Abstract.
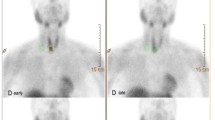
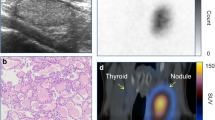
Various diagnostic techniques have been successfully used in the clinical management of cold nodules; however, the decision on whether to employ surgery or a conservative treatment is not always easy. This study was designed to appraise the diagnostic value of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) scintigraphy in the assessment of cold nodules detected using 99mTc-pertechnetate. Fifty-two patients were included in the study. All had already been selected for surgery, based on their clinical and laboratory findings, including fine-needle aspiration biopsy. The total number of cold nodules on 99mTc-pertechnetate scans was 59. The thyroid scan was performed 20-40 min after i.v. injection of 400 MBq of 99mTc-MIBI. Uptake of MIBI in thyroid nodules was compared with that in the surrounding normal thyroid tissue, and a score of between 0 and 3 was assigned to each nodule as follows: 0, cold; 1, decreased; 2, equal; 3, hot. Definitive histology revealed nodular goitre in 24 cases, adenoma in 19, thyroiditis in 1, differentiated cancer in 12, medullary cancer in 2, and anaplastic cancer in 1. None of the degenerative nodules were hot on MIBI scan, while the adenomas showed a variety of MIBI imaging patterns, most frequently the score 3 pattern. In the diagnosis of differentiated thyroid cancer the sensitivities of score 3 and score 2+3 MIBI uptake patterns were 83% (10/12) and 100%, respectively. The score 3 MIBI uptake pattern had a specificity of 100% and a positive predictive value of 100% with respect to thyroid (benign and malignant) neoplastic diseases, whereas a specificity of 72% and a positive predictive value of 43% were observed in the detection of differentiated cancer. After a cold nodule had been detected using 99mTc-pertechnetate, a second scan with high MIBI uptake increased by 7.8 times the probability that this nodule would be a differentiated cancer. In conclusion, 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy is a useful method in the differential diagnosis of cold thyroid nodules if the primary aim is to differentiate degenerative from neoplastic diseases rather than to differentiate benign from malignant nodules. High MIBI uptake considerably increases the probability of a differentiated thyroid cancer and facilitates immediate surgical removal, while decreased uptake actually excludes it. We suggest a combination of fine-needle aspiration biopsy and MIBI scan as a routine diagnostic approach to cold thyroid nodules.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 12 January and in revised form 18 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mezosi, E., Bajnok, L., Gyory, F. et al. The role of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of cold thyroid nodules. Eur J Nucl Med 26, 798–803 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050451
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050451