Abstract.
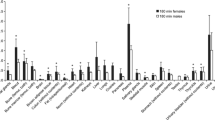
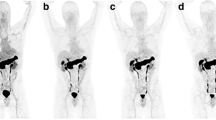
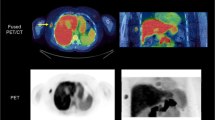
This study reports on the distribution and radiation dosimetry of iodine-123-labelled cis-11β-methoxy-17α-iodovinyloestradiol (Z-[123I]MIVE), a promising radioligand for imaging of oestrogen receptors (ERs) in human breast cancer. Whole-body scans were performed up to 24 h after intravenous injection of 138–193 MBq Z-[123I]MIVE in five healthy female volunteers, four with and one without thyroid blockade. Blood samples were taken at various times up to 24 h after injection. Urine was collected up to 24 h after injection in order to calculate renal clearance and to aid in the interpretation of whole-body clearance, including faecal excretion. Time-activity curves were generated for the thyroid, heart, brain, breasts and liver, by fitting the organ-specific geometric mean counts, obtained from regions of interest, to a multicompartmental model. The MIRD formulation, using 11 source organs, was applied to calculate the absorbed radiation doses for various organs upon administration of Z-[123I]MIVE. The images showed rapid hepatobiliary excretion which resulted in good imaging conditions for the thoracic region. Imaging of the abdominal region was impeded due to extensive bowel activity. Diffuse uptake and retention of activity was seen in breast tissue, the breast-to-non-specific uptake ratio increasing over time. Z-[123I]MIVE was cleared by both the kidneys and the gastrointestinal tract. At 50 h p.i. the mean excretion in urine was predicted to be 58%±14% (SD) and that in faeces 31%±19%. If the thyroid was not blocked, it was the most critical organ (0.33 mGy/MBq). In general, the excretory organs received the highest absorbed doses, i.e. the lower and upper large intestinal walls (0.11 and 0.098 mGy/MBq, respectively), the urinary bladder wall (0.090 mGy/MBq), the gallbladder wall (0.087 mGy/MBq) and the small intestine (0.043 mGy/MBq). The average effective dose equivalent of Z-[123I]MIVE was estimated to be 0.033 mSv/MBq. The amount of Z-[123I]MIVE required for adequate breast cancer ER imaging results in an acceptable effective dose equivalent to the patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 28 June and in revised form 26 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rijks, L., Busemann Sokole, E., Stabin, M. et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry of iodine-123-labelled Z-MIVE: an oestrogen receptor radioligand for breast cancer imaging. Eur J Nucl Med 25, 40–47 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050192
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050192