Abstract
Background
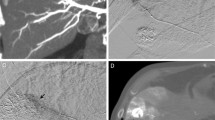
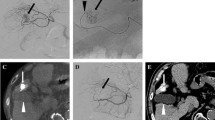
Hepatic arterial infusion (HAI) chemotherapy is effective for treating primary and metastatic carcinomas of the liver. Since hepatic arteries also supply the stomach and duodenum, HAI may result in unwanted infusion into the upper gastrointestinal tract and consequent gastric toxicity. Using fused images obtained with a combined SPECT/CT system, we assessed extrahepatic perfusion (EHP) and its correlation with gastrointestinal toxicity in patients receiving HAI.
Methods
We studied 41 patients with primary or metastatic carcinoma of the liver who received HAI chemotherapy consisting of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. All underwent abdominal SPECT using a 99mTc-MAA (185 MBq) instrument and an injection rate of 0.1 ml/min, identical to the chemotherapy infusion rate. Delivery was through an implantable port. We analyzed the distribution of the anticancer agent on fused images and the relationship between EHP of the right gastric arterial region and gastric toxicity. All patients underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS).
Results
Of the 41 patients, 11 (27%) manifested enhancement of the duodenal and gastric pyloric region on fused images. EGDS at the time of reservoir placement detected gastric ulcers in 10 of these patients.
Conclusion
Fusion imaging with combined SPECT/CT reflects the actual distribution of the infused anticancer agents. The detection of EHP on fused images is predictive of the direct gastric toxicity from anticancer agents in patients undergoing HAI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kemeny N, Daly J, Reichman B, et al. (1989) Intrahepatic or systemic infusion of fluorodeoxyuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Ann Intern Med 107:459–565
Rougier P, Laplanche A, Huguier M, et al. (1992) Hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma: Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 40:526–530
Arai Y, Inaba Y, Takeuchi Y, et al. (1997) Intermittent hepatic arterial infusion of high-dose 5FU on a weekly schedule for liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 40:526–530
Breedis C, Young G (1954) The blood supply of neoplasms in the liver. Am J Pathol 30:969–985
Healy JE (1965) Vascular patterns in human metastatic liver tumors. Surg Gynecol Obstet 120:1187–1193
Ensminger W, Niederhuber J, Dakhil S, et al. (1981) Totally implanted drug delivery system for hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep 65:393–400
Barone RM, Byfield JE, Goldfarb PB, et al. (1982) Intraarterial chemotherapy using an implantable infusion pump and liver irradiation for the treatment of hepatic metastases. Cancer 50:850–862
Fiorentini G, Poddie DB, Giorgi UD, et al. (2000) Global approach to hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: Indication and outcome of intra-arterial chemotherapy and other hepatic-directed treatments. Med Oncol 17:163–173
Doria MI, Doria LK, Faintuch J, et al. (1993) Gastric mucosal injury after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with floxuridine: A clinical and pathologic study. Cancer 74:2042–2047
Shike M, Gillin JS, Kemeny N, et al. (1986) Severe gastroduodenal ulcerations complicating hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy for metastatic colon cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 81:176–179
Narsete T, Ansfield F, Wirtanen G, et al. (1977) Gastric ulceration in patients receiving intrahepatic infusion 5-fluorouracil. Ann Surg 186:734–736
Niederhuber JE, Ensminger WD (1983) Surgical considerations in the management of hepatic neoplasia. Semin Oncol 10:135–147
Cady B (1973) Hepatic arterial patency and complications after catheterization for infusion chemotherapy. Ann Surg 178:156–161
Chuang VP, Wallace S, Stroehlein J, et al. (1981) Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy: Gastroduodenal complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 137:347–350
Jewell LD, Fields AL, Murray CJW, et al. (1985) Erosive gastroduodenitis with marked epithelial atypia after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol 80:421–424
Wells JJ, Nostrant TT, Wilson JAP, et al. (1985) Gastroduodenal ulcerations in patients receiving selective hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol 80:425–429
Kwee WS, Wils JA, Schlangen J, et al. (1994) Gastric epithelial atypia complicating hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Histopathology 24:151–154
Granmayeh M, Wallace S, Schwarten D (1979) Transcatheter occlusion of the gastroduodenal artery. Radiology 131:59–64
Arai Y, Inaba Y, Takeuchi Y (1997) Interventional techniques for hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. In: Castaneda-Zuniga WR (ed) Interventional Radiology, 3rd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 192–205
Inaba Y, Arai Y, Matsueda K, et al. (2001) Right gastric artery embolization to prevent acute gastric mucosal lesions in patients undergoing repeat hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:957–963
Michels NA (1955) Blood supply and anatomy of the upper abdominal organs. Lippincott, Philadelphia
Reuter SR, Redman HC, Cho KJ (1986) Gastrointestinal angiography, 3rd edn. Saunders, New York, pp 32–77
Luzca G (1974) X-ray anatomy of the vascular system. Butterworth, Budapest, pp 224–293
Pozniak MA, Bebel SG, Trump DL (1991) Complications of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. RadioGraphics 3:67–69
Hiramatsu K, Kouda E, Mouri M, et al. (1982) X-ray anatomy of the abdominal vascular system. Igaku-Shoin, Tokyo, pp 123–124
Hohn DC, Stagg RJ, Price DC, et al. (1985) Avoidance of gastroduodenal toxicity in patients receiving hepatic arterial 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyurine. J Clin Oncol 3:1257–1260
Bledin AG, Kim EE, Chuang VP, et al. (1984) Change of arterial blood flow patterns during infusion chemotherapy, as monitored by intra-arterial injected technetium-99m macroaggregated albumin. Br J Radiol 57:197–203
Civelek AC, Sitzmann JV, Chin BB, et al. (1993) Misperfusion of the liver during hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy: Value of preoperative angiography and postoperative pump scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 160:865–870
Lorenz M, Muller HH (2000) Randomized, multicenter trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin administered either via hepatic arterial or intravenous infusion versus fluorodeoxyuridine administered via hepatic arterial infusion in patients with nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 18:243–254
Krausz Y, Keidar Z, Kogant I, Even-Sapir E, Bar-Shalom R, Engel A, et al. (2003) SPECT/CT hybrid imaging with 111In-pentetreotide in assessment of neuroendocrine tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 59:565–573
Even-Sapir E, Lerman H, Lievshitz G, Khafif A, Fliss MD, Schwartz A, et al. (2003) Lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel node mapping using a hybrid SPECT/CT system. J Nucl Med 44:1413–1420
Koral KF, Dewaraja Y, Li J, Lin Q, Regan DD, Zasadny RK, et al. (2003) Update on hybrid conjugate-view SPECT tumor dosimetry and response in 131I-tositumomab therapy of previously untreated lymphoma patients. J Nucl Med 44:457–464
Allen-Mersh TG, Earlam S, Fordy C, et al. (1994) Quality of life and survival with continuous hepatic-artery floxuridine infusion for colorectal liver metastasis. Lancet 344:1255–1260
Valeri A, Mini E, Tonelli P, et al. (1994) Intra-arterial hepatic chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in the treatment of unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 14:2215–2219
Huk I, Entsheff P, Prager M, et al. (1990) Patency rate of implantable devices during long-term intraarterial chemotherapy. Angiology 41:936–941
Yamagami T, Nakamura T, Iida S, et al. (2002) Embolization of the right gastric artery before hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy to prevent gastric mucosal lesions: Approach through the hepatic artery versus the left gastric artery. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1605–1610
Shike M, Gillin JS, Kemeny N, et al. (1986) Severe gastroduodenal ulcerations complicating hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy for metastatic colon cancer. Am J Gastroentrol 81:176–179
Doria MI, Doria LK, Faintuch J, et al. (1994) Hepatic mucosal injury after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with Floxuridine. A clinical and pathologic study. Cancer 73:2043–2047
Ravizza D, Fazio N, Crosta C, et al. (2003) Iatrogenic gastroduodenal ulcers during hepatic intra-arterial chemotherapy. Hepato-Gastroenterology 50:49–53
Petras RE, Hart WR, Bukowski R (1985) Gastric epithelial atypia associated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Its distinction from early gastric carcinoma. Cancer 56:391–399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, O., Tamura, Y., Nakasone, Y. et al. Evaluation of Extrahepatic Perfusion of Anticancer Drugs in the Right Gastric Arterial Region on Fused Images Using Combined CT/SPECT: Is Extrahepatic Perfusion Predictive of Gastric Toxicity?. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30, 392–397 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0315-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0315-6