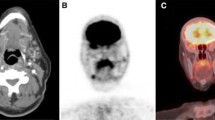
Abstract.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical use of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) on the basis of comparison with findings obtained using indium-111 pentetreotide (SMS), pentavalent technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), technetium-99m sestamibi (MIBI), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). One hundred FDG-PET examinations in 85 patients (40 males, 45 females) with elevated tumour marker levels and/or pathological findings on other imaging methods were evaluated retrospectively. Eighty-two patients were examined after total thyroidectomy, and the remaining three patients prior to surgery. Overall, 181 lesions could be identified with at least one of the imaging techniques. Fifty-five lesions were confirmed histologically. FDG-PET detected 123 of 181 sites, which is a lesion detection probability of 68%. In the 55 cases with histological confirmation, we found 32 true positive, 3 false positive, 11 true negative and 9 false negative lesions using FDG-PET, resulting in a sensitivity of 78% and a specificity of 79%. Sensitivity and specificity were, respectively, 25% and 92% for SMS, 33% and 78% for DMSA, 25% and 100% for MIBI, 50% and 20% for CT and 82% and 67% for MRI. Compared with morphological techniques and functional imaging methods with single-photon emitters, FDG-PET showed the highest lesion detection probability for MTC tissue, with a high sensitivity and specificity. It is concluded that FDG-PET is a useful method in the staging and follow-up of MTC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 27 March and in revised form 7 July 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diehl, M., Risse, J.H., Brandt-Mainz, K. et al. Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in medullary thyroid cancer: results of a multicentre study. Eur J Nucl Med 28, 1671–1676 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100614
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100614