Abstract
Purpose
Glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GLP-1) is an incretin peptide that augments glucose-stimulated insulin release following oral consumption of nutrients. Its message is transmitted via a G protein-coupled receptor called GLP-1R, which is colocalized with pancreatic β-cells. The GLP-1 system is responsible for enhancing insulin release, inhibiting glucagon production, inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis, inhibiting gastric mobility, and suppression of appetite. The abundance of GLP-1R in pancreatic β-cells in insulinoma, a cancer of the pancreas, and the activity of GLP-1 in the cardiovascular system have made GLP-1R a target for molecular imaging.
Methods
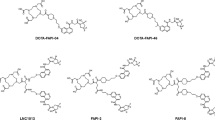
We prepared 18F radioligands for GLP-1R by the reaction of [18F]FBEM, a maleimide prosthetic group, with [Cys0] and [Cys40] analogs of exendin-4. The binding affinity, cellular uptake and internalization, in vitro stability, and uptake and specificity of uptake of the resulting compounds were determined in an INS-1 xenograft model in nude mice.
Results
The [18F]FBEM-[Cysx]-exendin-4 analogs were obtained in good yield (34.3 ± 3.4%, n = 11), based on the starting compound [18F]FBEM), and had a specific activity of 45.51 ± 16.28 GBq/μmol (1.23 ± 0.44 Ci/μmol, n = 7) at the end of synthesis. The C-terminal isomer, [18F]FBEM-[Cys40]-exendin-4, had higher affinity for INS-1 tumor cells (IC50 1.11 ± 0.057 nM) and higher tumor uptake (25.25 ± 3.39 %ID/g at 1 h) than the N-terminal isomer, [18F]FBEM-[Cys0]-exendin-4 (IC50 2.99 ± 0.06 nM, uptake 7.20 ± 1.26 %ID/g at 1 h). Uptake of both isomers into INS-1 tumor, pancreas, stomach, and lung could be blocked by preinjection of nonradiolabeled [Cysx]-exendin-4 (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
[18F]FBEM-[Cys40]-exendin-4 and [18F]FBEM-[Cys0]-exendin-4 have high affinity for GLP-1R and display similar in vitro cell internalization. The higher uptake into INS-1 xenograft tumors exhibited by [18F]FBEM-[Cys40]-exendin-4 suggests that this compound would be the better tracer for imaging GLP-1R.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Vilsboll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S. Glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:161–8.
Aaboe K, Krarup T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ. GLP-1: physiological effects and potential therapeutic applications. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:994–1003.
Tornehave D, Kristensen P, Romer J, Knudsen LB, Heller RS. Expression of the GLP-1 receptor in mouse, rat, and human pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem. 2008;56:841–51.
Deacon CF, Johnsen AH, Holst JJ. Degradation of glucagon-like peptide-1 by human plasma in-vitro yields an N-terminally truncated peptide that is a major endogenous metabolite in-vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:952–7.
Mukai E, Toyoda K, Kimura H, Kawashima H, Fujimoto H, Ueda M, et al. GLP-1 receptor antagonist as a potential probe for pancreatic beta-cell imaging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;389:523–6.
Wu Z, Kandeel F. Radionuclide probes for molecular imaging of pancreatic beta-cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62:1125–38.
Reubi JC, Waser B. Concomitant expression of several peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumours: molecular basis for in vivo multireceptor tumour targeting. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:781–93.
Hohmeier HE, Mulder H, Chen G, Henkel-Rieger R, Prentki M, Newgard CB. Isolation of INS-1-derived cell lines with robust ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent and -independent glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes. 2000;49:424–30.
Nielsen LL, Young AA, Parkes DG. Pharmacology of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4): a potential therapeutic for improved glycemic control of type 2 diabetes. Regul Pept. 2004;117:77–88.
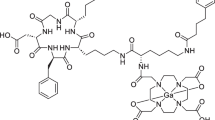
Wild D, Behe M, Wicki A, Storch D, Waser B, Gotthardt M, et al. [Lys40(Ahx-DTPA-111In)NH2]exendin-4, a very promising ligand for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor targeting. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:2025–33.
Wild D, Wicki A, Mansi R, Behe M, Keil B, Bernhardt P, et al. Exendin-4-based radiopharmaceuticals for glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor PET/CT and SPECT/CT. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1059–67.
Brom M, Oyen WJ, Joosten L, Gotthardt M, Boerman OC. 68Ga-labelled exendin-3, a new agent for the detection of insulinomas with PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1345–55.
Gotthardt M, Fischer M, Naeher I, Holz JB, Jungclas H, Fritsch HW, et al. Use of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) for the detection of insulinomas: initial experimental results. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:597–606.
Wicki A, Wild D, Storch D, Seemayer C, Gotthardt M, Behe M, et al. [Lys40(Ahx-DTPA-111In)NH2]-Exendin-4 is a highly efficient radiotherapeutic for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-targeted therapy for insulinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:3696–705.
Wild D, Macke H, Christ E, Gloor B, Reubi JC. Glucagon-like peptide 1-receptor scans to localize occult insulinomas. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:766–8.
Christ E, Wild D, Forrer F, Brandle M, Sahli R, Clerici T, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging for localization of insulinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:4398–405.
Pattou F, Kerr-Conte J, Wild D. GLP-1-receptor scanning for imaging of human beta cells transplanted in muscle. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1289–90.
Gao H, Niu G, Yang M, Quan Q, Ma Y, Murage E, et al. PET of insulinoma using 18F-FBEM-EM3106B, a new GLP-1 analog. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:1775–82.
Murage EN, Gao G, Bisello A, Ahn JM. Development of potent glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists with high enzyme stability via introduction of multiple lactam bridges. J Med Chem. 2010;53:6412–20.
Cai W, Zhang X, Wu Y, Chen X. A thiol-reactive F-18-labeling agent, N-[2-(4-F-18-fluorobenzamido)ethyl]maleimide, and synthesis of RGD peptide-based tracer for PET imaging of αvβ3 integrin expression. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1172–80.
Kiesewetter DO, Jacobson O, Lang L, Chen X. Automated radiochemical synthesis of [18F]FBEM: a thiol reactive synthon for radiofluorination of peptides and proteins. Appl Radiat Isot. 2011;69:410–4.
Chambers AF. MDA-MB-435 and M14 cell lines: identical but not M14 melanoma? Cancer Res. 2009;69:5292–3.
Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–5.
Grieve DJ, Cassidy RS, Green BD. Emerging cardiovascular actions of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1: potential therapeutic benefits beyond glycaemic control? Br J Pharmacol. 2009;157:1340–51.
Kiesewetter DO, Kramer-Marek G, Ma Y, Capala J. Radiolabeling of HER2 specific Affibody® molecule with F-18. J Fluor Chem. 2008;129:799–805.
Froelich JM, Reid GE. The origin and control of ex vivo oxidative peptide modifications prior to mass spectrometry analysis. Proteomics. 2008;8:1334–45.
Hargrove DM, Kendall ES, Reynolds JM, Lwin AN, Herich JP, Smith PA, et al. Biological activity of AC3174, a peptide analog of exendin-4. Regul Pept. 2007;141:113–9.
Chen J, Yu L, Wang L, Fang X, Li L, Li W. Stability of synthetic exendin-4 in human plasma in vitro. Protein Pept Lett. 2007;14:19–25.
Goke R, Fehmann HC, Linn T, Schmidt H, Krause M, Eng J, et al. Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9-39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-36)-amide receptor of insulin-secreting beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:19650–5.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health. The authors acknowledge the NIH Clinical Center PET department for radioisotope production. We thank Dr. Henry S. Eden for proof-reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dale O. Kiesewetter and Haokao Gao contributed equally to this work.
A related editorial commentary can be found at DOI 10.1007/s00259-011-2020-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiesewetter, D.O., Gao, H., Ma, Y. et al. 18F-radiolabeled analogs of exendin-4 for PET imaging of GLP-1 in insulinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39, 463–473 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1980-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1980-0