Abstract
Purpose
Translocator protein (TSPO) is a promising biomarker for neuroinflammation. We developed two new PET ligands, 18F-PBR06 and 11C-PBR28, to image TSPOs. Although our prior studies suggest that either of the two ligands could be used to quantify TSPOs in human brain, the studies were done in different sets of subjects. In this study, we directly compared 18F-PBR06 and 11C-PBR28 in eight human subjects to determine (1) whether either ligand provides more precise measurements of TSPOs and (2) whether the higher in vitro affinity of PBR06 compared to PBR28 led to higher in vivo binding of 18F-PBR06 compared to 11C-PBR28.
Methods
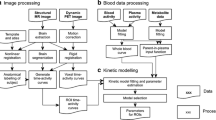
In vivo binding was calculated as total distribution volume (V T), using an unconstrained two-tissue compartment model. V T was corrected for plasma free fraction (f P) to measure ligand binding based on free ligand concentration in brain.
Results
Both ligands measured V T with similar precision, as evidenced by similarly good identifiability. However, V T for both radioligands increased with increasing lengths of data acquisition, consistent with the accumulation of radiometabolites in brain. Despite its higher lipophilicity and higher in vitro affinity, V T/f P of 18F-PBR06 was similar to that of 11C-PBR28.
Conclusion
Both 18F-PBR06 and 11C-PBR28 are similar in terms of precision, sensitivity to accumulation of radiometabolites, and magnitude of in vivo binding. Thus, selection between the two radioligands will be primarily determined by the logistical impact of the different half-lives of the two radionuclides (110 vs 20 min).





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Translocator protein was formerly named peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) because it was originally found as a binding site for diazepam in peripheral organs. To reflect its distribution in both central nervous system and peripheral organs and also to reflect its functions, PBR has been renamed as translocator protein [1].
References
Papadopoulos V, Baraldi M, Guilarte TR, Knudsen TB, Lacapère JJ, Lindemann P, et al. Translocator protein (18 kDa): new nomenclature for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor based on its structure and molecular function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2006;27:402–9.
Venneti S, Lopresti BJ, Wiley CA. The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (translocator protein 18 kDa) in microglia: from pathology to imaging. Prog Neurobiol 2006;80:308–22.
Chauveau F, Boutin H, Van Camp N, Dollé F, Tavitian B. Nuclear imaging of neuroinflammation: a comprehensive review of [11C]PK11195 challengers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:2304–19.
Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Siméon FG, Imaizumi M, Gourley JP, Shetty HU, et al. Single-step high-yield radiosynthesis and evaluation of a sensitive 18F-labeled ligand for imaging brain peripheral benzodiazepine receptors with PET. J Med Chem 2009;52:688–99.
Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Imaizumi M, Gourley JP, Shetty HU, Hong J, et al. Synthesis and evaluation in monkey of two sensitive 11C-labeled aryloxyanilide ligands for imaging brain peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in vivo. J Med Chem 2008;51:17–30.
Imaizumi M, Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Gourley JP, Hong J, Musachio JL, et al. Kinetic evaluation in nonhuman primates of two new PET ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in brain. Synapse 2007;61:595–605.
Imaizumi M, Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Gourley JP, Hong J, Fujimura Y, et al. Brain and whole-body imaging in nonhuman primates of [11C]PBR28, a promising PET radioligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Neuroimage 2008;39:1289–98.
Fujimura Y, Zoghbi SS, Simèon FG, Taku A, Pike VW, Innis RB, et al. Quantification of translocator protein (18 kDa) in the human brain with PET and a novel radioligand, (18)F-PBR06. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1047–53.
Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Zoghbi SS, Fujimura Y, Farris AG, Suhara T, et al. Kinetic analysis in healthy humans of a novel positron emission tomography radioligand to image the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, a potential biomarker for inflammation. Neuroimage 2008;40:43–52.
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN, et al. Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007;27:1533–39.
Lassen NA, Bartenstein PA, Lammertsma AA, Prevett MC, Turton DR, Luthra SK, et al. Benzodiazepine receptor quantification in vivo in humans using [11C]flumazenil and PET: application of the steady-state principle. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1995;15:152–65.
Owen DR, Howell OW, Tang SP, Wells LA, Bennacef I, Bergstrom M, et al. Two binding sites for [3H]PBR28 in human brain: implications for TSPO PET imaging of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2010;30:1608–18.
Brown AK, Fujita M, Fujimura Y, Liow J-S, Stabin M, Ryu YH, et al. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution in monkey and man of 11C-PBR28, a PET radioligand to image inflammation. J Nucl Med 2007;48:2072–79.
Fujimura Y, Kimura Y, Siméon FG, Dickstein LP, Pike VW, Innis RB, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry in humans of a new PET ligand, (18)F-PBR06, to image translocator protein (18 kDa). J Nucl Med 2010;51:145–9.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Intramural Program of NIMH (project #Z01-MH-002795-07 and #Z01-MH-002793-07). We thank Kacey Anderson, M. Desiree Ferraris Araneta, Robert L. Gladding, Kimberly Jenko, William C. Kreisl, Barbara Scepura, Cheryl Wallisch, and the staff of the PET Department for successful completion of the studies, PMOD Technologies (Zurich, Switzerland) for providing its image analysis and modeling software, and Jussi Hirvonen for assisting statistical analyses.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dickstein, L.P., Zoghbi, S.S., Fujimura, Y. et al. Comparison of 18F- and 11C-labeled aryloxyanilide analogs to measure translocator protein in human brain using positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 352–357 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1622-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1622-y