Abstract
Purpose
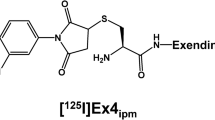
Radiolabelled glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have recently been shown to successfully image benign insulinomas in patients. For the somatostatin receptor targeting of tumours, however, it was recently reported that antagonist tracers were superior to agonist tracers. The present study therefore evaluated various forms of the 125iodinated-Bolton-Hunter (BH)-exendin(9–39) antagonist tracer for the in vitro visualization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing tissues in rats and humans and compared it with the agonist tracer 125I-GLP-1(7–36)amide.
Methods
Receptor autoradiography studies with 125I-GLP-1(7–36)amide agonist or 125I-BH-exendin(9–39) antagonist radioligands were performed in human and rat tissues.
Results
The antagonist 125I-BH-exendin(9–39) labelled at lysine 19 identifies all human and rat GLP-1 target tissues and GLP-1 receptor-expressing tumours. Binding is of high affinity and is comparable in all tested tissues in its binding properties with the agonist tracer 125I-GLP-1(7–36)amide. For comparison, 125I-BH-exendin(9–39) with the BH labelled at lysine 4 did identify the GLP-1 receptor in rat tissues but not in human tissues.
Conclusion
The GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin(9–39) labelled with 125I-BH at lysine 19 is an excellent GLP-1 radioligand that identifies human and rat GLP-1 receptors in normal and tumoural tissues. It may therefore be the molecular basis to develop suitable GLP-1 receptor antagonist radioligands for in vivo imaging of GLP-1 receptor-expressing tissues in patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev 2007;87:1409–39.
Körner M, Stöckli M, Waser B, Reubi JC. GLP-1 receptor expression in human tumors and human normal tissues: potential for in vivo targeting. J Nucl Med 2007;48:736–43.
Reubi JC, Waser B. Concomitant expression of several peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumours: molecular basis for in vivo multireceptor tumour targeting. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:781–93.
Holst JJ, Vilsbøll T, Deacon CF. The incretin system and its role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2009;297:127–36.
Drucker DJ, Dritselis A, Kirkpatrick P. Liraglutide. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010;9:267–8.
Wild D, Christ E, Caplin M, Kurzawinski TR, Forrer F, Brändle M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 versus somatostatin receptor targeting reveals 2 distinct forms of malignant insulinomas. J Nucl Med 2011;52:1073–8.
Christ E, Wild D, Reubi JC. Glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor: an example of translational research in insulinomas: a review. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2010;39:791–800.
Christ E, Wild D, Forrer F, Brändle M, Sahli R, Clerici T, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging for localization of insulinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:4398–405.
Wild D, Mäcke H, Christ E, Gloor B, Reubi JC. Glucagon-like peptide 1-receptor scans to localize occult insulinomas. N Engl J Med 2008;359:766–8.
Sowa-Staszczak A, Pach D, Mikołajczak R, Mäcke H, Jabrocka-Hybel A, Stefańska A, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging with [Lys40(Ahx-HYNIC- 99mTc/EDDA)NH2]-exendin-4 for the detection of insulinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013;40:524–31.
Christ E, Wild D, Ederer S, Béhé M, Nicolas G, Caplin ME, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging for the localisation of insulinomas: a prospective multicentre imaging study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2013;1:115–22.
Brom M, Joosten L, Oyen WJ, Gotthardt M, Boerman OC. Radiolabelled GLP-1 analogues for in vivo targeting of insulinomas. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2012;7:160–6.
Waser B, Tamma ML, Cescato R, Maecke HR, Reubi JC. Highly efficient in vivo agonist-induced internalization of sst2 receptors in somatostatin target tissues. J Nucl Med 2009;50:936–41.
Wild D, Fani M, Behe M, Brink I, Rivier J, Reubi JC, et al. First clinical evidence that imaging with somatostatin receptor antagonists is feasible. J Nucl Med 2011;52:1412–7.
Cescato R, Maina T, Nock B, Nikolopoulou A, Charalambidis D, Piccand V, et al. Bombesin receptor antagonists may be preferable to agonists for tumor targeting. J Nucl Med 2008;49:318–26.
Ginj M, Zhang H, Waser B, Cescato R, Wild D, Wang X, et al. Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:16436–41.
Thorens B, Porret A, Bühler L, Deng SP, Morel P, Widmann C. Cloning and functional expression of the human islet GLP-1 receptor. Demonstration that exendin-4 is an agonist and exendin-(9–39) an antagonist of the receptor. Diabetes 1993;42:1678–82.
Mukai E, Toyoda K, Kimura H, Kawashima H, Fujimoto H, Ueda M, et al. GLP-1 receptor antagonist as a potential probe for pancreatic beta-cell imaging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009;389:523–6.
Waser B, Reubi JC. Value of the radiolabelled GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin(9–39) for targeting of GLP-1 receptor-expressing pancreatic tissues in mice and humans. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38:1054–8.
Kähkönen E, Jambor I, Kemppainen J, Lehtiö K, Grönroos TJ, Kuisma A, et al. In vivo imaging of prostate cancer using [68Ga]-labeled bombesin analog BAY86-7548. Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:5434–43.
Connolly BM, Vanko A, McQuade P, Guenther I, Meng X, Rubins D, et al. Ex vivo imaging of pancreatic beta cells using a radiolabeled GLP-1 receptor agonist. Mol Imaging Biol 2012;14:79–87.
Cescato R, Waser B, Fani M, Reubi JC. Evaluation of 177Lu-DOTA-sst2 antagonist versus 177Lu-DOTA-sst2 agonist binding in human cancers in vitro. J Nucl Med 2011;52:1886–90.
Bodei L, Paganelli G, Mariani G. Receptor radionuclide therapy of tumors: a road from basic research to clinical applications. J Nucl Med 2006;47:375–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Werner Hassler and Ulrich Matthey, Zurich, Switzerland as well as Drs. Charles Pyke and Lotte Bjerre-Knudsen, Copenhagen, Denmark for helpful discussions.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waser, B., Reubi, J.C. Radiolabelled GLP-1 receptor antagonist binds to GLP-1 receptor-expressing human tissues. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41, 1166–1171 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2684-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2684-4