Abstract
Purpose
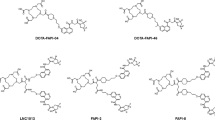
Targeting drugs to receptors involved in tumor angiogenesis has been demonstrated as a novel and promising approach to improve cancer treatment. In this study, we evaluated the anti-tumor efficacy of a dimeric RGD peptide–paclitaxel conjugate (RGD2–PTX) in an orthotopic MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model.
Methods
To assess the effect of conjugation and the presence of drug moiety on the MDA-MB-435 tumor and normal tissue uptake, the biodistribution of 3H–RGD2–PTX was compared with that of 3H–PTX. The treatment effect of RGD2–PTX and RGD2+PTX was measured by tumor size, 18F-FDG/PET, 18F-FLT/PET, and postmortem histopathology.
Results
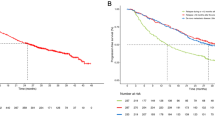
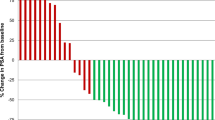
By comparing the biodistribution of 3H–RGD2–PTX and 3H–PTX, we found that 3H–RGD2–PTX had higher initial tumor exposure dose and prolonged tumor retention than 3H–PTX. Metronomic low-dose treatment of breast cancer indicated that RGD2–PTX is significantly more effective than PTX+RGD2 combination and solvent control. Although in vivo 18F-FLT/PET imaging and ex vivo Ki67 staining indicated little effect of the PTX-based drug on cell proliferation, 18F-FDG/PET imaging showed significantly reduced tumor metabolism in the RGD2–PTX-treated mice versus those treated with RGD2+PTX and solvent control. Terminal uridine deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining also showed that RGD2–PTX treatment also had significantly higher cell apoptosis ratio than the other two groups. Moreover, the microvessel density was significantly reduced after RGD2–PTX treatment as determined by CD31 staining.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that integrin-targeted delivery of paclitaxel allows preferential cytotoxicity to integrin-expressing tumor cells and tumor vasculature. The targeted delivery strategies developed in this study may also be applied to other chemotherapeutics for selective tumor killing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, Grumbine FC, Ettinger DS, Armstrong DK, et al. Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med 1989;111:273–9.
Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 1979;277:665–7.
Schiff PB, Horwitz SB. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1980;77:1561–5.
Yvon AM, Wadsworth P, Jordan MA. Taxol suppresses dynamics of individual microtubules in living human tumor cells. Mol Biol Cell 1999;10:947–59.
Jordan MA, Toso RJ, Thrower D, Wilson L. Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993;90:9552–6.
Eisenhauer E. Docetaxel: current status and future prospects. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:2865–8.
Chu Q, Vincent M, Logan D, Mackay JA, Evans WK. Taxanes as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and practice guideline. Lung Cancer 2005;50:355–74.
Esteva FJ. The current status of docetaxel for metastatic breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002;16:17–26.
van Hoesel QG, Verweij J, Catimel G, Clavel M, Kerbrat P, van Oosterom AT, et al. Phase II study with docetaxel (Taxotere) in advanced soft tissue sarcomas of the adult. EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. Ann Oncol 1994;5:539–42.
Sharma A, Straubinger RM. Novel taxol formulations: preparation and characterization of taxol-containing liposomes. Pharm Res 1994;11:889–96.
Bartoli MH, Boitard M, Fessi H, Beriel H, Devissaguet JP, Picot F, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumoral activity of free, and encapsulated taxol. J Microencapsul 1990;7:191–7.
Zhang X, Burt HM, Von Hoff D, Dexter D, Mangold G, Degen D, et al. An investigation of the antitumor activity and biodistribution of polymeric micellar paclitaxel. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997;40:81–6.
Nicolaou KC, Riemer C, Kerr MA, Rideout D, Wrasidlo W. Design, synthesis and biological activity of protaxols. Nature (London, UK) 1993;364:464–6.
Rose WC, Clark JL, Lee FYF, Casazza AM. Preclinical antitumor activity of water-soluble paclitaxel derivatives. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997;39:486–92.
Li C, Yu D-F, Newman RA, Cabral F, Stephens LC, Hunter N, et al. Complete regression of well-established tumors using a novel water-soluble poly(l-glutamic acid)–paclitaxel conjugate. Cancer Res 1998;58:2404–9.
Schally AV, Nagy A. Chemotherapy targeted to cancers through tumoral hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2004;15:300–10.
Chen X, Plasencia C, Hou Y, Neamati N. Synthesis and biological evaluation of dimeric RGD peptide-paclitaxel conjugate as a model for integrin-targeted drug delivery. J Med Chem 2005;48:1098–106.
Cheng YF, Kramer RH. Human microvascular endothelial cells express integrin-related complexes that mediate adhesion to the extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1989;139:275–86.
Temming K, Schiffelers RM, Molema G, Kok RJ. RGD-based strategies for selective delivery of therapeutics and imaging agents to the tumour vasculature. Drug Resist Updat. 2005;8:381–402.
Deutsch HM, Glinski JA, Hernandez M, Haugwitz RD, Narayanan VL, Suffness M, et al. Synthesis of congeners and prodrugs. 3. Water-soluble prodrugs of taxol with potent antitumor activity. J Med Chem 1989;32:788–92.
Visvikis D, Cheze-LeRest C, Costa DC, Bomanji J, Gacinovic S, Ell PJ. Influence of OSEM and segmented attenuation correction in the calculation of standardised uptake values for [18F]FDG PET. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:1326–35.
Jacobs AH, Rueger MA, Winkeler A, Li H, Vollmar S, Waerzeggers Y, et al. Imaging-guided gene therapy of experimental gliomas. Cancer Res 2007;67:1706–15.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank the cyclotron team at the Stanford University for 18F-FDG and 18F-FLT production. Grant support was from the National Cancer Institute (NCI; R01 120188, R01 CA119053, R21 CA121842, R21 CA102123, P50 CA114747, U54 CA119367, and R24 CA93862) and the Department of Defense (DOD; W81XWH-07-1-0374, W81XWH-04-1-0697, W81XWH-06-1-0665, W81XWH-06-1-0042, and DAMD17-03-1-0143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Q., Li, ZB., Chen, K. et al. Evaluation of biodistribution and anti-tumor effect of a dimeric RGD peptide–paclitaxel conjugate in mice with breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35, 1489–1498 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0744-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0744-y