Abstract
Purpose
Extracapsular spread (ECS) to the cervical lymph nodes is a major adverse prognostic factor in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). We prospectively examined the value of FDG PET immediately before postoperative radiotherapy/concurrent chemoradiotherapy (pre-RT/CCRT PET) to detect residual/relapsing disease in the early postsurgical follow-up period in high-risk OSCC patients with ECS.
Methods
We examined 183 high-risk OSCC patients with ECS who underwent preoperative FDG PET/CT for staging purposes. Of these patients, 29 underwent a second pre-RT/CCRT FDG PET/CT scan. The clinical utility of the second FDG PET/CT was examined using Kaplan-Meier curve analysis.
Results
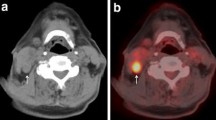
Patients who underwent the second FDG PET/CT scan had baseline clinicopathological characteristics similar to those who did not undergo a second scan. Of the patients who underwent the second scan, seven (24 %) had unexpected, newly discovered lesions. Five eventually died of the disease, and two had no evidence of recurrence after a change in RT field and dose. In an event-based analysis at 2 months, rates of neck control (6/29 vs. 6/154, p = 0.001), distant metastases (3/29 vs. 4/154, p = 0.046), and disease-free survival (7/29 vs. 10/154, p = 0.003) were significantly higher in patients who received a second PET scan than in those who did not. The second pre-RT/CCRT PET scan was of particular benefit for detecting new lesions in OSCC patients with both ECS and lymph node standardized uptake value (SUV) of ≥5.2 in the first PET scan.
Conclusion
The present findings support the clinical value of pre-RT/CCRT FDG PET for defining treatment strategy in OSCC patients with both ECS and high nodal SUV, even when FDG PET had already been performed during the initial staging work-up.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao CT, Wang HM, Chang JT, Lin CY, Ng SH, Huang SF, et al. Influence of pathological nodal status and maximal standardized uptake value of the primary tumor and regional lymph nodes on treatment plans in patients with advanced oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77:421–9.
Liao CT, Huang SF, Chen IH, Chang JT, Wang HM, Ng SH, et al. Risk stratification of patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and contralateral neck recurrence following radical surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:159–70.
Liao CT, Chang JT, Wang HM, Ng SH, Hsueh C, Lee LY, et al. Pretreatment primary tumor SUVmax measured by FDG-PET and pathologic tumor depth predict for poor outcomes in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and pathologically positive lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;73:764–71.
Ng SH, Yen TC, Chang JT, Chan SC, Ko SF, Wang HM, et al. Prospective study of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma with palpably negative neck. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4371–6.
Liao CT, Chang JT, Wang HM, Ng SH, Hsueh C, Lee LY, et al. Salvage therapy in relapsed squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: how and when? Cancer. 2008;112:94–103.
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 6th ed. New York: Springer; 2002.
Wang HM, Wang CS, Chen JS, Chen IH, Liao CT, Chang TC. Cisplatin, tegafur, and leucovorin: a moderately effective and minimally toxic outpatient neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 2002;94:2989–95.
Bachaud JM, Cohen-Jonathan E, Alzieu C, David JM, Serrano E, Daly-Schveitzer N. Combined postoperative radiotherapy and weekly cisplatin infusion for locally advanced head and neck carcinoma: final report of a randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;36:999–1004.
Liao CT, Lee LY, Huang SF, Chen IH, Kang CJ, Lin CY, et al. Outcome analysis of patients with oral cavity cancer and extracapsular spread in neck lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:930–7.
Liao CT, Chang JT, Wang HM, Ng SH, Hsueh C, Lee LY, et al. Preoperative [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography standardized uptake value of neck lymph nodes predicts neck cancer control and survival rates in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and pathologically positive lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:1054–61.
Woolgar JA. Histopathological prognosticators in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2006;42:229–39.
Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, Jacobs J, Campbell BH, Saxman SB, et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1937–44.
Bernier J, Domenge C, Ozsahin M, Matuszewska K, Lefèbvre JL, Greiner RH, et al. Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1945–52.
Bernier J, Cooper JS, Pajak TF, van Glabbeke M, Bourhis J, Forastiere A, et al. Defining risk levels in locally advanced head and neck cancers: a comparative analysis of concurrent postoperative radiation plus chemotherapy trials of the EORTC (#22931) and RTOG (# 9501). Head Neck. 2005;27:843–50.
Shaw RJ, Lowe D, Woolgar JA, Brown JS, Vaughan ED, Evans C, et al. Extracapsular spread in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2010;32:714–22.
Liao CT, Wang HM, Chang JT, Ng SH, Hsueh C, Lee LY, et al. Analysis of risk factors for distant metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer. 2007;110:1501–8.
Palme CE, Gullane PJ, Gilbert RW. Current treatment options in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2004;13:47–70.
Blom RL, Schreurs WM, Belgers HJ, Oostenbrug LE, Vliegen RF, Sosef MN. The value of post-neoadjuvant therapy PET-CT in the detection of interval metastases in esophageal carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011;37:774–8.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers, V. II. 2011. http://www.nccn.org/. Accessed 20 January 2012.
Bruzzi JF, Swisher SG, Truong MT, Munden RF, Hofstetter WL, Macapinlac HA, et al. Detection of interval distant metastases: clinical utility of integrated CT-PET imaging in patients with esophageal carcinoma after neoadjuvant therapy. Cancer. 2007;109:125–34.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by grants CMRPG370063 and CMRPG371502 from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital at Linkou.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Drs. Chien-Yu Lin and Chun-Ta Liao contributed equally to this work.
Dr. Hung-Ming Wang co-corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, CT., Fan, KH., Lin, CY. et al. Impact of a second FDG PET scan before adjuvant therapy for the early detection of residual/relapsing tumours in high-risk patients with oral cavity cancer and pathological extracapsular spread. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39, 944–955 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2103-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2103-2