Abstract
Purpose
To assess the diagnostic performance of a novel ultrafast cardiac gamma camera with cadmium-zinc-telluride (CZT) solid-state semiconductor detectors for nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).
Methods
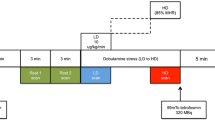
The study group comprised 75 consecutive patients (55 men, BMI range 19–45 kg/m2) who underwent a 1-day 99mTc-tetrofosmin adenosine-stress/rest imaging protocol. Scanning was performed first on a conventional dual-detector SPECT gamma camera (Ventri, GE Healthcare) with a 15-min acquisition time each for stress and rest. All scans were immediately repeated on an ultrafast CZT camera (Discovery 530 NMc, GE Healthcare) with a 3-min scan time for stress and a 2-min scan time for rest. Clinical agreement (normal, ischaemia, scar) between CZT and SPECT was assessed for each patient and for each coronary territory using SPECT MPI as the reference standard. Segmental myocardial tracer uptake values (percent of maximum) using a 20-segment model and left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) values obtained using CZT were compared with those obtained using conventional SPECT by intraclass correlation and by calculating Bland-Altman limits of agreement.
Results
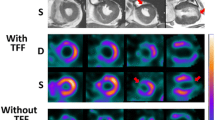
There was excellent clinical agreement between CZT and conventional SPECT on a per-patient basis (96.0%) and on a per-vessel territory basis (96.4%) as shown by a highly significant correlation between segmental tracer uptake values (r=0.901, p<0.001). Similarly, EF values for both scanners were highly correlated (r=0.976, p<0.001) with narrow Bland-Altman limits of agreement (−5.5–10.6%).
Conclusion
The novel CZT camera allows a more than fivefold reduction in scan time and provides clinical information equivalent to conventional standard SPECT MPI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas GS, Miyamoto MI, Morello AP 3rd, Majmundar H, Thomas JJ, Sampson CH, et al. Technetium 99m sestamibi myocardial perfusion imaging predicts clinical outcome in the community outpatient setting. The Nuclear Utility in the Community (NUC) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:213–23.
Seo Y, Mari C, Hasegawa BH. Technological development and advances in single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography. Semin Nucl Med 2008;38:177–98.
Giorgetti A, Rossi M, Stanislao M, Valle G, Bertolaccini P, Maneschi A, et al. Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of a gated SPECT early-imaging protocol: a multicenter study of the Myoview Imaging Optimization Group. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1670–5.
Kapur A, Latus KA, Davies G, Dhawan RT, Eastick S, Jarritt PH, et al. A comparison of three radionuclide myocardial perfusion tracers in clinical practice: the ROBUST study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:1608–16.
Husmann L, Valenta I, Gaemperli O, Adda O, Treyer V, Wyss CA, et al. Feasibility of low-dose coronary CT angiography: first experience with prospective ECG-gating. Eur Heart J 2008;29:191–7.
Rybicki FJ, Otero HJ, Steigner ML, Vorobiof G, Nallamshetty L, Mitsouras D, et al. Initial evaluation of coronary images from 320-detector row computed tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2008;24:535–46.
Berman DS, Kang X, Tamarappoo B, Wolak A, Hayes SW, Nakazato R, et al. Stress thallium-201/rest technetium-99m sequential dual isotope high-speed myocardial perfusion imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2009;2:273–82.
Herzog BA, Buechel RR, Katz R, Brueckner M, Husmann L, Burger IA, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a novel cadmium-zinc-telluride detector technique: optimized protocol for scan time reduction. J Nucl Med 2010;51:46–51.
Hesse B, Tagil K, Cuocolo A, Anagnostopoulos C, Bardies M, Bax J, et al. EANM/ESC procedural guidelines for myocardial perfusion imaging in nuclear cardiology. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:855–97.
Hansen CL, Goldstein RA, Akinboboye OO, Berman DS, Botvinick EH, Churchwell KB, et al. Myocardial perfusion and function: single photon emission computed tomography. J Nucl Cardiol 2007;14:e39–60.
Ali I, Ruddy TD, Almgrahi A, Anstett FG, Wells RG. Half-time SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging with attenuation correction. J Nucl Med 2009;50:554–62.
Valenta I, Treyer V, Husmann L, Gaemperli O, Schindler MJ, Herzog BA, et al. New reconstruction algorithm allows shortened acquisition time for myocardial perfusion SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;in press. doi:10.1007/s00259-009-1300-0
Madsen MT. Recent advances in SPECT imaging. J Nucl Med 2007;48:661–73.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation and by the ZIHP (Zurich Center for Integrative Human Physiology, University of Zurich). We would like to thank Edlira Loga, Ennio Mueller, Josephine Trinckauf, Verena Wechselbaumer and Mirjam De Bloeme for their technical support.
Conflicts of interest
The University Hospital Zurich holds a research contract with GE Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ronny R. Buechel and Bernhard A. Herzog contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1805-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buechel, R.R., Herzog, B.A., Husmann, L. et al. Ultrafast nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging on a new gamma camera with semiconductor detector technique: first clinical validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37, 773–778 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1375-7