Abstract
Purpose
[18F]FPEB is a promising PET radioligand for the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5), a potential target for the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the test–retest reproducibility of [18F]FPEB in the human brain.
Methods
Seven healthy male subjects were scanned twice, 3 – 11 weeks apart. Dynamic data were acquired using bolus plus infusion of 162 ± 32 MBq [18F]FPEB. Four methods were used to estimate volume of distribution (V T): equilibrium analysis (EQ) using arterial (EQA) or venous input data (EQV), MA1, and a two-tissue compartment model (2 T). Binding potential (BP ND) was also estimated using cerebellar white matter (CWM) or gray matter (CGM) as the reference region using EQ, 2 T and MA1. Absolute test–retest variability (aTRV) of V T and BP ND were calculated for each method. Venous blood measurements (C V) were compared with arterial input (C A) to examine their usability in EQ analysis.
Results
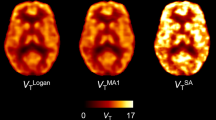
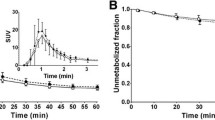
Regional V T estimated by the four methods displayed a high degree of agreement (r 2 ranging from 0.83 to 0.99 among the methods), although EQA and EQV overestimated V T by a mean of 9 % and 7 %, respectively, compared to 2 T. Mean values of aTRV of V T were 11 % by EQA, 12 % by EQV, 14 % by MA1 and 14 % by 2 T. Regional BP ND also agreed well among the methods and mean aTRV of BP ND was 8 – 12 % (CWM) and 7 – 9 % (CGM). Venous and arterial blood concentrations of [18F]FPEB were well matched during equilibrium (C V = 1.01 · C A, r 2 = 0.95).
Conclusion
[18F]FPEB binding shows good TRV with minor differences among analysis methods. Venous blood can be used as an alternative for input function measurement instead of arterial blood in EQ analysis. Thus, [18F]FPEB is an excellent PET imaging tracer for mGluR5 in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meldrum BS. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr. 2000;130:1007S–15S.
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J. Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res. 2003;140:1–47.
Fitzjohn SM, Bashir ZI. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity. In: Gereau RW, Swanson GT, editors. The receptors: the glutamate receptors. Totowa: Humana Press; 2008. p. 509–28.
Benarroch EE. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic modulators and therapeutic targets for neurologic disease. Neurology. 2008;70:964–8. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000306315.03021.2a.
Olive MF. Metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands as potential therapeutics for addiction. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2009;2:83–98.
Bruno V, Battaglia G, Copani A, D’Onofrio M, Di Iorio P, De Blasi A, et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes as targets for neuroprotective drugs. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:1013–33. doi:10.1097/00004647-200109000-00001.
Bird MK, Lawrence AJ. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: involvement in drug-seeking and drug-induced plasticity. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009;2:83–94.
Lujan R, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Shigemoto R, Somogyi P. Perisynaptic location of metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR1 and mGluR5 on dendrites and dendritic spines in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:1488–500.
De Blasi A, Conn PJ, Pin J, Nicoletti F. Molecular determinants of metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:114–20.
Patel S, Ndubizu O, Hamill T, Chaudhary A, Burns HD, Hargreaves R, et al. Screening cascade and development of potential positron emission tomography radiotracers for mGluR5: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Mol Imaging Biol. 2005;7:314–23. doi:10.1007/s11307-005-0005-4.
Wang JQ, Tueckmantel W, Zhu A, Pellegrino D, Brownell AL. Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of 3-[(18)F]fluoro-5-(2-pyridinylethynyl)benzonitrile as a PET radiotracer for imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Synapse. 2007;61:951–61. doi:10.1002/syn.20445.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders, clinician version (SCID-CV). Washington: American Psychiatric Press; 1996.
Lim K, Labaree D, Li S, Huang Y. Preparation of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) PET tracer [(18)F]FPEB for human use: an automated radiosynthesis and a novel one-pot synthesis of its radiolabeling precursor. Appl Radiat Isot. 2014;94C:349–54. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2014.09.006.
Sullivan JM, Lim K, Labaree D, Lin SF, McCarthy TJ, Seibyl JP, et al. Kinetic analysis of the metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 tracer [(18)F]FPEB in bolus and bolus-plus-constant-infusion studies in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:532–41. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.195.
Carson RE, Barker WC, Liow JS, Johnson CA. Design of a motion-compensation OSEM list-mode algorithm for resolution-recovery reconstruction for the HRRT. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec. 2003;5:3281–5
Carson RE, Channing MA, Blasberg RG, Dunn BB, Cohen RM, Rice KC, et al. Comparison of bolus and infusion methods for receptor quantitation: application to [18F]cyclofoxy and positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:24–42. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1993.6.
Lassen NA. Neuroreceptor quantitation in vivo by the steady-state principle using constant infusion or bolus injection of radioactive tracers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992;12:709–16. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1992.101.
Ichise M, Toyama H, Innis RB, Carson RE. Strategies to improve neuroreceptor parameter estimation by linear regression analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:1271–81. doi:10.1097/00004647-200210000-00015.
Patel S, Hamill TG, Connolly B, Jagoda E, Li W, Gibson RE. Species differences in mGluR5 binding sites in mammalian central nervous system determined using in vitro binding with [18F]F-PEB. Nucl Med Biol. 2007;34:1009–17. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.07.009.
DeLorenzo C, Milak MS, Brennan KG, Kumar JS, Mann JJ, Parsey RV. In vivo positron emission tomography imaging with [11C]ABP688: binding variability and specificity for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in baboons. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:1083–94. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1723-7.
Wong DF, Waterhouse R, Kuwabara H, Kim J, Brasic JR, Chamroonrat W, et al. 18F-FPEB, a PET radiopharmaceutical for quantifying metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors: a first-in-human study of radiochemical safety, biokinetics, and radiation dosimetry. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:388–96. doi:10.2967/jnumed.112.107995.
Kuwabara H, Chamroonrat W, Mathews W, Waterhouse R, Brasic J, Guevara MR, et al. Evaluation of 11C-ABP688 and 18F-FPEB for imaging mGluR5 receptors in the human brain. J Nucl Med. 2011;52 Suppl 1:390.
DeLorenzo C, Kumar JS, Mann JJ, Parsey RV. In vivo variation in metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 binding using positron emission tomography and [11C]ABP688. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:2169–80. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.105.
Martinez D, Slifstein M, Nabulsi N, Grassetti A, Urban NB, Perez A, et al. Imaging glutamate homeostasis in cocaine addiction with the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 positron emission tomography radiotracer [11C]ABP688 and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:165–71. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.06.026.
Milella MS, Marengo L, Larcher K, Fotros A, Dagher A, Rosa-Neto P, et al. Limbic system mGluR5 availability in cocaine dependent subjects: a high-resolution PET [11C]ABP688 study. Neuroimage. 2014;98:195–202. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.061.
Deschwanden A, Karolewicz B, Feyissa AM, Treyer V, Ametamey SM, Johayem A, et al. Reduced metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 density in major depression determined by [11C]ABP688 PET and postmortem study. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168:727–34. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.09111607.
DeLorenzo C, DellaGioia N, Bloch M, Sanacora G, Nabulsi N, Abdallah C, et al. In vivo ketamine-induced changes in [11C]ABP688 binding to metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:266–75. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.06.024.
Kagedal M, Cselenyi Z, Nyberg S, Raboisson P, Stahle L, Stenkrona P, et al. A positron emission tomography study in healthy volunteers to estimate mGluR5 receptor occupancy of AZD2066 – estimating occupancy in the absence of a reference region. Neuroimage. 2013;82:160–9. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.006.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the staff of the Yale University PET Center for their technical expertise and support.
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Funding
This study was supported by the Yale Pfizer Bioimaging Alliance. This study was also made possible by CTSA grant number UL1 RR024139 from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and NIH roadmap for Medical Research.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 117 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, E., Sullivan, J.M., Planeta, B. et al. Test–retest reproducibility of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 ligand [18F]FPEB with bolus plus constant infusion in humans. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42, 1530–1541 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3094-6