Abstract
Purpose
A new PET ligand, 3-fluoro-5-(2-(2-18F-(fluoromethyl)-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)benzonitrile (18F-SP203), is a positron emission tomographic radioligand selective for metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors. The purposes of this study were to estimate the radiation-absorbed doses of 18F-SP203 in humans and to determine from the distribution of radioactivity in bone structures with various proportions of bone and red marrow whether 18F-SP203 undergoes defluorination.
Methods
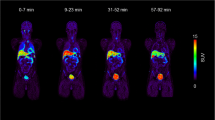
Whole-body images were acquired for 5 h after injecting 18F-SP203 in seven healthy humans. Urine was collected at various time points. Radiation-absorbed doses were estimated by the Medical Internal Radiation Dose scheme.
Results
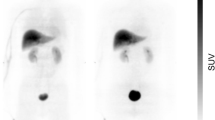
After injecting 18F-SP203, the two organs with highest radiation exposure were urinary bladder wall and gallbladder wall, consistent with both urinary and fecal excretion. In the skeleton, most of the radioactivity was in bone structures that contain red marrow and not in those without red marrow. Although the dose to red marrow (30.9 μSv/MBq) was unusually high, the effective dose (17.8 μSv/MBq) of 18F-SP203 was typical of that of other 18F radiotracers.
Conclusion
18F-SP203 causes an effective dose in humans typical of several other 18F radioligands and undergoes little defluorination.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kenny PJ, Markou A. The ups and downs of addiction: role of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004;25:265–72.
Ametamey SM, Treyer V, Streffer J, Wyss MT, Schmidt M, Blagoev M, et al. Human PET studies of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 with 11C-ABP688. J Nucl Med 2007;48:247–52.
Brown AK, Kimura Y, Zoghbi SS, Siméon FG, Liow JS, Kreisl WC, et al. Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors are quantified in the human brain with a novel radioligand for PET. J Nucl Med 2008;49:2042–8.
Ametamey SM, Kessler LJ, Honer M, Wyss MT, Buck A, Hintermann S, et al. Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of 11C-ABP688 as a probe for imaging the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. J Nucl Med 2006;47:698–705.
Hamill TG, Krause S, Ryan C, Bonnefous C, Govek S, Seiders TJ, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and first successful monkey imaging studies of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5) PET radiotracers. Synapse 2005;56:205–16.
Siméon FG, Brown AK, Zoghbi SS, Patterson VM, Innis RB, Pike VW. Synthesis and simple 18F-labeling of 3-fluoro-5-(2-(2-(fluoromethyl)thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)benzonitrile as a high affinity radioligand for imaging monkey brain metabotropic glutamate subtype-5 receptors with positron emission tomography. J Med Chem 2007;50:3256–66.
Sprague DR, Chin FT, Liow JS, Fujita M, Burns HD, Hargreaves R, et al. Human biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the tachykinin NK1 antagonist radioligand [18F]SPA-RQ: comparison of thin-slice, bisected, and 2-dimensional planar image analysis. J Nucl Med 2007;48:100–7.
Cristy M. Active bone marrow distribution as a function of age in humans. Phys Med Biol 1981;26:389–400.
The International Commission on Radiological Protection. Basic anatomical and physiological data: the skeleton. ICRP Publication 70. Ann ICRP 1995;25:1–80.
The International Commission on Radiological Protection. Basic anatomical and physiological data for use in radiological protection: reference values. ICRP Publication 89. Ann ICRP. 2002;32:1–277.
Cloutier RJ, Smith SA, Watson EE, Snyder WS, Warner GG. Dose to the fetus from radionuclides in the bladder. Health Phys 1973;25:147–61.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1023–7.
Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21: Food and Drugs. Chapter 1 – Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. Part 361 – Prescription drugs for human use generally recognized as safe and effective and not misbranded: drugs used in research. Sect. 361.1: Radioactive drugs for certain research uses; 2010
International Commission on Radiological Protection. Radiological protection in biomedical research. ICRP Publication 62. Ann ICRP 1993;22:A1.
Ryu YH, Liow JS, Zoghbi S, Fujita M, Collins J, Tipre D, et al. Disulfiram inhibits defluorination of 18F-FCWAY, reduces bone radioactivity, and enhances visualization of radioligand binding to serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in human brain. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1154–61.
Shetty HU, Zoghbi SS, Simeon FG, Liow JS, Brown AK, Kannan P, et al. Radiodefluorination of 3-fluoro-5-(2-(2-[18F](fluoromethyl)-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)benzonitrile ([18F]SP203), a radioligand for imaging brain metabotropic glutamate subtype-5 receptors with positron emission tomography, occurs by glutathionylation in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008;327:727–35.
Bogaards JJ, Venekamp JC, Salmon FG, van Bladeren PJ. Conjugation of isoprene monoepoxides with glutathione, catalyzed by α, μ, π and θ-class glutathione S-transferases of rat and man. Chem Biol Interact 1999;117:1–14.
Cannady EA, Chien C, Jones TM, Borel AG. In vitro metabolism of the epoxide substructure of cryptophycins by cytosolic glutathione S-transferase: species differences and stereoselectivity. Xenobiotica 2006;36:659–70.
Vesselle H, Grierson J, Peterson LM, Muzi M, Mankoff DA, Krohn KA. 18F-Fluorothymidine radiation dosimetry in human PET imaging studies. J Nucl Med 2003;44:1482–8.
Zanzonico PB, Finn R, Pentlow KS, Erdi Y, Beattie B, Akhurst T, et al. PET-based radiation dosimetry in man of 18F-fluorodihydrotestosterone, a new radiotracer for imaging prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1966–71.
Deterding TA, Votaw JR, Wang CK, Eshima D, Eshima L, Keil R, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the dopamine transporter ligand [18F]FECNT. J Nucl Med 2001;42:376–81.
Koole M, Lewis DM, Buckley C, Nelissen N, Vandenbulcke M, Brooks DJ, et al. Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 18F-GE067: a radioligand for in vivo brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med 2009;50:818–22.
Obrzut SL, Koren AO, Mandelkern MA, Brody AL, Hoh CK, London ED. Whole-body radiation dosimetry of 2-[18F]fluoro-A-85380 in human PET imaging studies. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:869–74.
Brown WD, Oakes TR, DeJesus OT, Taylor MD, Roberts AD, Nickles RJ, et al. Fluorine-18-fluoro-L-DOPA dosimetry with carbidopa pretreatment. J Nucl Med 1998;39:1884–91.
Robeson W, Dhawan V, Belakhlef A, Ma Y, Pillai V, Chaly T, et al. Dosimetry of the dopamine transporter radioligand 18F-FPCIT in human subjects. J Nucl Med 2003;44:961–6.
Deloar HM, Fujiwara T, Shidahara M, Nakamura T, Watabe H, Narita Y, et al. Estimation of absorbed dose for 2-[F-18]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using whole-body positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Nucl Med 1998;25:565–74.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Program of the National Institute of Mental Health (projects Z01-MH-002795-07 and Z01-MH-002852-04). We thank Leah P. Dickstein, Maria D. Ferraris Araneta, Gerald L. Hodges, Nobuyo Kimura, Barbara Scepura, Cheryl Wallisch, Yi Zhang, Jeih-San Liow, Robert L. Gladding, Amira K. Brown, and the staff of the PET Department for successful completion of the studies; and Dr. Michael G. Stabin for his suggestions concerning the data analysis; and PMOD Technologies (Zurich, Switzerland) for providing its image analysis and modeling software.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, Y., Siméon, F.G., Hatazawa, J. et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of a positron emission tomographic ligand, 18F-SP203, to image metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors in humans. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37, 1943–1949 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1447-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1447-8