of radioembolization in patients with unresectable liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors (NETLMs).
Materials and Methods
Forty-two patients (mean age of 62 years) with treatment-refractory NETLMs underwent radioembolization using yttrium-90 (90Y) resin microspheres. Posttreatment tumor response was assessed by cross-sectional imaging using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) and tumor-marker levels. Laboratory and clinical toxicities and clinical symptoms were monitored.
Results
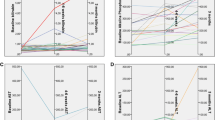
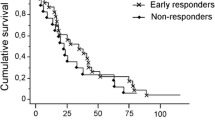
The median activity delivered was 1.63 GBq (range 0.63–2.36). Imaging follow-up using RECIST at 3-month follow-up demonstrated partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease in 22.5, 75.0, and 2.5% of patients, respectively. In 97.5% of patients, the liver lesions appeared hypovascular or partially necrotic. The mean follow-up was 16.2 months with 40 patients (95.2%) remaining alive. The median decrease in tumor-marker levels at 3 months was 54.8% (chromogranin A) and 37.3% (serotonin), respectively. There were no acute or delayed toxicities greater than grade 2 according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events [CTCAE (v3.0)]. No radiation-induced liver disease was noted. Improvement of clinical symptoms 3 months after treatment was observed in 36 of 38 symptomatic patients.
Conclusion
Radioembolization with 90Y-microspheres is a safe and effective treatment option in patients with otherwise treatment-refractory NETLMs. Antitumoral effect is supported by good local tumor control, decreased tumor-marker levels, and improved clinical symptoms. Further investigation is warranted to define the role of radioembolization in the treatment paradigm for NETLMs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams RA, King D, Wilson JF (1987) Objective response of malignant carcinoid to radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 13(6):869–873
Akerstrom G, Hellman P, Hessman O, Osmak L (2005) Management of midgut carcinoids. J Surg Oncol 89(3):161–169
Brown KT, Koh BY, Brody LA et al (1999) Particle embolization of hepatic neuroendocrine metastases for control of pain and hormonal symptoms. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10(4):397–403
Cao CQ, Yan TD, Bester L, Liauw W, Morris DL (2010) Radioembolization with yttrium microspheres for neuroendocrine tumour liver metastases. Br J Surg 97(4):537–543
Capurso G, Bettini R, Rinzivillo M, Boninsegna L, Delle Fave G, Falconi M (2011) Role of resection of the primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour only in patients with unresectable metastatic liver disease: a systematic review. Neuroendocrinology. doi:10.1159/000324770
Carr BI (2004) Hepatic arterial 90Yttrium glass microspheres (Therasphere) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: interim safety and survival data on 65 patients. Liver Transpl 10(2 Suppl 1):S107–S110
Chakravarthy A, Abrams RA (1995) Radiation therapy in the management of patients with malignant carcinoid tumors. Cancer 75(6):1386–1390
Chamberlain RS, Canes D, Brown KT et al (2000) Hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: does intervention alter outcomes? J Am Coll Surg 190(4):432–445
Chen H, Hardacre JM, Uzar A, Cameron JL, Choti MA (1998) Isolated liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: does resection prolong survival? J Am Coll Surg 187(1):88–92; discussion 92–93
Coldwell DM, Sewell PE (2005) The expanding role of interventional radiology in the supportive care of the oncology patient: from diagnosis to therapy. Semin Oncol 32(2):169–173
Delcore R, Friesen SR (1994) Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. J Am Coll Surg 178(2):187–211
Duffaud F, Therasse P (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. Bull Cancer 87(12):881–886
Eriksson BK, Larsson EG, Skogseid BM, Lofberg AM, Lorelius LE, Oberg KE (1998) Liver embolizations of patients with malignant neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumors. Cancer 83(11):2293–2301
Gaitan-Gaitan A, Rider WD, Bush RS (1975) Carcinoid tumor-cure by irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 1(1–2):9–13
Gray B, Van Hazel G, Hope M et al (2001) Randomised trial of SIR-Spheres plus chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy alone for treating patients with liver metastases from primary large bowel cancer. Ann Oncol 12(12):1711–1720
Gupta S, Johnson MM, Murthy R et al (2005) Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: variables affecting response rates and survival. Cancer 104(8):1590–1602
Hibi T, Sano T, Sakamoto Y et al (2007) Surgery for hepatic neuroendocrine tumors: a single institutional experience in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37(2):102–107
Jakobs TF, Hoffmann RT, Tatsch K, Trumm C, Reiser MF, Helmberger TK (2007) Developments and perspectives in radioablative techniques. Radiologe 47(12):1083–1088
Jakobs TF, Hoffmann RT, Tatsch K, Trumm C, Reiser MF (2008) Therapy response of liver tumors after selective internal radiation therapy. Radiologe 48(9):839–849
Keane TJ, Rider WD, Harwood AR, Thomas GM, Cummings BJ (1981) Whole abdominal radiation in the management of metastatic gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 7(11):1519–1521
Kennedy A, Nag S, Salem R et al (2007) Recommendations for radioembolization of hepatic malignancies using yttrium-90 microsphere brachytherapy: a consensus panel report from the radioembolization Brachytherapy Oncology Consortium. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 68(1):13–23
Kennedy AS, Dezarn WA, McNeillie P et al (2008) Radioembolization for unresectable neuroendocrine hepatic metastases using resin 90Y-microspheres: early results in 148 patients. Am J Clin Oncol 31(3):271–279
King J, Quinn R, Glenn DM et al (2008) Radioembolization with selective internal radiation microspheres for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Cancer 113(5):921–929
Kress O, Wagner HJ, Wied M, Klose KJ, Arnold R, Alfke H (2003) Transarterial chemoembolization of advanced liver metastases of neuroendocrine tumors―a retrospective single-center analysis. Digestion 68(2–3):94–101
Madoff DC, Gupta S, Ahrar K, Murthy R, Yao JC (2006) Update on the management of neuroendocrine hepatic metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(8):1235–1249; quiz 1250
McStay MK, Maudgil D, Williams M et al (2005) Large-volume liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: hepatic intraarterial 90Y-DOTA-lanreotide as effective palliative therapy. Radiology 237(2):718–726
Modlin IM, Sandor A (1997) An analysis of 8305 cases of carcinoid tumors. Cancer 79(4):813–829
Modlin IM, Kidd M, Latich I, Zikusoka MN, Shapiro MD (2005) Current status of gastrointestinal carcinoids. Gastroenterology 128(6):1717–1751
Moertel CG, Johnson CM, McKusick MA et al (1994) The management of patients with advanced carcinoid tumors and islet cell carcinomas. Ann Intern Med 120(4):302–309
Murthy R, Nunez R, Szklaruk J et al (2005) Yttrium-90 microsphere therapy for hepatic malignancy: devices, indications, technical considerations, and potential complications. Radiographics 25(Suppl 1):S41–S55
Musunuru S, Chen H, Rajpal S et al (2006) Metastatic neuroendocrine hepatic tumors: resection improves survival. Arch Surg 141(10):1000–1004; discussion 1005
Nave H, Mossinger E, Feist H, Lang H, Raab H (2001) Surgery as primary treatment in patients with liver metastases from carcinoid tumors: a retrospective, unicentric study over 13 years. Surgery 129(2):170–175
Norton JA (2005) Endocrine tumours of the gastrointestinal tract. Surgical treatment of neuroendocrine metastases. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 19(4):577–583
Norton JA, Kerlan RK (2003) Hepatic artery embolization for treatment of patients with metastatic carcinoid tumors: a commentary. Cancer J 9(4):241–243
Oberg K (1999) Neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumors—a condensed overview of diagnosis and treatment. Ann Oncol 10(Suppl 2):S3–S8
Oberg K (2002) Carcinoid tumors: molecular genetics, tumor biology, and update of diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Oncol 14(1):38–45
Osborne DA, Zervos EE, Strosberg J et al (2006) Improved outcome with cytoreduction versus embolization for symptomatic hepatic metastases of carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 13(4):572–581
Paprottka PM, Jakobs TF, Reiser MF, Hoffmann RT (2011) Practical vascular anatomy in the preparation of radioembolization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 34:287–294
Que FG, Nagorney DM, Batts KP, Linz LJ, Kvols LK (1995) Hepatic resection for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am J Surg 169(1):36–42; discussion 42–33
Reddy PS, Burroughs KD, Hales LM et al (2007) Seneca Valley virus, a systemically deliverable oncolytic picornavirus, and the treatment of neuroendocrine cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(21):1623–1633
Ruszniewski P, Malka D (2000) Hepatic arterial chemoembolization in the management of advanced digestive endocrine tumors. Digestion 62(Suppl 1):79–83
Safford SD, Coleman RE, Gockerman JP et al (2004) Iodine-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine treatment for metastatic carcinoid. Results in 98 patients. Cancer 101(9):1987–1993
Salem R, Thurston KG (2006) Radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres: a state-of-the-art brachytherapy treatment for primary and secondary liver malignancies. Part 3. Comprehensive literature review and future direction. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(10):1571–1593
Samlowski WE, Eyre HJ, Sause WT (1986) Evaluation of the response of unresectable carcinoid tumors to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 12(3):301–305
Sarmiento JM, Que FG (2003) Hepatic surgery for metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 12(1):231–242
Schupak KD, Wallner KE (1991) The role of radiation therapy in the treatment of locally unresectable or metastatic carcinoid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physiol 20(3):489–495
Soreide O, Berstad T, Bakka A et al (1992) Surgical treatment as a principle in patients with advanced abdominal carcinoid tumors. Surgery 111(1):48–54
Therasse E, Breittmayer F, Roche A et al (1993) Transcatheter chemoembolization of progressive carcinoid liver metastasis. Radiology 189(2):541–547
Veenendaal LM, Borel Rinkes IH, Lips CJ, van Hillegersberg R (2006) Liver metastases of neuroendocrine tumours: early reduction of tumour load to improve life expectancy. World J Surg Oncol 4:35
Yao KA, Talamonti MS, Nemcek A et al (2001) Indications and results of liver resection and hepatic chemoembolization for metastatic gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 130(4):677–682; discussion 682–675
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paprottka, P.M., Hoffmann, RT., Haug, A. et al. Radioembolization of Symptomatic, Unresectable Neuroendocrine Hepatic Metastases Using Yttrium-90 Microspheres. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 334–342 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0248-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0248-1