Abstract
Aim
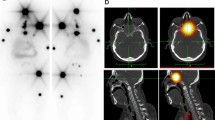
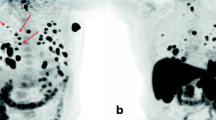
This study assessed the ability of visual and quantitative 124-iodine positron emission tomography (124I PET) data to detect disseminated iodine-avid lung metastases (DILM) of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
Materials and methods
Using “post-therapy” 131-iodine (131I) whole-body scintigraphy (TxWBS) and thoracic computed tomography (CT), we retrospectively divided 70 consecutive DTC patients undergoing 124I PET dosimetry ∼1 week before 131I therapy into subgroups positive (n = 7) or negative (n = 63) for DILM, defined as lung metastases visible on TxWBS but not thoracic CT. To determine whether 124I PET data could distinguish patients with versus without DILM, we compared these data with the TxWBS findings. The 124I PET data were acquired via whole-body PET scans ∼24 h after oral administration of 124I, 24 ± 2 MBq. Quantitative data comprised absolute lung 124I activity concentrations and lung-to-background (L/B) 124I uptake ratios.
Results
Only 1/7 DILM-positive patients had visible disseminated lung uptake. Absolute 124I lung uptake activities overlapped considerably between both groups and did not differ significantly (P = 0.150). Mean L/B ratios, however, differed significantly between the DILM-positive and negative groups (P < 0.001). Nevertheless, L/B ratios overlapped between the groups (0.62–1.37 versus 0.13–0.69).
Conclusion
Quantitative analysis of 124I PET data using the L/B ratio is a promising tool to detect patients suspicious for DILM. However, L/B ratios overlapped between the groups to an extent that an unequivocal diagnosis based solely on this criterion was impossible in some patients. In those cases, additional diagnostic tests are necessary for diagnosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frey P, Townsend D, Flattet A, et al. Tomographic imaging of the human thyroid using I-124. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986;63:918–27.
Jentzen W, Freudenberg L, Heinze M, Eising EG, Knust J, Bockisch A. Analyse der Jod-124 Zeitaktivitätskurven bei der Läionsdosimetrie beim differenzierten Schilddrüsenkarzinom: Das 3-Tage-Protokoll ist ausreichend. Nuklearmedizin 2006;45:A28.
Pentlow KS, Graham MC, Lambrecht RM, et al. Quantitative imaging of iodine-124 with PET. J Nucl Med 1996;37:1557–62.
Erdi YE, Macapinlac H, Larson SM, et al. Radiation dose assessment for I-131 therapy of thyroid cancer using I-124 PET imaging. Clin Pos Imaging 1999;2:41–6.
Eschmann SM, Reischl G, Bilger K, et al. Evaluation of dosimetry of radioiodine therapy in benign and malignant thyroid disorders by means of iodine-124 and PET. Eur J Nucl Med 2002;29:760–7.
Frey P, Townsend D, Jeavons A, et al. In vivo imaging of the human thyroid with a positron camera using 124I. Eur J Nucl Med 1985;10:472–6.
Lambrecht RM, Woodhouse N, Phillips R, et al. Investigational study of iodine-124 with a positron camera. Am J Physiol Imag 1988;3:197–200.
Jentzen W, Freudenberg L, Eising EG, Heinze M, Brandau W, Bockisch A. Segmentation of PET volumes by iterative image thresholding. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1–8.
Sgouros G, Kolbert K, Sheikh A, et al. Patient-specific dosimetry for 131I thyroid cancer therapy using 124I PET and 3-dimensional-internal dosimetry (3D-ID) software. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1366–72.
Freudenberg LS, Jentzen W, Görges R, et al. 124I–positron emission tomography dosimetry in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: therapeutic impact. Nuklearmedizin 2007;46(4):121–8.
Freudenberg LS, Jentzen W, Marlowe RJ, Koska WW, Luster M, Bockisch A. 124-Iodine positron emission tomography/computed tomography dosimetry in pediatric patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes (in press).
Jentzen W, Weise R, Kupferschläger J, et al. Iodine-124 PET dosimetry in differentiated thyroid cancer: recovery coefficient in 2D and 3D modes for PET(/CT) systems. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007 Oct 10 (in press).
Maxon HR, Thomas SR, Hertzberg VS, et al. Relation between effective radiation dose and outcome of radioiodine therapy for thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 1983;309:937–41.
Maxon HR, Thomas SR, Samaratunga RC. Dosimetric considerations in the radioiodine treatment of macrometastases and micrometastases from differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 1997;7:183–7.
Benua RS, Cicale NR, Sonenberg M, Rawson RW. The relation of radioiodine dosimetry to results and complications in the treatment of metastatic thyroid cancer. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1962;87:171–82.
Dietlein M, Dressler J, Farahati F, et al. Procedure guidelines for radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid cancer (version 2). Nuklearmedizin 2004:43;115–20.
Stewart BW, Kleihues P. Thyroid cancer. In: Stewart BW, Kleihues P, editors. World cancer report. Lyon, France: Lyon IARC Press; 2003, p. 257–60.
Massin JP, Savoie JC, Garnier H, Guiraudon G, Leger FA, Bacourt F. Pulmonary metastases in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Study of 58 cases with implications for the primary tumor treatment. Cancer 1984;53:982–92.
Casara D, Rubello D, Saladini G, et al. Different features of pulmonary metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer: natural history and multivariate statistical analysis of prognostic variables. J Nucl Med 1993;34:1626–31.
Sisson JC, Giordano TJ, Jamadar DA, et al. 131-I treatment of micronodular pulmonary metastases from papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 1996;78:2184–92.
Brink JS, Heerden JA, McIver B, et al. Papillary thyroid cancer with pulmonary metastases in children: long-term prognosis. Surgery 2000;128:881–7.
Maxon HR, Smith HS. Radioiodine-131 in the diagnosis and treatment of metastatic well differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1990;19:685–718.
Sisson JC, Jamadar DA, Kazerooni EA, et al. Treatment of micronodular lung metastases of papillary thyroid cancer: are the tumors too small for effective irradiation from radioiodine? Thyroid 1998;8:215–21.
Ilgan S, Karacalioglu O, Pabuscu Y, et al. Iodine-131 treatment and high-resolution CT: results in patients with lung metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:825–30.
Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:2892–9.
Schlumberger MJ. Papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1998;29;338:297–306.
Fleming ID, Cooper JS, Henson DE, editors. AJCC cancer staging manual, 5th edn. American Joint Committee on Cancer. Philadelphia: Lippincott–Raven; 1997.
Knust EJ, Dutschka K, Weinreich R. Preparation of I-124 solutions after thermodistillation of irradiated 124TeO2 targets. Appl Radiat Isotopes 2000;52:181–4.
Guttman I. Statistical tolerance regions: classical and Bayesian. London: Charles Griffin; 1970.
Freudenberg LS, Antoch G,Knust J, et al. Value of 124I-PET/CT in staging of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur Radiol 2004;14:2092–8.
Song H, He B, Prideaux A, Du Y, Frey E, Kasecamp W, et al. Lung dosimetry for radioiodine treatment planning in the case of diffuse lung metastases. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1985–94.
Sgouros G, Song H, Ladenson PW, Wahl RL. Lung toxicity in radioiodine therapy of thyroid carcinoma: development of a dose-rate method and dosimetric implications of the 80-mCi rule. J Nucl Med 2006;47 12:1977–84.
Benua RS, Leeper RD. A method and rationale for treating metastatic thyroid carcinoma with the largest safe dose of 131I. In: Medeiros-Neta G, Gaitan E, editors. Frontiers in thyroidology. New York, NY: Plenum Medical; 1986, p. 1317–21.
Filesi M, Signore A, Ventroni G, Melacrinis FF, Ronga G. Role of initial iodine-131 whole-body scan and serum thyroglobulin in differentiated thyroid carcinoma metastases. J Nucl Med 1998;39:1542–6.
Schlumberger M, Challeton C, De Vathaire F, et al. Radioactive iodine treatment and external radiotherapy for lung and bone metastases from thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1996;37:598–605.
Hindie E, Melliere D, Lange F, et al. Functioning pulmonary metastases of thyroid cancer: does radioiodine influence the prognosis? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:974–81.
Acknowledgement
We thank Gerald Antoch, MD, and Hilmar Kühl, MD, for interpreting the CT images and Jochen Knust, PhD, and Wolfgang Brandau, PhD, for production of 124I. Furthermore, we are indebted to Robert J. Marlowe for critically reviewing the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freudenberg, L.S., Jentzen, W., Müller, S.P. et al. Disseminated iodine-avid lung metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer: a challenge to 124I PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35, 502–508 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0601-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0601-4