Abstract
Purpose
The ∼15 kDa variable domains of camelid heavy-chain-only antibodies (called Nanobodies®) have the flexibility to be formatted as monovalent, monospecific, multivalent or multispecific single chain proteins with either fast or slow pharmacokinetics. We report the evaluation of the fast kinetic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Nanobody 7D12, labelled with 68Ga via the novel bifunctional chelate (BFC) p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine (Df-Bz-NCS). Df-Bz-NCS has recently been introduced as the chelate of choice for 89Zr immuno-positron emission tomography (PET).
Methods
Nanobody 7D12 was premodified with Df-Bz-NCS at pH 9. Radiolabelling with purified 68Ga was performed at pH 5.0–6.5 for 5 min at room temperature. For in vitro stability measurements in storage buffer (0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5) at 4°C or in human serum at 37°C, a mixture of 67Ga and 68Ga was used. Biodistribution and immuno-PET studies of 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 were performed in nude mice bearing A431 xenografts using 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 as the reference conjugate.
Results
The Df-Bz-NCS chelate was conjugated to Nanobody 7D12 with a chelate to Nanobody molar substitution ratio of 0.2:1. The overall 68Ga radiochemical yield was 55–70% (not corrected for decay); specific activity was 100–500 MBq/mg. Radiochemical purity of the conjugate was >96%, while the integrity and immunoreactivity were preserved. 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was stable in storage buffer as well as in human serum during a 5-h incubation period (<2% radioactivity loss). In biodistribution studies the 68Ga-labelled Nanobody 7D12 showed high uptake in A431 tumours (ranging from 6.1 ± 1.3 to 7.2 ± 1.5%ID/g at 1–3 h after injection) and high tumour to blood ratios, which increased from 8.2 to 14.4 and 25.7 at 1, 2 and 3 h after injection, respectively. High uptake was also observed in the kidneys. Biodistribution was similar to that of the reference conjugate 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12. Tumours were clearly visualized in a PET imaging study.
Conclusion
Via a rapid procedure under mild conditions a 68Ga-Nanobody was obtained that exhibited high tumour uptake and tumour to normal tissue ratios in nude mice bearing A431 xenografts. Fast kinetic 68Ga-Nanobody conjugates can be promising tools for tumour detection and imaging of target expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, HER1, ERb1) is a transmembrane protein of the tyrosine kinase receptor family. Activation of EGFR causes signalling that may lead to cell division, increased motility, angiogenesis and suppression of apoptosis [1]. EGFR over-expression or constitutive activation has been shown to be associated with poor survival and recurrences in many human malignancies [2]. Detection of EGFR expression via nuclear medicine visualization may provide advantages over immunohistochemical staining of tumour biopsies, since evaluation of both the primary tumour as well as the metastases can be achieved. In addition, such confirmation of EGFR expression can be of value as a scouting procedure to select patients for anti-EGFR therapy with approved monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) like cetuximab or panitumumab or small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitors. On this latter topic several studies with intact anti-EGFR (αEGFR) mAbs or mAb fragments labelled with single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (111In, 99mTc) or positron emission tomography (PET) (64Cu, 89Zr) radionuclides have been reported [3–9].
Nanobody technology provides new perspectives for mono- as well as multitarget tumour detection and therapy [10–12]. Nanobodies are derived from a unique antibody format that is present in species from the family of Camelidae, including llama, camel and dromedary. These animals contain, besides their conventional antibody repertoire, an antibody class consisting of heavy chains only [10, 13]. The variable region of the heavy-chain-only antibodies (VHH) represents the complete binding unit of the antibody. Because of the small size of these VHH fragments (∼15 kDa), this binding unit is also called Nanobody®. Although being smaller than a scFv fragment, a Nanobody has full antigen-binding potential and does not show aggregation problems, because of hydrophilic instead of hydrophobic patches in the VH and VL domains. Due to their single domain character, standard molecular biology techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) allow for the facile purification and selection of appropriate Nanobody candidates from the full antibody repertoire of immunized animals [14]. Unique features of the Nanobody technology platform in comparison to conventional mAb technology are easy and rapid drug development, and the easy and cheap production in bacteria and yeast [10, 15].
For a proof of concept we used the Nanobody technology platform to construct two αEGFR Nanobodies [11]. The biodistribution of a 177Lu-labelled bivalent αEGFR Nanobody (αEGFR-αEGFR) in A431 tumour-bearing nude mice showed a tumour uptake of 5.0 ± 1.4 percentage of the injected dose per gram of tissue (%ID/g) at 6 h after injection and high tumour to normal tissue ratios (e.g. tumour to blood ratio >80) due to rapid blood clearance. Simple fusion of an anti-albumin Nanobody building block gave a 50-kDa single-chain construct (αEGFR-αEGFR-αAlb) that showed pharmacokinetics and tumour uptake (up to 35.2 ± 7.5%ID/g) comparable to cetuximab, but faster and deeper tumour penetration. Therefore, such Nanobody formats might be ideal for imaging and therapeutic purposes, respectively.
In the present study we evaluated the in vivo diagnostic potential of fast kinetic αEGFR Nanobody 7D12 with the immuno-PET approach. For this purpose the short-lived positron emitter 68Ga (T ½ = 68 min, Eβ+max 1.92 MeV) was chosen. 68Ga is an attractive positron-emitting radionuclide since it is cyclotron-independently available via the 68Ge/68Ga generator system.
In aqueous solutions the three-valent gallium forms a complex with many bifunctional chelates (BFCs) containing oxygen and nitrogen as donor atoms. The only clinically used BFC for 68Ga is 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-N,N′,N″,N′″-tetraacetic acid (DOTA), but fast complex formation requires a high temperature [16–19]. More recently, several new chelates have been described for labelling of 68Ga to heat-labile proteins at ambient temperature including 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4-7-triacetic acid (NOTA) and N,N′-bis[2-hydroxy-5-(carboxyethyl)benzyl]ethylenediamine-N,N′-diacetic acid (HBED-CC) [19–21]. However, this new generation of BFCs is not yet available for clinical immuno-PET applications.
For coupling of the long-lived positron emitter 89Zr (T ½ = 78.4 h, Eβ+max 0.9 MeV) (23%) to intact mAbs, we recently introduced the novel BFC p-isothiocyanatobenzyl derivative of desferrioxamine B (Df-Bz-NCS) [22, 23]. The choice of desferrioxamine B is attractive because it has been used safely in the clinical setting for many years. Since the hydroxamate function in desferrioxamine B has also been used for coupling of 67Ga in the past [24–27], we investigated whether this same Df-Bz-NCS can be used for labelling of 68Ga under mild conditions. If so, a similar kind of GMP-compliant radiochemistry can be used for labelling of slow kinetic mAbs with 89Zr, and fast kinetic mAb fragments with 68Ga.
In this study, after establishing optimal 68Ga labelling procedures by using a control intact IgG mAb, the bifunctional chelate Df-Bz-NCS was conjugated to αEGFR Nanobody 7D12 and subsequently radiolabelled with 68Ga. The resulting 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 conjugate was analysed for stability at 4°C in storage buffer and at 37°C in serum, whereas its in vivo behaviour was investigated via biodistribution and animal PET studies, using 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 as the reference.
Materials and methods
Materials
All reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) unless otherwise stated. Deionized water (18 MΩ*cm) and ultra pure HCl (Ga content 0.02 ng natGa/g) was used. No other special measures were taken regarding working under strict metal-free conditions. Df-Bz-NCS was purchased from Macrocyclics (Dallas, TX, USA, catalog No. B-705). Nanobody 7D12 was generated by Ablynx NV (Ghent, Belgium) as described previously [14] and kindly provided to us. The selection, production and characterization of chimeric mAb U36 (cmAb U36 11.53 mg/ml) directed against CD44v6 has been described elsewhere [28]. The human epidermoid cervical carcinoma cell line A431 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (www.atcc.com), ATCC number: CRL-1555. The head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell line UM-SCC-11B was obtained from Dr. T.E. Carey (Ann Arbor, MI, USA) [29]. 68Ga was obtained from a commercial 68Ge/68Ga generator based on a TiO2 bedding with 1.85 GBq 68Ge-loaded activity (IGG100; Eckert & Ziegler, Berlin, Germany). 67Ga was purchased as 67Ga-citrate (74 MBq/ml) from Covidien (Mansfield, MA, USA). [89Zr]Zr-oxalate in 1.0 M oxalic acid (≥ 0.15 GBq/nmol) was from IBA Molecular (www.iba.be/molecular).
Purification and concentration of 68Ga and 67Ga
The 68Ga was eluted from the 68Ge/68Ga generator as described by Velikyan et al. [16]. In short, the generator was eluted according to the manufacturer’s protocol with 3.5 ml ultra pure 0.1 M HCl solution. To that solution 3.5 ml ultra pure 8 M HCl was added under stirring, to give a final concentration of ∼ 4 M HCl. The solution was passed through a pre-treated (1 ml 100% ethanol, 1 ml deionized water, 1 ml 4 M HCl) anion exchange column [Chromafix, PS-HCO3 (s), Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany], the column was washed with 2 ml of 4 M HCl, flushed with air, and then the 68Ga was eluted from the Chromafix column with 200 μl deionized water (elution efficiency >85%). The use of ultra pure HCl implies that this procedure attributes at most 1.1 pmol natGa to this eluate.
67GaCl3 was obtained from 67Ga-citrate. To this end, 67Ga-citrate was mixed with an equal volume of ultra pure 8 M HCl. This solution was passed through a pre-treated Chromafix column and eluted as described for 68Ga.
In all preparations for in vitro evaluation 68/67Ga was used, while for in vivo evaluation only 68Ga was applied.
Preparation of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-cmAb U36
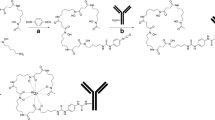
For development of labelling procedures, the 150-kDa intact cmAb U36 was used as the control mAb. cmAb U36 was premodified with Df-Bz-NCS as described by Perk et al. [22] (Fig. 1). In short, 5 mg cmAb U36 (33 nmol) reacted with 20 μl Df-Bz-NCS (100 nmol) in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) for 30 min at 37°C at pH 9 in a shaker, in a total volume of 1 ml. Nonconjugated chelate was removed by size exclusion chromatography using a PD-10 column (GE Healthcare Life Science) with 0.25 M NaOAc pH 5.5 as eluant. The flow through and the first 1.5 ml were discarded. The next 2 ml containing the premodified mAb were stored.
Ga-Df complex chelate formation conditions were selected by varying pH and protein concentration. As a result, the following procedure was developed; to 10–200 μl (=a) 68Ga and/or 67Ga in deionized water (3× a μl), 3 M NH4OAc buffer pH 7.2 were added and mixed for 5 min at room temperature. Subsequently the premodified cmAb U36 (100–1,000 μg) in 0.25 M NaOAc pH5.5 was added; the final reaction volume was 2 ml. The reaction was stopped after 5 min at room temperature by the addition of 50 μl 50 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetate acid (EDTA), followed by PD-10 column purification using 0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5, as eluant. The flow through and the first 1 ml were discarded. The next 2 ml containing the 68/67Ga-labelled cmAb U36 was collected and used for further experiments.
Preparation of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12
The same protocol was applied for the modification and radiolabelling of the αEGFR Nanobody 7D12. In short, 2 mg 7D12 (125 nmol) was conjugated with 375 nmol Df-Bz-NCS and after PD-10 column purification the premodified 7D12 (200–1,000 μg) was labelled with 68/67Ga as described for cmAb U36.
Preparation of 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12
The 7D12 nanobody was premodified as described above with a threefold molar excess of Df-Bz-NCS chelate. After PD-10 column purification the premodified 7D12 was labelled with 89Zr as described by Perk et al. [22]. In short, Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 (100–1,000 μg) was labelled with 89Zr (37 MBq) in 0.25 M HEPES buffer pH 7.0 at room temperature in a total volume of 2 ml. The 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was purified by PD-10 column using 0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5, as eluant. After discarding the flow through and the first 1 ml, the next 2 ml containing the 89Zr-labelled 7D12 was collected for further experiments.
Determination of Df to 7D12 molar ratio
The Df-Bz-NCS to 7D12 molar ratio was determined following a general method using a known nanomolar excess of GaCl3 spiked with 67Ga. In short, 250 nmol GaCl3 (in 4 M ultra pure HCl) was mixed with ∼37 MBq 67Ga and purified according to the aforementioned method using the anion Chromafix column. Thereafter, 500 μg of premodified Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was labelled according to the developed protocol with 20–60 nmol of the above prepared 67Ga-GaCl3, and the Df to 7D12 molar ratio was calculated. For comparison the Df to 7D12 molar ratio was also determined with the use of zirconium oxalate spiked with 89Zr.
Analysis
68Ga was measured using Eγ = 511 KeV and 67Ga with Eγ = 185 KeV. When dual isotope labelling products were produced, 67Ga radioactivity measurements were performed at least 20 h after production (after decay of 68Ga). Each 68/67Ga-labelled product was analysed by instant thin-layer chromatography (ITLC) to determine the radiochemical labelling efficiency and radiochemical purity. The integrity of the Nanobody and mAb was analysed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) followed by phosphor imaging (Storm 820, GE Healthcare). Immunoreactivity was determined by a cell-binding assay, 3 h at 37°C or overnight at 4°C. ITLC analysis of the 68/67Ga-labelled products was performed on chromatography strips (Biodex, Shirley, NY, USA); 2 μl was spotted on an ITLC strip with 50 mM EDTA in Milli-Q as mobile phase. HPLC analysis was performed on a Jasco HPLC system using a Superdex™ peptide size exclusion column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) when a labelled Nanobody was injected, or a Superdex™ 200 10/300 GL size exclusion column when labelled cmAb U36 was injected, with a mixture of 0.05 M sodium phosphate and 0.15 M sodium chloride (pH 6.8) as eluant at flow rates of 1.0 and 0.5 ml min−1, respectively. Gel electrophoresis was performed on a PhastGel System (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) using high-density SDS-PAGE gels when a labelled Nanobody was applied or 7.5% SDS-PAGE gels when labelled U36 was applied, under non-reducing conditions. Immunoreactivity was determined by measuring the binding of the 68/67Ga-7D12 or 68/67Ga-cmAb U36 to a serial dilution of 2% paraformaldehyde fixed A431 cells or 0.2% glutaraldehyde fixed 11B cells, respectively, essentially as described by Lindmo et al. [30].
In vitro stability
To determine the in vitro stability of the gallium-labelled Nanobodies, 500 μg 68/67Ga-labelled 7D12 product was stored at 4°C up to 24 h in 0.25 M NaOAc pH 5.5, containing 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid as antioxidant and compared with 89Zr-7D12. Amounts of activity at the start of storage were 120 MBq of 68Ga, 20 MBq of 67Ga and 20 MBq of 89Zr. After 5 and 24 h storage aliquots were taken and analysed by ITLC, HPLC and SDS-PAGE.
Stability of 68/67Ga-labelled 7D12 was also tested in freshly prepared human serum and compared with 89Zr-7D12. Activity amounts at the start of storage were 80 MBq 68Ga, 18 MBq 67Ga and 18 MBq 89Zr. The labelled 7D12 (300 μg) was incubated at 37°C in a CO2-enriched atmosphere (5% CO2) with freshly prepared human serum (1:4) in the presence of 0.02% NaN3. Aliquots were taken after 5 and 24 h storage and analysed by ITLC and HPLC.
Biodistribution study
The distribution of 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was examined using nude mice (Hsd:Athymic Nude-Foxn1 nu, 20–30 g, Harlan Laboratories, Horst, the Netherlands) bearing subcutaneously implanted human xenografts of the vulvar tumour cell line A431 at two lateral sides. All animal experiments were done according to NIH Principles of Laboratory Animal Care and Dutch national law (Wet op de dierproeven, Stb 1985, 336).
In this experiment mice bearing A431 xenografts were injected with 0.35 MBq 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 (6 μg) via the retro-orbital plexus. As reference compound, 0.35 MBq 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 (6 μg) was used. Unlabelled 7D12 was added to the injection mixture to obtain a final dose of 50 μg per mouse. At 1, 2 and 3 h post-injection (p.i.) four mice were anaesthetized, bled, killed and dissected. Blood, tumour and normal tissues were weighed and radioactivity was measured in a gamma counter (Wallac, Turku, Finland). Radioactivity uptake for each sample was calculated as %ID/g.
PET study
PET imaging was performed on a HRRT PET scanner (Siemens/CTI [31]), a dedicated human brain scanner. Three A431 xenograft-bearing mice were anaesthetized by inhalation of 2% isoflurane, injected with 5 MBq 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 (85 μg) via the retro-orbital plexus and scanned for 3 h. In addition, three mice were injected with 2.5 MBq 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 (85 μg). Unlabelled 7D12 was added to the injection mixture to obtain a final dose of 100 μg per mouse. Transmission scans for attenuation and scatter correction were routinely obtained with each emission scan. Three-dimensional emission scans were acquired in list mode during 180 min. A single frame static image was reconstructed using ordinary Poisson ordered subsets expectation maximization (OP-OSEM). For visualization of the images, the freely available Amide’s A Medical Imaging Data Examiner (AMIDE) program was used [32].
Statistical analysis
Differences in tissue uptake between injected conjugates were statistically analysed for each different time point with SPSS 15.0 software using Student’s t test for unpaired data. Two-sided significance levels were calculated and p <0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Preparation of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-cmAb U36
The Ga-Df formation conditions were investigated by performing experiments with premodified Df-Bz-NCS-cmAb U36. The Df-Bz-NCS chelate was coupled at pH 9 to the lysine groups in a threefold molar excess via a 30-min incubation at 37°C.
When labelling was performed for 5 min in a 2 ml acetate solution at a pH in the range of 5.0–6.5 and an activity level of 200 MBq 68Ga (2 pmol) and 37 MBq 67Ga (25 pmol), the labelling yield was consistently >90% provided the amount of mAb was >200 μg (measured up to 1,000 μg), i.e. >0.7 nmol bound Df-groups. For 100 μg (i.e. 0.35 nmol bound Df-groups) a labelling yield of 80% was obtained. When using a naked cmAb U36 under these conditions, < 1% of Ga was co-eluted with the PD-10 protein fraction.
After PD-10 purification the labelled cmAb U36 was stored in 2 ml 0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5, and analysed. The radiochemical purity was always 96–99%, as determined with ITLC and HPLC. The immunoreactive fraction was determined by an overnight immunoreactivity assay (when using 67Ga) and was 81–86%. The integrity of the labelled cmAb U36 was optimal as determined with SDS-PAGE and HPLC analysis (data not shown). The radiation dose derived from labelling with 200 MBq 68Ga and its subsequent full decay did not affect the integrity and immunoreactivity of the 68/67Ga product, which means that our chosen 0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5 buffer protected adequately against radiation damage. Dilution of the 68/67Ga-cmAb U36 product with human serum to a solution containing 70 pmol/ml Df showed <1% loss of label. Upon storage of this solution at 37°C, the radiochemical purity of cmAb U36 decreased during 5 h an additional 2% and during 24 h an additional 10%, as determined by ITLC and confirmed with HPLC.
Preparation of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 and 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12
The aforementioned conditions applied to Nanobody 7D12 gave 0.2 desferal groups per Nanobody molecule. Labelling (200–1,000 μg) of the Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 with 68/67Ga resulted in overall radioactivity yields of 55–70% (not corrected for decay). Radiochemical purity was always 96–99%, as determined by HPLC and ITLC. Immunoreactivity was 40–60% for the 3-h incubation assay at 37°C while the overnight assay at 4°C using 67Ga showed 80–85%. The integrity of the Nanobody was preserved as determined with SDS-PAGE and HPLC analysis (see Fig. 2).
For the 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 the overall radioactivity yield was 59–73%, radiochemical purity was always 97–99% and the immunoreactivity was 80–85% (determined with the overnight assay at 4°C).
In vitro stability
In vitro stability of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was compared with 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12. Radiochemical purity of 68/67Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 was 98 ± 1% at the start and only slightly decreased during 5 h incubation in buffer at 4°C (1.5−2.0% release of 68/67Ga); after 24 h the decrease was 6–7% as determined with ITLC and confirmed with HPLC. For 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 the radiochemical purity was also 98 ± 1% at the start, which decreased to 97 ± 1% after 24 h at 4°C. The integrity of both labelled 7D12 Nanobodies was not affected after 24 h at 4°C, as determined with SDS-PAGE and HPLC.
In human serum at 37°C, radiochemical purity of both labelled 7D12 Nanobodies slightly decreased during 5 h in human serum (1–2% release for both compounds), and after 24 h the percentage of 68/67Ga that was dissociated was 7–8% and 1–2% for 89Zr as determined by ITLC and confirmed with HPLC.
Biodistribution study
For the biodistribution study nude mice bearing A431 xenografts were injected with either 0.35 ± 0.05 MBq 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 or 0.35 ± 0.01 MBq 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 as the control group (Fig. 3). After 1 h high uptake was seen in tumour tissue for both radioisotopes (6.1 ± 1.3%ID/g for 68Ga and 7.5 ± 1.9%ID/g for 89Zr), a level which remained constant up to 3 h p.i. (6.1 ± 0.9 and 7.6 ± 1.9%ID/g at 2 h, and 7.2 ± 1.5 and 7.4 ± 1.6%ID/g at 3 h p.i. for 68Ga and 89Zr, respectively). High radioactivity uptake was found in the kidneys, urine and bladder. Except for some liver uptake (2.1 ± 0.1 and 0.7 ± 0.1%ID/g at 1 h p.i. for 68Ga and 89Zr, respectively) all other organs showed low uptake at all time points (< 0.5 ± 0.2%ID/g for 68Ga and < 0.3 ± 0.1%ID/g for 89Zr). For both radioisotopes tumour to blood ratios increased at later time points. At 1 h the tumour to blood ratio for 68Ga was 8.2 and increased to 14.4 at 2 h and 25.7 at 3 h p.i., while the tumour to blood ratios for 89Zr were 14.8, 35.2 and 42.4 at 1, 2 and 3 h, respectively. In general, the overall biodistribution of both radioisotopes was very similar. For all time points significant differences between 68Ga and 89Zr were seen in liver and kidney, and at 1 h p.i. a significant difference was also observed for spleen (p < 0.001).
PET study
To exclude possible radioactivity uptake in non-evaluated tissues in the biodistribution studies a PET imaging study was performed. In Fig. 4 representative PET images are shown; a static PET image obtained 2–3 h after injection of 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 is seen in the left image while the right image represents a mouse 2–3 h after injection of 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-Df. In both images the tumours are clearly visible, with good tumour to background contrast. High accumulation in the kidney and bladder was observed.
Discussion
In this study, we describe a method for labelling of αEFGR Nanobody 7D12 with 68Ga using the novel bifunctional desferal chelate (Df-Bz-NCS) which was previously introduced for the coupling of 89Zr to intact mAbs [22, 23]. Using this method, stable 68Ga-7D12 radioimmunoconjugates were produced as demonstrated by stability testing in storage buffer as well as in human serum with only slightly less stability as compared with the reference compound 89Zr-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12. In addition, high and selective tumour uptake was observed in biodistribution and PET imaging experiments in nude mice bearing A431 xenografts, which was similar for 68Ga-7D12 and the reference conjugate 89Zr-7D12. The latter indicates that Df-Bz-NCS is equally well suited for immuno-PET imaging, irrespective of whether the short-lived positron emitter 68Ga or the long-lived positron emitter 89Zr is used. 89Zr-Df antibodies have been extensively evaluated in clinical immuno-PET studies [33].
Crucial in the labelling procedures described herein are (1) the use of ultra pure HCl, to keep the natGa concentrations as low as possible and also to minimize the amounts of Al, Fe and Zr, being strong competitors for complexation with Df, (2) the purification and concentration of 68Ga by use of an anion exchange column, to further minimize the amounts of Al, Fe and Zr, to get rid of contaminating metals originating from the generator and to keep [68GaCl −4 ] volumes for labelling small [16, 34], (3) the addition of a highly concentrated NH4OAc solution to the [68GaCl −4 ] solution for efficient radiolabelling and stable complex formation (avoidance of the formation of gallium-oxo-chloro intermediates), (4) the use of a commercially available desferrioxamine B chelate that has been applied safely in the clinical setting for many years [23], (5) radiolabelling at room temperature within a relatively wide pH range of 5.0–6.5 and (6) the use of 0.25 M NaOAc with 5 mg ml−1 gentisic acid, pH 5.5 for protection during storage of the purified 68Ga-labelled conjugate. These procedures appeared efficient and mild, thus avoiding denaturation of protein, and resulted in optimal quality conjugates at an overall radiochemical yield of 55–70% (not corrected for decay). Therefore, these generic procedures seem suitable for GMP-compliant labelling, irrespective of the intrinsic stability of the biomolecule.
The only chelate that has been used for 68Ga labelling of mAbs or mAb-like molecules for clinical purposes is DOTA [35]. With DOTA the best labelling kinetics were obtained in sodium acetate buffers at low pH [36]. Tolmachev et al. evaluated the 68Ga labelling kinetics of the DOTA-containing anti-HER2 Affibody ABY-002. Labelling at room temperature for 5 min appeared inefficient (decay-corrected yield of less than 5%). Only after elevation of the temperature to 60°C or 90°C did the yield increase to ∼30 and ∼90%, respectively. The binding and pharmacokinetic characteristics of this particular Affibody did not become affected upon labelling, but it is open to question whether other proteins can resist the harsh labelling conditions of low pH and high temperature [35, 37]. The same is true for microwave heating that has been used for labelling of DOTA bioconjugates with 68Ga [16, 38]. In our initial studies, using DOTA-Bz-NCS, less than 60% labelling was obtained after 20 min at 45°C, while the thus obtained labelled product was unstable. We postulate that at lower temperature no full N-coordination occurs. This means that the 68Ga atom becomes ligated to the carboxyl functions of the DOTA molecule with still having water molecules in its coordination sphere instead of N, and that only concordant heating at elevated temperatures [37, 39] creates the additional N-coordination of the DOTA molecule leading to the 68Ga-DOTA complex that is suitable for in vivo applications. This important aspect of complex formation is fully analogous to what has been shown by us for the synthesis of the 186Re-MAG3 complex [40].
NOTA and its derivatives as well as the recently introduced HBED-CC chelates might have advantages over DOTA, since labelling with these chelates can be performed at room temperature and modest pH [19–21, 41]. These chelates, however, have not been clinically evaluated yet, and for us this was the reason to evaluate the desferrioxamine B derivative. Some controversy exists about the conditional stability constant of the Ga-Df complex at neutral pH. The in vitro stability we found corresponds well with the earlier findings of Smith-Jones et al. [25], Fani et al. [27] and Furukawa et al. [24], but seems to be rather in contrast with the findings of Caraco et al. [42] and Govindan et al. [26]. We feel that this is only an apparent controversy because the conditions under which Caraco et al. produced their Ga-Df complex are completely different. We observed that a product formed at pH = 7.4 indeed suffered from instability indicating that at this pH a certain amount of weak complexes are formed containing partly hydrolyzed Ga ions and so being only mono- or bidentate bound to the three hydroxamate functions. With respect to the findings of Govindan et al. [26], they already suggested themselves that their findings are most probably mixed up by the fact that the linkages between their mAb and Df are intrinsically instable.
EGFR, a tyrosine kinase receptor, is highly expressed in many epithelial cancer cells and is a prime target for detection and therapeutic applications. Nuclear imaging techniques have a proven advantage over immunohistological techniques since nuclear imaging is noninvasive and whole-body scans can be obtained [43]. The use of Nanobodies as imaging moiety might have advantages over the use of intact mAbs, since a molecular weight of only 15 kDa allows for faster kinetics than intact mAbs in vivo. To our knowledge, Nanobodies have never been used for immuno-PET applications. In this study, 68Ga-labelled Nanobody 7D12 showed high and selective uptake in A431 tumours, ranging from 6.1 to 7.2%ID/g at 1–3 h p.i., which was comparable to the reference compound 89Zr-7D12 (7.5 to 7.4%ID/g at 1–3 h). Significant differences in liver and kidney uptake were observed between the 68Ga-7D12 and 89Zr-7D12 conjugates. These differences most probably reflect the slightly lower stability observed in the in vitro stability experiments. Maybe metabolite analyses might provide further insight.
Huang et al. [44] and Gainkam et al. [45] studied the same (αEGFR) Nanobody 7D12 in the same A431 xenograft model, but labelled with 99mTc for SPECT applications. Tumour uptake of 99mTc-7D12 was 4.9%ID/g at 1 h p.i. (assessed by quantitative analysis of SPECT images) and 6.1%ID/g at 1.5 h p.i. (assessed by radioactivity counting of dissected tumours). Like 68Ga-7D12, 99mTc-7D12 showed high kidney uptake. However, uptake of 99mTc-7D12 in lung and spleen was higher than that of 68Ga-7D12: 2.1 and 1.4%ID/g versus 0.5 and 0.6%ID/g at 1 h p.i. Given the superior properties of PET in comparison to SPECT for clinical quantitative imaging, these data suggest that 68Ga-7D12 is the more attractive Nanobody-based probe for assessment of EGFR expression [46, 47].
68Ga-7D12 allowed high contrast imaging at relatively early time points (1 h p.i.) in comparison with radiolabelled conventional intact mAbs used in other preclinical imaging studies. For example, in recent immuno-PET studies with 64Cu- and 89Zr-labelled anti-EGFR mAb cetuximab tumours could only be clearly delineated 16–24 h p.i. [7, 9, 48]. Another interesting small molecular protein was introduced for imaging of EGFR, namely the 8-kDa Affibody ZEGFR:2377 [49]. PET imaging studies in A431-bearing nude mice showed higher tumour contrast when 50 μg of 111In-labelled ZEGFR:2377 was injected in comparison to 5 μg, whereas for both doses high liver uptake was observed. For the 50 μg 111In-ZEGFR:2377 group, tumour and liver uptake at 4 h p.i. was 2.4 and 5.1%ID/g, respectively. In comparison, tumour uptake of 68Ga-7D12 in the present study was substantially higher (7.2%ID/g at 3 h p.i.), while liver uptake was lower (2.0%ID/g at 3 h p.i.). These interesting differences in uptake can be ascribed to differences in reactivity with murine EGFR. Both probes can bind to human EGFR expressed in human xenografts, but only 111In-ZEGFR:2377 can also bind to the murine EGFR in the liver. In accordance, initial clinical imaging studies with 111In-labelled anti-EGFR mAb 225 showed high liver uptake, requiring relatively high mAb doses for imaging of EGFR expression [50].
The aforementioned data indicate 68Ga-7D12 Nanobody has potential for assessment of EGFR tumour expression; however, for clinical application thorough dose optimization might be needed to obtain optimal imaging results. The latter will be easier for 68Ga-labelled Nanobodies directed against targets that show predominantly expression in the tumour, as was recently illustrated in PET imaging studies with 68Ga-labelled Affibody ABY-002 directed against the HER2 receptor [35].
Conclusion
The newly developed GMP-compliant two-step procedure for coupling desferal to a Nanobody allows efficient and rapid preparation of 68Ga-Nanobodies for clinical use with high labelling yields, high radiochemical purity and preservation of immunoreactivity. The anti-EGFR 68Ga-Df-Bz-NCS-7D12 Nanobody showed high accumulation in A431 xenografts in nude mice in biodistribution studies as well as in immuno-PET, which indicates that this conjugate can be a promising fast kinetic noninvasive imaging probe for the detection of EGFR expression in tumours.
References
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:127–37.
Lurje G, Lenz HJ. EGFR signaling and drug discovery. Oncology 2009;77:400–10.
Dadparvar S, Krishna L, Miyamoto C, Brady LW, Brown SJ, Bender H, et al. Indium-111-labeled anti-EGFr-425 scintigraphy in the detection of malignant gliomas. Cancer 1994;73:884–9.
Vallis KA, Reilly RM, Chen P, Oza A, Hendler A, Cameron R, et al. A phase I study of 99mTc-hR3 (DiaCIM), a humanized immunoconjugate directed towards the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nucl Med Commun 2002;23:1155–64.
Schechter NR, Wendt RE, Yang DJ, Azhdarinia A, Erwin WD, Stachowiak AM, et al. Radiation dosimetry of 99mTc-labeled C225 in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1683–7.
Niu G, Li Z, Xie J, Le QT, Chen X. PET of EGFR antibody distribution in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma models. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1116–23.
Cai W, Chen K, He L, Cao Q, Koong A, Chen X. Quantitative PET of EGFR expression in xenograft-bearing mice using 64Cu-labeled cetuximab, a chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:850–8.
Ping Li W, Meyer LA, Capretto DA, Sherman CD, Anderson CJ. Receptor-binding, biodistribution, and metabolism studies of 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab, a PET-imaging agent for epidermal growth-factor receptor-positive tumors. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2008;23:158–71.
Aerts HJ, Dubois L, Perk L, Vermaelen P, van Dongen GA, Wouters BG, et al. Disparity between in vivo EGFR expression and 89Zr-labeled cetuximab uptake assessed with PET. J Nucl Med 2009;50:123–31.
Roovers RC, van Dongen GA, van Bergen en Henegouwen PM. Nanobodies in therapeutic applications. Curr Opin Mol Ther 2007;9:327–35.
Tijink BM, Laeremans T, Budde M, Stigter-van Walsum M, Dreier T, de Haard HJ, et al. Improved tumor targeting of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor Nanobodies through albumin binding: taking advantage of modular Nanobody technology. Mol Cancer Ther 2008;7:2288–97.
Kolkman JA, Law DA. Nanobodies – from llamas to therapeutic proteins. Drug Discov Today: Technol 2010. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2010.03.002.
Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, et al. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993;363:446–8.
Roovers RC, Laeremans T, Huang L, De Taeye S, Verkleij AJ, Revets H, et al. Efficient inhibition of EGFR signaling and of tumour growth by antagonistic anti-EFGR Nanobodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2007;56:303–17.
Els Conrath K, Lauwereys M, Wyns L, Muyldermans S. Camel single-domain antibodies as modular building units in bispecific and bivalent antibody constructs. J Biol Chem 2001;276:7346–50.
Velikyan I, Beyer GJ, Långström B. Microwave-supported preparation of (68)Ga bioconjugates with high specific radioactivity. Bioconjug Chem 2004;15:554–60.
Hoffend J, Mier W, Schuhmacher J, Schmidt K, Mitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Strauss LG, et al. Gallium-68-DOTA-albumin as a PET blood-pool marker: experimental evaluation in vivo. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:287–92.
Blom E, Långström B, Velikyan I. 68Ga-labeling of biotin analogues and their characterization. Bioconjug Chem 2009;20:1146–51.
Ferreira CL, Lamsa E, Woods M, Duan Y, Fernando P, Bensimon C, et al. Evaluation of bifunctional chelates for the development of gallium-based radiopharmaceuticals. Bioconjug Chem 2010;21:531–6.
Eder M, Wangler B, Knackmuss S, LeGall F, Little M, Haberkorn U, et al. Tetrafluorophenolate of HBED-CC: a versatile conjugation agent for 68Ga-labeled small recombinant antibodies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:1878–86.
Eder M, Knackmuss S, Le Gall F, Reusch U, Rybin V, Little M, et al. (68)Ga-labelled recombinant antibody variants for immuno-PET imaging of solid tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:1397–407.
Perk LR, Vosjan MJ, Visser GW, Budde M, Jurek P, Kiefer GE, et al. p-Isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine: a new bifunctional chelate for facile radiolabeling of monoclonal antibodies with zirconium-89 for immuno-PET imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;37:250–9.
Vosjan MJ, Perk LR, Visser GW, Budde M, Jurek P, Kiefer GE, et al. Conjugation and radiolabeling of monoclonal antibodies with zirconium-89 for PET imaging using the bifunctional chelate p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine. Nat Protoc 2010;5:739–43.
Furukawa T, Fujibayashi Y, Fukunaga M, Saga T, Endo K, Yokoyama A. An approach for immunoradiometric assay with metallic radionuclides: gallium-67-deferoxamine-dialdehyde starch-IgG. J Nucl Med 1991;32:825–9.
Smith-Jones PM, Stolz B, Bruns C, Albert R, Reist HW, Fridrich R, et al. Gallium-67/gallium-68-[DFO]-octreotide–a potential radiopharmaceutical for PET imaging of somatostatin receptor-positive tumors: synthesis and radiolabeling in vitro and preliminary in vivo studies. J Nucl Med 1994;35:317–25.
Govindan SV, Michel RB, Griffiths GL, Goldenberg DM, Mattes MJ. Deferoxamine as a chelator for 67Ga in the preparation of antibody conjugates. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:513–9.
Fani M, André JP, Maecke HR. 68Ga-PET: a powerful generator-based alternative to cyclotron-based PET radiopharmaceuticals. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2008;3:67–77.
Schrijvers AH, Quak JJ, Uyterlinde AM, van Walsum M, Meijer CJ, Snow GB, et al. MAb U36, a novel monoclonal antibody successful in immunotargeting of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Res 1993;53:4383–90.
Welters MJ, Fichtinger-Schepman AM, Baan RA, Hermsen MA, van der Vijgh WJ, Cloos J, et al. Relationship between the parameters cellular differentiation, doubling time and platinum accumulation and cisplatin sensitivity in a panel of head and neck cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 1997;71:410–5.
Lindmo T, Boven E, Cuttitta F, Fedorko J, Bunn PA. Determination of the immunoreactive fraction of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies by linear extrapolation to binding at infinite antigen excess. J Immunol Methods 1984;72:77–89.
de Jong HW, van Velden FH, Kloet RW, Buijs FL, Boellaard R, Lammertsma AA. Performance evaluation of the ECAT HRRT: an LSO-LYSO double layer high resolution, high sensitivity scanner. Phys Med Biol 2007;52:1505–26.
Loening AM, Gambhir SS. AMIDE: a free software tool for multimodality medical image analysis. Mol Imaging 2003;2:131–7.
van Dongen GA, Vosjan MJ. Immuno-positron emission tomography: shedding light on clinical antibody therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2010;25:375–85.
Gebhardt P, Opfermann T, Saluz HP. Computer controlled 68Ga milking and concentration system. Appl Radiat Isot 2010;68:1057–9.
Baum RP, Prasad V, Muller D, Schuchardt C, Orlova A, Wennborg A, et al. Molecular imaging of HER2-expressing malignant tumors in breast cancer patients using synthetic 111In- or 68Ga-labeled affibody molecules. J Nucl Med 2010;51:892–7.
Tolmachev V, Stone-Elander S. Radiolabelled proteins for positron emission tomography: pros and cons of labelling methods. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1800:487–510.
Tolmachev V, Velikyan I, Sandström M, Orlova A. A HER2-binding Affibody molecule labelled with (68)Ga for PET imaging: direct in vivo comparison with the (111)In-labelled analogue. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:1356–67.
Velikyan I, Sundberg AL, Lindhe O, Höglund AU, Eriksson O, Werner E, et al. Preparation and evaluation of (68)Ga-DOTA-hEGF for visualization of EGFR expression in malignant tumors. J Nucl Med 2005;46(11):1881–8.
Ren G, Zhang R, Liu Z, Webster JM, Miao Z, Gambhir SS, et al. A 2-helix small protein labeled with 68Ga for PET imaging of HER2 expression. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1492–9.
Visser GW, Gerretsen M, Herscheid JD, Snow GB, van Dongen G. Labeling of monoclonal antibodies with rhenium-186 using the MAG3 chelate for radioimmunotherapy of cancer: a technical protocol. J Nucl Med 1993;34:1953–63.
Riss PJ, Kroll C, Nagel V, Rösch F. NODAPA-OH and NODAPA-(NCS)n: synthesis, 68Ga-radiolabelling and in vitro characterisation of novel versatile bifunctional chelators for molecular imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2008;18:5364–7.
Caraco C, Aloj L, Eckelman WC. The gallium-deferoxamine complex: stability with different deferoxamine concentrations and incubation conditions. Appl Radiat Isot 1998;49:1477–9.
Weissleder R. Molecular imaging in cancer. Science 2006;312:1168–71.
Huang L, Gainkam LO, Caveliers V, Vanhove C, Keyaerts M, De Baetseliers P, et al. SPECT imaging with (99m)Tc-labeled EGFR-specific Nanobody for in vivo monitoring of EGFR expression. Mol Imaging Biol 2008;10:167–75.
Gainkam LO, Huang L, Caveliers V, Keyaerts M, Hernot S, Vaneycken I, et al. Comparison of the biodistribution and tumor targeting of two 99mTc-labeled anti-EGFR Nanobodies in mice, using pinhole SPECT/micro-CT. J Nucl Med 2008;49:788–95.
Verel I, Visser GW, van Dongen GA. The promise of immuno-PET in radioimmunotherapy. J Nucl Med 2005;46 Suppl 1:164S–71.
Börjesson PK, Jauw YW, de Bree R, Roos JC, Castelijns JA, Leemans CR, et al. Radiation dosimetry of 89Zr-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody U36 as used for immuno-PET in head and neck cancer patients. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1828–36.
Perk LR, Visser GW, Vosjan MJ, Stigter-van Walsum M, Tijink BM, Leemans CR, et al. (89)Zr as a PET surrogate radioisotope for scouting biodistribution of the therapeutic radiometals (90)Y and (177)Lu in tumor-bearing nude mice after coupling to the internalizing antibody cetuximab. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1898–906.
Tolmachev V, Rosik D, Wållberg H, Sjöberg A, Sandström M, Hansson M, et al. Imaging of EGFR expression in murine xenografts using site-specifically labelled anti-EGFR 111In-DOTA-Z EGFR:2377 Affibody molecule: aspect of the injected tracer amount. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:613–22.
Divgi CR, Welt S, Kris M, Real FX, Yeh SD, Gralla R, et al. Phase I and imaging trial of indium 111-labeled anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody 225 in patients with squamous cell lung carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 1991;83:97–104.
Acknowledgements
This project was financially supported by the Dutch Technology Foundation (STW, grant 10074) and partly performed within the framework of CTMM, the Center for Translational Molecular Medicine (www.ctmm.nl), project AIRFORCE number 030-103. The authors thank Leo van Rooij and Peter Schollema of the radionuclide center for their assistance with the 68Ga/68Ge generator and Marc Huisman for PET analysis.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Vosjan, M.J.W.D., Perk, L.R., Roovers, R.C. et al. Facile labelling of an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor Nanobody with 68Ga via a novel bifunctional desferal chelate for immuno-PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 753–763 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1700-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1700-1