Abstract.
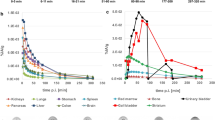
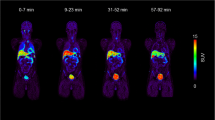
This study reports on the biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of iodine-123-labelled N-ω-(flu- oropropyl)-2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane ([123I]FP-CIT), a promising radioligand for the imaging of dopamine transporters. In 12 healthy volunteers, conjugate whole-body scans were performed up to 48 h following intravenous injection of approximately 100 MBq [123I]FP-CIT. Attenuation correction was performed using a transmission whole-body scan obtained prior to injection of the radioligand, employing a 123I flood source. Blood samples were taken and urine was freely collected up to 48 h after injection of the radiotracer. For each subject, the percentage of injected activity measured in regions of interest over brain, striatum, lungs and liver were fitted to a multicompartmental model to give time-activity curves. The cumulative urine activity curve was used to model the urinary excretion rate and, indirectly, to predict faecal excretion. Using the MIRD method, nine source organs were considered in estimating absorbed radiation doses for organs of the body. The images showed rapid lung uptake and hepatobiliary excretion. Diffuse uptake and retention of activity was seen in the brain, especially in the striatum. At 48 h following the injection of [123I]FP-CIT, mean measured urine excretion was 60%±9% (SD), and mean predicted excretion in faeces was 14%±1%. In general, the striatum received the highest absorbed dose (average 0.23 mGy/MBq), followed by the urinary bladder wall (average 0.054 mGy/MBq) and lungs (average 0.043 mGy/MBq). The average effective dose equivalent of [123I]FP-CIT was estimated to be 0.024 mSv/MBq. The amount of [123I]FP-CIT required for adequate dopamine transporter imaging results in an acceptable effective dose equivalent to the patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 14 July and in revised form 26 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Booij, J., Busemann Sokole, E., Stabin, M. et al. Human biodistribution and dosimetry of [123I]FP-CIT: a potent radioligand for imaging of dopamine transporters. Eur J Nucl Med 25, 24–30 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050190
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590050190