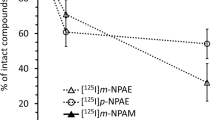
Abstract
Position emission tomography imaging of angiogenesis may provide non-invasive insights into the corresponding molecular processes and may be applied for individualized treatment planning of antiangiogenic therapies. At the moment, most strategies are focusing on the development of radiolabelled proteins and antibody formats targeting VEGF and its receptor or the ED-B domain of a fibronectin isoform as well as radiolabelled matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors or αvβ3 integrin antagonists. Great efforts are being made to develop suitable tracers for different target structures. All of the major strategies focusing on the development of radiolabelled compounds for use with positron emission tomography are summarized in this review. However, because the most intensive work is concentrated on the development of radiolabelled RGD peptides for imaging αvβ3 expression, which has successfully made its way from bench to bedside, these developments are especially emphasized.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creamer D, Sullivan D, Bicknell R, Barker J. Angiogenesis in psoriasis. Angiogenesis 2002;5:231–6.
Bishop GG, McPherson JA, Sanders JM, Hesselbacher SE, Feldman MJ, McNamara CA, et al. Selective alpha(v)beta(3)-receptor blockade reduces macrophage infiltration and restenosis after balloon angioplasty in the atherosclerotic rabbit. Circulation 2001;103:1906–11.
Storgard CM, Stupack DG, Jonczyk A, Goodman SL, Fox RI, Cheresh DA. Decreased angiogenesis and arthritic disease in rabbits treated with an alphavbeta3 antagonist. J Clin Invest 1999;103:47–54. See comment J Clin Invest 1999;103:3–4.
Chavakis E, Riecke B, Lin J, Linn T, Bretzel RG, Preissner KT, et al. Kinetics of integrin expression in the mouse model of proliferative retinopathy and success of secondary intervention with cyclic RGD peptides. Diabetologia 2002;45:262–7.
Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 2002;29(6 Suppl 16):15–8.
Loges S, Roncal C, Carmeliet P. Development of targeted angiogenic medicine. J Thromb Haemost 2009;7:21–33.
Ellis LM, Liu W, Fan F, Jung YD, Reinmuth N, Stoeltzing O, et al. Synopsis of angiogenesis inhibitors in oncology. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002;16:14–22.
Kuwano M, Fukushi J, Okamoto M, Nishie A, Goto H, Ishibashi T, et al. Angiogenesis factors. Intern Med 2001;40:565–72.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000;407:249–57.
Hagedorn M, Bikfalvi A. Target molecules for anti-angiogenic therapy: from basic research to clinical trials. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2000;34:89–110.
Vihinen P, Kähäri VM. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer 2002;99:157–66.
Rundhaug JE. Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 2005;9:267–85.
Hynes RO, Bader BL, Hodivala-Dilke K. Integrins in vascular development. Braz J Med Biol Res 1999;32:501–10.
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. Role of alpha v integrins during angiogenesis. Cancer J 2000;6 Suppl 3:S245–9.
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 1994;79:1157–64.
Brooks PC, Strömblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 1995;96:1815–22. See comment J Clin Invest 1995;96:1696–7.
Hammes HP, Brownlee M, Jonczyk A, Sutter A, Preissner KT. Subcutaneous injection of a cyclic peptide antagonist of vitronectin receptor-type integrins inhibits retinal neovascularization. Nat Med 1996;2:529–33.
Hynes RO. A reevaluation of integrins as regulators of angiogenesis. Nat Med 2002;8:918–21.
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J. Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 2000;407:242–8.
Rosen L. Antiangiogenic strategies and agents in clinical trials. Oncologist 2000;5(Suppl 1):20–7.
Gasparini G, Longo R, Toi M, Ferrara N. Angiogenic inhibitors: a new therapeutic strategy in oncology. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2005;2:562–77.
Ferrara N. VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:795–803.
Roodhart JM, Langenberg MH, Witteveen E, Voest EE. The molecular basis of class side effects due to treatment with inhibitors of the VEGF/VEGFR pathway. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2008;3:132–43.
Underiner TL, Mallamo JP, Singh J. Syntheses of C12,N13 heterocyclic bridged fused indenopyrrolocarbazoles. J Org Chem 2002;67:3235–41.
Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 2004;25:581–611.
Hsu AR, Chen X. Advances in anatomic, functional, and molecular imaging of angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 2008;49:511–4.
Nagengast WB, de Vries EG, Hospers GA, Mulder NH, de Jong JR, Hollema H, et al. In vivo VEGF imaging with radiolabeled bevacizumab in a human ovarian tumor xenograft. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1313–9.
Park JE, Keller GA, Ferrara N. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms: differential deposition into the subepithelial extracellular matrix and bioactivity of extracellular matrix-bound VEGF. Mol Biol Cell 1993;4:1317–26.
Yuan F, Chen Y, Dellian M, Safabakhsh N, Ferrara N, Jain RK. Time-dependent vascular regression and permeability changes in established human tumor xenografts induced by an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996;93:14765–70.
Wang Y, Fei D, Vanderlaan M, Song A. Biological activity of bevacizumab, a humanized anti-VEGF antibody in vitro. Angiogenesis 2004;7:335–45.
Collingridge DR, Carroll VA, Glaser M, Aboagye EO, Osman S, Hutchinson OC, et al. The development of [(124)I]iodinated-VG76e: a novel tracer for imaging vascular endothelial growth factor in vivo using positron emission tomography. Cancer Res 2002;62:5912–9.
Jayson GC, Zweit J, Jackson A, Mulatero C, Julyan P, Ranson M, et al. Molecular imaging and biological evaluation of HuMV833 anti-VEGF antibody: implications for trial design of antiangiogenic antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002;94:1484–93.
Scheer MG, Stollman TH, Boerman OC, Verrijp K, Sweep FC, Leenders WP, et al. Imaging liver metastases of colorectal cancer patients with radiolabelled bevacizumab: lack of correlation with VEGF-A expression. Eur J Cancer 2008;44:1835–40.
Niu G, Chen X. PET imaging of angiogenesis. PET Clin 2009;4:17–38.
Lu E, Wagner WR, Schellenberger U, Abraham JA, Klibanov AL, Woulfe SR, et al. Targeted in vivo labeling of receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor: approach to identification of ischemic tissue. Circulation 2003;108:97–103.
Blankenberg FG, Mandl S, Cao YA, O’Connell-Rodwell C, Contag C, Mari C, et al. Tumor imaging using a standardized radiolabeled adapter protein docked to vascular endothelial growth factor. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1373–80.
Li S, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Kienast O, Preitfellner J, Hamilton G, Kurtaran A, et al. Imaging gastrointestinal tumours using vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165) receptor scintigraphy. Ann Oncol 2003;14:1274–7.
Li S, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Kienast O, Preitfellner J, Havlik E, Schima W, et al. Iodine-123-vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (123I-VEGF165). Biodistribution, safety and radiation dosimetry in patients with pancreatic carcinoma. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;48:198–206.
Li S, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Koller E, Koller F, Kaserer K, Kreil A, et al. Characterization of (123)I-vascular endothelial growth factor-binding sites expressed on human tumour cells: possible implication for tumour scintigraphy. Int J Cancer 2001;91:789–96.
Cai W, Chen K, Mohamedali KA, Cao Q, Gambhir SS, Rosenblum MG, et al. PET of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. J Nucl Med 2006;47:2048–56.
Fuh G, Garcia KC, de Vos AM. The interaction of neuropilin-1 with vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor flt-1. J Biol Chem 2000;275:26690–5.
Blankenberg FG, Backer MV, Levashova Z, Patel V, Backer JM. In vivo tumor angiogenesis imaging with site-specific labeled (99m)Tc-HYNIC-VEGF. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:841–8.
Backer MV, Levashova Z, Patel V, Jehning BT, Claffey K, Blankenberg FG, et al. Molecular imaging of VEGF receptors in angiogenic vasculature with single-chain VEGF-based probes. Nat Med 2007;13:504–9.
Keyt BA, Nguyen HV, Berleau LT, Duarte CM, Park J, Chen H, et al. Identification of vascular endothelial growth factor determinants for binding KDR and FLT-1 receptors. Generation of receptor-selective VEGF variants by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 1996;271:5638–46.
Wang H, Cai W, Chen K, Li ZB, Kashefi A, He L, et al. A new PET tracer specific for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:2001–10.
Levashova Z, Backer M, Backer JM, Blankenberg FG. Direct site-specific labeling of the Cys-tag moiety in scVEGF with technetium 99m. Bioconjug Chem 2008;19:1049–54.
Cai W, Guzman R, Hsu AR, Wang H, Chen K, Sun G, et al. Positron emission tomography imaging of poststroke angiogenesis. Stroke 2009;40:270–7.
Rodriguez-Porcel M, Cai W, Gheysens O, Willmann JK, Chen K, Wang H, et al. Imaging of VEGF receptor in a rat myocardial infarction model using PET. J Nucl Med 2008;49:667–73.
Blankenberg FG, Levashova Z, Sarkar SK, Pizzonia J, Backer MV, Backer JM. Noninvasive assessment of tumor VEGF receptors in response to treatment with pazopanib: a molecular imaging study. Transl Oncol 2010;3:56–64.
Hynes R. Molecular biology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1985;1:67–90.
Castellani P, Dorcaratto A, Pau A, Nicola M, Siri A, Gasparetto B, et al. The angiogenesis marker ED-B+ fibronectin isoform in intracranial meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2000;142:277–82.
Neri D, Carnemolla B, Nissim A, Leprini A, Querzè G, Balza E, et al. Targeting by affinity-matured recombinant antibody fragments of an angiogenesis associated fibronectin isoform. Nat Biotechnol 1997;15:1271–5.
Tarli L, Balza E, Viti F, Borsi L, Castellani P, Berndorff D, et al. A high-affinity human antibody that targets tumoral blood vessels. Blood 1999;94:192–8.
Santimaria M, Moscatelli G, Viale GL, Giovannoni L, Neri G, Viti F, et al. Immunoscintigraphic detection of the ED-B domain of fibronectin, a marker of angiogenesis, in patients with cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2003;9:571–9.
Borsi L, Balza E, Bestagno M, Castellani P, Carnemolla B, Biro A, et al. Selective targeting of tumoral vasculature: comparison of different formats of an antibody (L19) to the ED-B domain of fibronectin. Int J Cancer 2002;102:75–85.
Berndorff D, Borkowski S, Sieger S, Rother A, Friebe M, Viti F, et al. Radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors by targeting extra domain B fibronectin: identification of the best-suited radioimmunoconjugate. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:7053s–63.
Rossin R, Berndorff D, Friebe M, Dinkelborg LM, Welch MJ. Small-animal PET of tumor angiogenesis using a (76)Br-labeled human recombinant antibody fragment to the ED-B domain of fibronectin. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1172–9.
Tijink BM, Perk LR, Budde M, Stigter-van Walsum M, Visser GW, Kloet RW, et al. (124)I-L19-SIP for immuno-PET imaging of tumour vasculature and guidance of (131)I-L19-SIP radioimmunotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;36:1235–44.
Curran S, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinases: molecular aspects of their roles in tumour invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer 2000;36:1621–30.
Hidalgo M, Eckhardt SG. Development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001;93:178–93.
Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol 1997;74:111–22.
Foda HD, Zucker S. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Drug Discov Today 2001;6:478–82.
Iwata H, Kobayashi S, Iwase H, Masaoka A, Fujimoto N, Okada Y. Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 1996;87:602–11.
Nguyen M, Arkell J, Jackson CJ. Human endothelial gelatinases and angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2001;33:960–70.
Matter A. Tumor angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov Today 2001;6:1005–24.
Koivunen E, Arap W, Valtanen H, Rainisalo A, Medina OP, Heikkilä P, et al. Tumor targeting with a selective gelatinase inhibitor. Nat Biotechnol 1999;17:768–74.
Kuhnast B, Bodenstein C, Haubner R, Wester HJ, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R, Schwaiger M, et al. Targeting of gelatinase activity with a radiolabeled cyclic HWGF peptide. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:337–44.
Levy DE, Lapierre F, Liang W, Ye W, Lange CW, Li X, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: a structure-activity study. J Med Chem 1998;41:199–223.
Kiyama R, Tamura Y, Watanabe F, Tsuzuki H, Ohtani M, Yodo M. Homology modeling of gelatinase catalytic domains and docking simulations of novel sulfonamide inhibitors. J Med Chem 1999;42:1723–38.
Pelmenschikov V, Siegbahn PE. Catalytic mechanism of matrix metalloproteinases: two-layered ONIOM study. Inorg Chem 2002;41:5659–66.
Aranapakam V, Davis JM, Grosu GT, Baker J, Ellingboe J, Zask A, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of N-substituted 4-arylsulfonylpiperidine-4-hydroxamic acids as novel, orally active matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis. J Med Chem 2003;46:2376–96.
Furumoto S, Iwata R, Ido T. Design and synthesis of fluorine-18 labeled matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for cancer imaging. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2002;45:975–86.
Kuhnast B, Bodenstein C, Wester HJ, Weber WA. Carbon-11 labelling of an N-sulfonylamino acid derivative: a potential tracer for MMP-2 and MMP-9 imaging. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2003;46:1093–103.
Fei X, Zheng QH, Hutchins GD, Liu X, Stone KL, Carlson KA, et al. Synthesis of MMP inhibitor radiotracers [11C]methyl-CGS 27023A and its analogs, new potential PET breast cancer imaging agents. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2002;45:449–70.
Fei X, Zheng Q-H, Liu X, Wang J-Q, Stone KL, Miller KD, et al. Synthesis of MMP inhibitor radiotracer [11C]CGS 25966, a new potential PET tumor imaging agent. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2003;46:343–51.
Zheng QH, Fei X, DeGrado TR, Wang JQ, Lee Stone K, Martinez TD, et al. Synthesis, biodistribution and micro-PET imaging of a potential cancer biomarker carbon-11 labeled MMP inhibitor (2R)-2-[[4-(6-fluorohex-1-ynyl)phenyl]sulfonylamino]-3-methylbutyric acid [(11)C]methyl ester. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:753–60.
Zheng QH, Fei X, Liu X, Wang JQ, Bin Sun H, Mock BH, et al. Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of MMP inhibitor radiotracers [11C]methyl-halo-CGS 27023A analogs, new potential PET breast cancer imaging agents. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:761–70.
Fei X, Zheng QH, Liu X, Wang JQ, Sun HB, Mock BH, et al. Synthesis of radiolabeled biphenylsulfonamide matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as new potential PET cancer imaging agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2003;13:2217–22.
Oltenfreiter R, Staelens L, Lejeune A, Dumont F, Frankenne F, Foidart JM, et al. New radioiodinated carboxylic and hydroxamic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor tracers as potential tumor imaging agents. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:459–68.
Oltenfreiter R, Staelens L, Hillaert U, Heremans A, Noel A, Frankenne F, et al. Synthesis, radiosynthesis, in vitro and preliminary in vivo evaluation of biphenyl carboxylic and hydroxamic matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors as potential tumor imaging agents. Appl Radiat Isot 2005;62:903–13.
Zheng QH, Fei X, Liu X, Wang JQ, Stone KL, Martinez TD, et al. Comparative studies of potential cancer biomarkers carbon-11 labeled MMP inhibitors (S)-2-(4′-[11C]methoxybiphenyl-4-sulfonylamino)-3-methylbutyric acid and N-hydroxy-(R)-2-[[(4′-[11C]methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]benzylamino]-3-methylbutanamide. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:77–85.
Oltenfreiter R, Staelens L, Labied S, Kersemans V, Frankenne F, Noël A, et al. Tryptophane-based biphenylsulfonamide matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as tumor imaging agents. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2005;20:639–47.
Hood JD, Cheresh DA. Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:91–100.
Ruoslahti E. Specialization of tumour vasculature. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:83–90.
Taga T, Suzuki A, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Gilles FH, Stins M, Shimada H, et al. alpha v-Integrin antagonist EMD 121974 induces apoptosis in brain tumor cells growing on vitronectin and tenascin. Int J Cancer 2002;98:690–7.
Dredge K, Dalgleish AG, Marriott JB. Recent developments in antiangiogenic therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2002;2:953–66.
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science 1987;238:491–7.
Aumailley M, Gurrath M, Müller G, Calvete J, Timpl R, Kessler H. Arg-Gly-Asp constrained within cyclic pentapeptides. Strong and selective inhibitors of cell adhesion to vitronectin and laminin fragment P1. FEBS Lett 1991;291:50–4.
Haubner RH, Wester HJ, Weber WA, Schwaiger M. Radiotracer-based strategies to image angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med 2003;47:189–99.
Indrevoll B, Kindberg GM, Solbakken M, Bjurgert E, Johansen JH, Karlsen H, et al. NC-100717: a versatile RGD peptide scaffold for angiogenesis imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006;16:6190–3.
Harris TD, Kalogeropoulos S, Nguyen T, Dwyer G, Edwards DS, Liu S, et al. Structure-activity relationships of 111In- and 99mTc-labeled quinolin-4-one peptidomimetics as ligands for the vitronectin receptor: potential tumor imaging agents. Bioconjug Chem 2006;17:1294–313.
Sulyok GA, Gibson C, Goodman SL, Holzemann G, Wiesner M, Kessler H. Solid-phase synthesis of a nonpeptide RGD mimetic library: new selective alphavbeta3 integrin antagonists. J Med Chem 2001;44:1938–50.
Haubner R, Kuhnast B, Mang C, Weber WA, Kessler H, Wester HJ, et al. [18F]Galacto-RGD: synthesis, radiolabeling, metabolic stability, and radiation dose estimates. Bioconjug Chem 2004;15:61–9.
Poethko T, Schottelius M, Thumshirn G, Herz M, Haubner R, Henriksen G, et al. Chemoselective pre-conjugate radiohalogenation of unprotected mono- and multimeric peptides via oxime formation. Radiochim Acta 2004;92:317–27.
Poethko T, Schottelius M, Thumshirn G, Hersel U, Herz M, Henriksen G, et al. Two-step methodology for high-yield routine radiohalogenation of peptides: (18)F-labeled RGD and octreotide analogs. J Nucl Med 2004;45:892–902.
Schirrmacher E, Wängler B, Cypryk M, Bradtmöller G, Schäfer M, Eisenhut M, et al. Synthesis of p-(di-tert-butyl[18F]fluorosilyl)benzaldehyde ([18F]SiFA-A) with high specific activity by isotopic exchange: a convenient labeling synthon for the 18F-labeling of N-amino-oxy derivatized peptides. Bioconjug Chem 2007;18:2085–9.
Lee YS, Jeong JM, Kim HW, Chang YS, Kim YJ, Hong MK, et al. An improved method of 18F peptide labeling: hydrazone formation with HYNIC-conjugated c(RGDyK). Nucl Med Biol 2006;33:677–83.
Glaser M, Morrison M, Solbakken M, Arukwe J, Karlsen H, Wiggen U, et al. Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of cyclic RGD peptides conjugated with novel [18F]fluorinated aldehyde-containing prosthetic groups. Bioconjug Chem 2008;19:951–7.
Prante O, Einsiedel J, Haubner R, Gmeiner P, Wester HJ, Kuwert T, et al. 3,4,6-Tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoroglucopyranosyl phenylthiosulfonate: a thiol-reactive agent for the chemoselective 18F-glycosylation of peptides. Bioconjug Chem 2007;18:254–62.
Cai W, Zhang X, Wu Y, Chen X. A thiol-reactive 18F-labeling agent, N-[2-(4-18F-fluorobenzamido)ethyl]maleimide, and synthesis of RGD peptide-based tracer for PET imaging of alpha v beta 3 integrin expression. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1172–80.
Glaser M, Solbakken M, Turton DR, Pettitt R, Barnett J, Arukwe J, et al. Methods for 18F-labeling of RGD peptides: comparison of aminooxy [18F]fluorobenzaldehyde condensation with ‘click labeling’ using 2-[18F]fluoroethylazide, and S-alkylation with [18F]fluoropropanethiol. Amino Acids 2009;37:717–24.
Kolb H, Walsh J, Liang Q, Zhao T, Gao D, Secrest J, et al. 18F-RGD-K5: a cyclic triazole-bearing RGD peptide for imaging integrin avb3 expression in vivo. J Nucl Med 2009;50(Suppl 2):329.
Chen X, Park R, Tohme M, Shahinian AH, Bading JR, Conti PS. MicroPET and autoradiographic imaging of breast cancer alpha v-integrin expression using 18F- and 64Cu-labeled RGD peptide. Bioconjug Chem 2004;15:41–9.
Decristoforo C, Hernandez Gonzalez I, Carlsen J, Rupprich M, Huisman M, Virgolini I, et al. (68)Ga- and (111)In-labelled DOTA-RGD peptides for imaging of alphavbeta3 integrin expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:1507–15.
Jeong JM, Hong MK, Chang YS, Lee YS, Kim YJ, Cheon GJ, et al. Preparation of a promising angiogenesis PET imaging agent: 68Ga-labeled c(RGDyK)-isothiocyanatobenzyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid and feasibility studies in mice. J Nucl Med 2008;49:830–6.
Eisenwiener KP, Prata MI, Buschmann I, Zhang HW, Santos AC, Wenger S, et al. NODAGATOC, a new chelator-coupled somatostatin analogue labeled with [67/68Ga] and [111In] for SPECT, PET, and targeted therapeutic applications of somatostatin receptor (hsst2) expressing tumors. Bioconjug Chem 2002;13:530–41.
Knetsch P, Petrik M, Rangger C, Fani M, Helbok A, von Guggenberg E, et al. Ga-68 labelled RGD peptide for monitoring angiogenesis. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2009;52:S413.
Haubner R, Wester HJ, Weber WA, Mang C, Ziegler SI, Goodman SL, et al. Noninvasive imaging of alpha(v)beta3 integrin expression using 18F-labeled RGD-containing glycopeptide and positron emission tomography. Cancer Res 2001;61:1781–5.
Haubner R, Wester HJ, Burkhart F, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R, Weber W, Goodman SL, et al. Glycosylated RGD-containing peptides: tracer for tumor targeting and angiogenesis imaging with improved biokinetics. J Nucl Med 2001;42:326–36.
Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, Vabuliene E, Reim D, Sarbia M, et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated alphavbeta3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med 2005;2:e70.
Hultsch C, Schottelius M, Auernheimer J, Alke A, Wester HJ. 18)F-Fluoroglucosylation of peptides, exemplified on cyclo(RGDfK). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;36:1469–74.
Maschauer S, Einsiedel J, Haubner R, Hocke C, Ocker M, Hübner H, et al. Labeling and glycosylation of peptides using click chemistry: a general approach to (18)F-glycopeptides as effective imaging probes for positron emission tomography. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2010;49:976–9.
Harris JM, Martin NE, Modi M. Pegylation: a novel process for modifying pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 2001;40:539–51.
Harris JM, Chess RB. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003;2:214–21.
Chen X, Park R, Shahinian AH, Bading JR, Conti PS. Pharmacokinetics and tumor retention of 125I-labeled RGD peptide are improved by PEGylation. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:11–9.
Chen X, Park R, Hou Y, Khankaldyyan V, Gonzales-Gomez I, Tohme M, et al. MicroPET imaging of brain tumor angiogenesis with 18F-labeled PEGylated RGD peptide. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:1081–9.
Chen X, Hou Y, Tohme M, Park R, Khankaldyyan V, Gonzales-Gomez I, et al. Pegylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide: 64Cu labeling and PET imaging of brain tumor alphavbeta3-integrin expression. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1776–83.
Liu S, Liu Z, Chen K, Yan Y, Watzlowik P, Wester HJ, et al. (18)F-Labeled Galacto and PEGylated RGD dimers for PET imaging of alpha(v)beta (3) integrin expression. Mol Imaging Biol 2009.
Janssen ML, Oyen WJ, Dijkgraaf I, Massuger LF, Frielink C, Edwards DS, et al. Tumor targeting with radiolabeled alpha(v)beta(3) integrin binding peptides in a nude mouse model. Cancer Res 2002;62:6146–51.
Janssen M, Oyen WJ, Massuger LF, Frielink C, Dijkgraaf I, Edwards DS, et al. Comparison of a monomeric and dimeric radiolabeled RGD-peptide for tumor targeting. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2002;17:641–6.
Thumshirn G, Hersel U, Goodman SL, Kessler H. Multimeric cyclic RGD peptides as potential tools for tumor targeting: solid-phase peptide synthesis and chemoselective oxime ligation. Chemistry 2003;9:2717–25.
Chen X, Tohme M, Park R, Hou Y, Bading JR, Conti PS. Micro-PET imaging of alphavbeta3-integrin expression with 18F-labeled dimeric RGD peptide. Mol Imaging 2004;3:96–104.
Zhang X, Xiong Z, Wu Y, Cai W, Tseng JR, Gambhir SS, et al. Quantitative PET imaging of tumor integrin {alpha}v{beta}3 expression with 18F-FRGD2. J Nucl Med 2006;47:113–21.
Wu Z, Li ZB, Cai W, He L, Chin FT, Li F, et al. (18)F-labeled mini-PEG spacered RGD dimer ((18)F-FPRGD2): synthesis and microPET imaging of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:1823–31.
Chen X, Liu S, Hou Y, Tohme M, Park R, Bading JR, et al. MicroPET imaging of breast cancer alphav-integrin expression with 64Cu-labeled dimeric RGD peptides. Mol Imaging Biol 2004;6:350–9.
Wu Y, Zhang X, Xiong Z, Cheng Z, Fisher DR, Liu S, et al. microPET imaging of glioma integrin {alpha}v{beta}3 expression using (64)Cu-labeled tetrameric RGD peptide. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1707–18.
Li ZB, Cai W, Cao Q, Chen K, Wu Z, He L, et al. (64)Cu-labeled tetrameric and octameric RGD peptides for small-animal PET of tumor alpha(v)beta(3) integrin expression. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1162–71.
Sancey L, Ardisson V, Riou LM, Ahmadi M, Marti-Batlle D, Boturyn D, et al. In vivo imaging of tumour angiogenesis in mice with the alpha(v)beta (3) integrin-targeted tracer (99m)Tc-RAFT-RGD. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:2037–47.
Dijkgraaf I, Rijnders AY, Soede A, Dechesne AC, van Esse GW, Brouwer AJ, et al. Synthesis of DOTA-conjugated multivalent cyclic-RGD peptide dendrimers via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and their biological evaluation: implications for tumor targeting and tumor imaging purposes. Org Biomol Chem 2007;5:935–44.
Wadas TJ, Deng H, Sprague JE, Zheleznyak A, Weilbaecher KN, Anderson CJ. Targeting the alphavbeta3 integrin for small-animal PET/CT of osteolytic bone metastases. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1873–80.
Morrison MS, Ricketts SA, Barnett J, Cuthbertson A, Tessier J, Wedge SR. Use of a novel Arg-Gly-Asp radioligand, 18F-AH111585, to determine changes in tumor vascularity after antitumor therapy. J Nucl Med 2009;50:116–22.
Beer AJ, Haubner R, Wolf I, Goebel M, Luderschmidt S, Niemeyer M, et al. PET-based human dosimetry of 18F-galacto-RGD, a new radiotracer for imaging alpha v beta3 expression. J Nucl Med 2006;47:763–9.
Beer AJ, Haubner R, Sarbia M, Goebel M, Luderschmidt S, Grosu AL, et al. Positron emission tomography using [18F]Galacto-RGD identifies the level of integrin alpha(v)beta3 expression in man. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:3942–9.
Beer AJ, Grosu AL, Carlsen J, Kolk A, Sarbia M, Stangier I, et al. [18F]Galacto-RGD positron emission tomography for imaging of {alpha}v{beta}3 expression on the neovasculature in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:6610–6.
Schnell O, Krebs B, Carlsen J, Miederer I, Goetz C, Goldbrunner RH, et al. Imaging of integrin {alpha}v{beta}3 expression in patients with malignant glioma by [18F] Galacto-RGD positron emission tomography. Neuro Oncol 2009;11:861–70.
Bach-Gansmo T, Bogsrud TV, Skretting A. Integrin scintimammography using a dedicated breast imaging, solid-state gamma-camera and (99m)Tc-labelled NC100692. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2008;28:235–9.
McParland BJ, Miller MP, Spinks TJ, Kenny LM, Osman S, Khela MK, et al. The biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the Arg-Gly-Asp peptide 18F-AH111585 in healthy volunteers. J Nucl Med 2008;49:1664–7.
Kenny LM, Coombes RC, Oulie I, Contractor KB, Miller M, Spinks TJ, et al. Phase I trial of the positron-emitting Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide radioligand 18F-AH111585 in breast cancer patients. J Nucl Med 2008;49:879–86.
Winick J. A proof-of-concept study to assess the ability of [18F]AH-111585 PET imaging to detect tumours and angiogenesis. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007;November 28, 2007 ed: US National Institutes of Health.
Cho HJ, Lee JD, Park JY, Yun M, Kang WJ, Walsh JC, et al. First in human evaluation of a newly developed PET tracer, 18F-RGD-K5 in patients with breast cancer: comparison with 18F-FDG uptake pattern and microvessel density. J Nucl Med 2009;50(Suppl 2):1910.
Doss M, Alpaugh RK, Yu JQ. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of angiogenesis marker [18F]RGD-K5 measured using human PET. J Nucl Med 2009;50(Suppl 2):447.
Zhang J. Efficacy study of [18F]RGD-K5 positron emission tomography (PET) as a tool to monitor response to an anti-angiogenic drug (K5-101). ClinicalTrials.gov 2009;October 1, 2009 ed: US National Institutes of Health.
Fanti S, Farsad M, Mansi L. PET-CT beyond FDG: a quick guide to image interpretation. 1st ed. Berlin: Springer; 2010.
Judenhofer MS, Wehrl HF, Newport DF, Catana C, Siegel SB, Becker M, et al. Simultaneous PET-MRI: a new approach for functional and morphological imaging. Nat Med 2008;14:459–65.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haubner, R., Beer, A.J., Wang, H. et al. Positron emission tomography tracers for imaging angiogenesis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37 (Suppl 1), 86–103 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1503-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1503-4