Abstract
Purpose
To correlate the clinical stage and prognosis of pancreatic or periampullary cancer with the imaging biomarkers on diffusion-weighted imaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy and glucose metabolic activity derived from integrated PET/MRI.
Methods
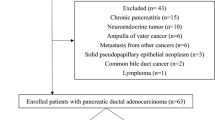
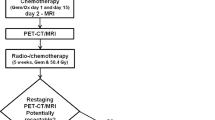
This prospective study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was obtained. The study group comprised 60 consecutive patients with pancreatic or periampullary cancer who underwent PET/MRI before treatment. The imaging biomarkers were the minimal apparent diffusion coefficient (ADCmin), choline levels, standardized uptake values, metabolic tumour volume (MTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG) of the tumours. The relationships between these biomarkers and clinical TNM stage were evaluated using the Pearson test and the Mann-Whitney U test. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was used to evaluate accuracy. The correlation between the imaging biomarker and progression-free survival (PFS) was investigated using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
ADCmin was significantly lower in N1 and TNM stage 3+ tumours. Choline levels significantly higher in T4 tumours. TLG was significantly higher in T4, N1 and TNM stage 3+ tumours. MTV was significantly higher in T4, N1, M1, and TNM stage 3+ tumours (all P < 0.05). The MTV/ADCmin ratio exhibited the highest AUROC for predicting T4, N1, M1, and advanced TNM stages tumours, and was an independent predictor of PFS (P = 0.018) after adjustment for age, sex, tumour size and stage.
Conclusion
The imaging biomarkers from integrated PET/MRI may predict clinical stage and PFS in patients with pancreatic or periampullary cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30.
Ma J, Jemal A. The rise and fall of cancer mortality in the USA: why does pancreatic cancer not follow the trend? Future Oncol. 2013;9:917–9.
Huellner MW, Appenzeller P, Kuhn FP, Husmann L, Pietsch CM, Burger IA, et al. Whole-body nonenhanced PET/MR versus PET/CT in the staging and restaging of cancers: preliminary observations. Radiology. 2014;273:859–69.
Fattahi R, Balci NC, Perman WH, Hsueh EC, Alkaade S, Havlioglu N, et al. Pancreatic diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI): comparison between mass-forming focal pancreatitis (FP), pancreatic cancer (PC), and normal pancreas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:350–6.
Barral M, Taouli B, Guiu B, Koh DM, Luciani A, Manfredi R, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the pancreas: current status and recommendations. Radiology. 2015;274:45–63.
Glunde K, Bhujwalla ZM, Ronen SM. Choline metabolism in malignant transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:835–48.
Penet MF, Shah T, Bharti S, Krishnamachary B, Artemov D, Mironchik Y, et al. Metabolic imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma detects altered choline metabolism. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:386–95.
Ying H, Kimmelman AC, Lyssiotis CA, Hua S, Chu GC, Fletcher-Sananikone E, et al. Oncogenic Kras maintains pancreatic tumors through regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism. Cell. 2012;149:656–70.
Rakheja R, Chandarana H, DeMello L, Jackson K, Geppert C, Faul D, et al. Correlation between standardized uptake value and apparent diffusion coefficient of neoplastic lesions evaluated with whole-body simultaneous hybrid PET/MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201:1115–9.
Schaarschmidt BM, Buchbender C, Nensa F, Grueneisen J, Gomez B, Kohler J, et al. Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) with the standardized uptake value (SUV) in lymph node metastases of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients using hybrid 18F-FDG PET/MRI. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0116277.
Baba S, Isoda T, Maruoka Y, Kitamura Y, Sasaki M, Yoshida T, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of pretreatment SUV in 18F-FDG/PET in breast cancer: comparison with apparent diffusion coefficient from diffusion-weighted MR imaging. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:736–42.
Shih IL, Yen RF, Chen CA, Chen BB, Wei SY, Chang WC, et al. Standardized uptake value and apparent diffusion coefficient of endometrial cancer evaluated with integrated whole-body PET/MR: correlation with pathological prognostic factors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42:1723–32. doi:10.1002/jmri.24932.
Grueneisen J, Beiderwellen K, Heusch P, Buderath P, Aktas B, Gratz M, et al. Correlation of standardized uptake value and apparent diffusion coefficient in integrated whole-body PET/MRI of primary and recurrent cervical cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9, e96751.
Yu X, Lee EY, Lai V, Chan Q. Correlation between tissue metabolism and cellularity assessed by standardized uptake value and apparent diffusion coefficient in peritoneal metastasis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;40:99–105.
Tozaki M, Hoshi K. 1H MR spectroscopy of invasive ductal carcinoma: correlations with FDG PET and histologic prognostic factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194:1384–90.
Yamaguchi T, Lee J, Uemura H, Sasaki T, Takahashi N, Oka T, et al. Prostate cancer: a comparative study of 11C-choline PET and MR imaging combined with proton MR spectroscopy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:742–8.
Ma C, Liu L, Li J, Wang L, Chen LG, Zhang Y, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a preliminary study of the effect of region of interest on ADC values and interobserver variability. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43:407–13. doi:10.1002/jmri.25007.
Wahl RL, Jacene H, Kasamon Y, Lodge MA. From RECIST to PERCIST: evolving considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J Nucl Med. 2009;50 Suppl 1:122S–50.
Romesser PB, Qureshi MM, Subramaniam RM, Sakai O, Jalisi S, Truong MT. A prognostic volumetric threshold of gross tumor volume in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37:154–61.
Chirindel A, Alluri KC, Chaudhry MA, Wahl RL, Pawlik TM, Herman JM, et al. Prognostic value of FDG PET/CT-derived parameters in pancreatic adenocarcinoma at initial PET/CT staging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204:1093–9.
Larson SM, Erdi Y, Akhurst T, Mazumdar M, Macapinlac HA, Finn RD, et al. Tumor treatment response based on visual and quantitative changes in global tumor glycolysis using PET-FDG imaging. The visual response score and the change in total lesion glycolysis. Clin Positron Imaging. 1999;2:159–71.
Shrikhande SV, Kleeff J, Reiser C, Weitz J, Hinz U, Esposito I, et al. Pancreatic resection for M1 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:118–27.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Muraoka N, Uematsu H, Kimura H, Imamura Y, Fujiwara Y, Murakami M, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient in pancreatic cancer: characterization and histopathological correlations. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27:1302–8.
Wang Y, Chen ZE, Nikolaidis P, McCarthy RJ, Merrick L, Sternick LA, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatic adenocarcinomas: association with histopathology and tumor grade. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;33:136–42.
Hayano K, Miura F, Amano H, Toyota N, Wada K, Kato K, et al. Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient measured by diffusion-weighted MRI and clinicopathologic features in pancreatic cancer patients. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:243–8.
Niwa T, Ueno M, Ohkawa S, Yoshida T, Doiuchi T, Ito K, et al. Advanced pancreatic cancer: the use of the apparent diffusion coefficient to predict response to chemotherapy. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:28–34.
Kurosawa J, Tawada K, Mikata R, Ishihara T, Tsuyuguchi T, Saito M, et al. Prognostic relevance of apparent diffusion coefficient obtained by diffusion-weighted MRI in pancreatic cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42:1532–7. doi:10.1002/jmri.24939.
Lee JW, Kang CM, Choi HJ, Lee WJ, Song SY, Lee JH, et al. Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis on preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with pancreatic cancer. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:898–904.
Shi S, Ji S, Qin Y, Xu J, Zhang B, Xu W, et al. Metabolic tumor burden is associated with major oncogenomic alterations and serum tumor markers in patients with resected pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;360:227–33.
Xu HX, Chen T, Wang WQ, Wu CT, Liu C, Long J, et al. Metabolic tumour burden assessed by 18F-FDG PET/CT associated with serum CA19-9 predicts pancreatic cancer outcome after resection. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:1093–102.
Choi HJ, Lee JW, Kang B, Song SY, Lee JD, Lee JH. Prognostic significance of volume-based FDG PET/CT parameters in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer treated with chemoradiation therapy. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55:1498–506.
Dholakia AS, Chaudhry M, Leal JP, Chang DT, Raman SP, Hacker-Prietz A, et al. Baseline metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis are associated with survival outcomes in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer receiving stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;89:539–46.
Sakane M, Tatsumi M, Kim T, Hori M, Onishi H, Nakamoto A, et al. Correlation between apparent diffusion coefficients on diffusion-weighted MRI and standardized uptake value on FDG-PET/CT in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Acta Radiol. 2015;56:1034–41.
Soussan M, Cyrta J, Pouliquen C, Chouahnia K, Orlhac F, Martinod E, et al. Fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT volume-based indices in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: prediction of residual viable tumor after induction chemotherapy. Radiology. 2014;272:875–84.
Soret M, Bacharach SL, Buvat I. Partial-volume effect in PET tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:932–45.
Davison J, Mercier G, Russo G, Subramaniam RM. PET-based primary tumor volumetric parameters and survival of patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200:635–40.
Chang KP, Tsang NM, Liao CT, Hsu CL, Chung MJ, Lo CW, et al. Prognostic significance of 18F-FDG PET parameters and plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:21–8.
Dibble EH, Alvarez AC, Truong MT, Mercier G, Cook EF, Subramaniam RM. 18F-FDG metabolic tumor volume and total glycolytic activity of oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer: adding value to clinical staging. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:709–15.
Tesiram YA, Lerner M, Stewart C, Njoku C, Brackett DJ. Utility of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for pancreatic cancer studies. Pancreas. 2012;41:474–80.
Yao X, Zeng M, Wang H, Fei S, Rao S, Ji Y. Metabolite detection of pancreatic carcinoma by in vivo proton MR spectroscopy at 3T: initial results. Radiol Med. 2012;117:780–8.
Ahn SJ, Park MS, Lee JD, Kang WJ. Correlation between 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and pathologic differentiation in pancreatic cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 2014;28:430–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was funded by National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan; Contract grant number: A1 project no. NTUH103-A124.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Research Committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, BB., Tien, YW., Chang, MC. et al. PET/MRI in pancreatic and periampullary cancer: correlating diffusion-weighted imaging, MR spectroscopy and glucose metabolic activity with clinical stage and prognosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 1753–1764 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3356-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3356-y