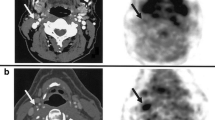
Abstract
Functional characterization of atherosclerosis is a promising application of molecular imaging. Radionuclide-based techniques for molecular imaging in the large arteries (e.g. aorta and carotids), along with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have been studied both experimentally and in clinical studies. Technical factors including cardiac and respiratory motion, low spatial resolution and partial volume effects mean that noninvasive molecular imaging of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries is not ready for prime time. Positron emission tomography imaging with fluorodeoxyglucose can measure vascular inflammation in the large arteries with high reproducibility, and signal change in response to anti-inflammatory therapy has been described. MRI has proven of value for quantifying carotid artery inflammation when iron oxide nanoparticles are used as a contrast agent. Macrophage accumulation of the iron particles allows regression of inflammation to be measured with drug therapy. Similarly, contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging is also being evaluated for functional characterization of atherosclerotic plaques. For all of these techniques, however, large-scale clinical trials are mandatory to define the prognostic importance of the imaging signals in terms of risk of future vascular events.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaziano JM. Global burden of cardiovascular disease, in Braunwald’s heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine. 8th ed. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia; 2008.
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2009;119:480–6.
Ambrose JA, Fuster V. The risk of coronary occlusion is not proportional to the prior severity of coronary stenoses. Heart 1998;79:3–4.
Sanz J, Fayad ZA. Imaging of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nature 2008;451:953–7.
Langer HF, Haubner R, Pichler BJ, Gawaz M. Radionuclide imaging: a molecular key to the atherosclerotic plaque. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:1–12.
Hartung D, Petrov A, Haider N, Fujimoto S, Blankenberg F, Fujimoto A, et al. Radiolabeled monocyte chemotactic protein 1 for the detection of inflammation in experimental atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1816–21.
Ishino S, Mukai T, Kuge Y, Kume N, Ogawa M, Takai N, et al. Targeting of lectinlike oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 (LOX-1) with 99mTc-labeled anti-LOX-1 antibody: potential agent for imaging of vulnerable plaque. J Nucl Med 2008;49:1677–85.
Fujimoto S, Hartung D, Ohshima S, Edwards DS, Zhou J, Yalamanchili P, et al. Molecular imaging of matrix metalloproteinase in atherosclerotic lesions: resolution with dietary modification and statin therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:1847–57.
Isobe S, Tsimikas S, Zhou J, Fujimoto S, Sarai M, Branks MJ, et al. Noninvasive imaging of atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E-deficient and low-density-lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice with annexin A5. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1497–505.
Gawaz M, Konrad I, Hauser AI, Sauer S, Li Z, Wester HJ, et al. Non-invasive imaging of glycoprotein VI binding to injured arterial lesions. Thromb Haemost 2005;93:910–3.
Davies JR, Rudd JH, Weissberg PL, Narula J. Radionuclide imaging for the detection of inflammation in vulnerable plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:C57–68.
Tawakol A, Migrino RQ, Bashian GG, Bedri S, Vermylen D, Cury RC, et al. In vivo 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging provides a noninvasive measure of carotid plaque inflammation in patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:1818–24.
Rudd JH, Warburton EA, Fryer TD, Jones HA, Clark JC, Antoun N, et al. Imaging atherosclerotic plaque inflammation with [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Circulation 2002;105:2708–11.
Tahara N, Kai H, Nakaura H, Mizoguchi M, Ishibashi M, Kaida H, et al. The prevalence of inflammation in carotid atherosclerosis: analysis with fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography. Eur Heart J 2007;28:2243–8.
Davies JR, Rudd JH, Fryer TD, Graves MJ, Clark JC, Kirkpatrick PJ, et al. Identification of culprit lesions after transient ischemic attack by combined 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 2005;36:2642–7.
Rudd JH, Myers KS, Bansilal S, Machac J, Woodward M, Fuster V, et al. Relationships among regional arterial inflammation, calcification, risk factors, and biomarkers: a prospective fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography imaging study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2009;2:107–15.
Tahara N, Kai H, Yamagishi S, Mizoguchi M, Nakaura H, Ishibashi M, et al. Vascular inflammation evaluated by [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is associated with the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:1533–9.
Paulmier B, Duet M, Khayat R, Pierquet-Ghazzar N, Laissy JP, Maunoury C, et al. Arterial wall uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose on PET imaging in stable cancer disease patients indicates higher risk for cardiovascular events. J Nucl Cardiol 2008;15:209–17.
Rominger A, Saam T, Wolpers S, Cyran CC, Schmidt M, Foerster S, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT identifies patients at risk for future vascular events in an otherwise asymptomatic cohort with neoplastic disease. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1611–20.
Tahara N, Kai H, Ishibashi M, Nakaura H, Kaida H, Baba K, et al. Simvastatin attenuates plaque inflammation: evaluation by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:1825–31.
Rudd JH, Myers KS, Bansilal S, Machac J, Pinto CA, Tong C, et al. Atherosclerosis inflammation imaging with 18F-FDG PET: carotid, iliac, and femoral uptake reproducibility, quantification methods, and recommendations. J Nucl Med 2008;49:871–8.
Saam T, Rominger A, Wolpers S, Nikolaou K, Rist C, Greif M, et al. Association of inflammation of the left anterior descending coronary artery with cardiovascular risk factors, plaque burden and pericardial fat volume: a PET/CT study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:1203–12.
Wykrzykowska J, Lehman S, Williams G, Parker JA, Palmer MR, Varkey S, et al. Imaging of inflamed and vulnerable plaque in coronary arteries with 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with suppression of myocardial uptake using a low-carbohydrate, high-fat preparation. J Nucl Med 2009;50:563–8.
Teräs M, Kokki T, Durand-Schaefer N, Noponen T, Pietilä M, Kiss J, et al. Dual-gated cardiac PET-clinical feasibility study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:505–16.
Rogers IS, Nasir K, Figueroa AL, Cury RC, Hoffmann U, Vermylen DA, et al. Feasibility of FDG imaging of the coronary arteries: comparison between acute coronary syndrome and stable angina. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2010;3:388–97.
Kato K, Nishio A, Kato N, Usami H, Fujimaki T, Murohara T. Uptake of 18F-FDG in acute aortic dissection: a determinant of unfavorable outcome. J Nucl Med 2010;51:674–81.
Wilensky RL, Song HK, Ferrari VA. Role of magnetic resonance and intravascular magnetic resonance in the detection of vulnerable plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:C48–56.
Kawahara I, Morikawa M, Honda M, Kitagawa N, Tsutsumi K, Nagata I, et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging using gadolinium-based contrast agent for atherosclerotic carotid plaque. Surg Neurol 2007;68:60–5.
Winter PM, Neubauer AM, Caruthers SD, Harris TD, Robertson JD, Williams TA, et al. Endothelial alpha(v)beta3 integrin-targeted fumagillin nanoparticles inhibit angiogenesis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26:2103–9.
Winter PM, Caruthers SD, Zhang H, Williams TA, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. Antiangiogenic synergism of integrin-targeted fumagillin nanoparticles and atorvastatin in atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2008;1:624–34.
Hyafil F, Laissy JP, Mazighi M, Tchétché D, Louedec L, Adle-Biassette H, et al. Ferumoxtran-10-enhanced MRI of the hypercholesterolemic rabbit aorta: relationship between signal loss and macrophage infiltration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26:176–81.
Trivedi RA, U-King-Im JM, Graves MJ, Cross JJ, Horsley J, Goddard MJ, et al. In vivo detection of macrophages in human carotid atheroma: temporal dependence of ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide-enhanced MRI. Stroke 2004;35:1631–5.
Howarth SP, Tang TY, Trivedi R, Weerakkody R, U-King-Im J, Gaunt ME, et al. Utility of USPIO-enhanced MR imaging to identify inflammation and the fibrous cap: a comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals. Eur J Radiol 2009;70:555–60.
Sosnovik DE. Molecular imaging in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: current perspective and future potential. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2008;19:59–68.
Villanueva FS, Wagner WR. Ultrasound molecular imaging of cardiovascular disease. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2008;5:S26–32.
Coli S, Magnoni M, Sangiorgi G, Marrocco-Trischitta MM, Melisurgo G, Mauriello A, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of intraplaque neovascularization in carotid arteries: correlation with histology and plaque echogenicity. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:223–30.
Weissberg PL. Noninvasive imaging of atherosclerosis: the biology behind the pictures. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1794–5.
Ben-Haim S, Kupzov E, Tamir A, Frenkel A, Israel O. Changing patterns of abnormal vascular wall F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on follow-up PET/CT studies. J Nucl Cardiol 2006;13:791–800.
Menezes LJ, Kayani I, Ben-Haim S, Hutton B, Ell PJ, Groves AM. What is the natural history of 18F-FDG uptake in arterial atheroma on PET/CT? Implications for imaging the vulnerable plaque. Atherosclerosis 2010;211:136–40.
Acknowledgement
Work described in this manuscript was part supported by Cambridge NIHR Biomedical Research Funding.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrone-Filardi, P., Dellegrottaglie, S., Rudd, J.H.F. et al. Molecular imaging of atherosclerosis in translational medicine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 969–975 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1697-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1697-5