Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine whether the follow-up of pain processing recovery in hyperalgesic fibromyalgia (FM) could be objectively evaluated with brain perfusion ethyl cysteinate dimer single photon computerized tomography (ECD-SPECT) after administration of ketamine.
Materials and methods
We enrolled 17 hyperalgesic FM women patients (48.5 ± 11 years, range 25–63). After treatment with subcutaneous ketamine, 11 patients were considered as “good responders”, with a decrease in pain intensity, evaluated by visual analog scale (VAS), greater than 50%. On the other hand, six patients were considered as “poor responders”. A voxel-based analysis of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) was conducted (p voxel < 0.001uc), in the two subgroups of patients, before and after treatment, in comparison to a group of ten healthy subjects, matched for age and gender.
Results
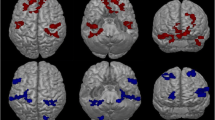
In comparison to baseline brain SPECT, midbrain rCBF showed a greater increase after ketamine in the responder group than in the nonresponder group (p cluster = 0.016c). In agreement with the clinical response, the change in midbrain rCBF after ketamine was highly correlated with the reduction of VAS pain score (r = 0.7182; p = 0.0041).
Conclusion
This prospective study suggests that blockade of facilitatory descending modulation of pain with ketamine can be evaluated in the periaqueductal grey with brain perfusion SPECT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33:160–72.
Hocking G, Cousins MJ. Ketamine in chronic pain management: an evidence-based review. Anesth Analg 2003;97:1730–9.
Guedj E, Taieb D, Cammilleri S, Lussato D, de Laforte C, Niboyet J, et al. 99mTc-ECD brain perfusion SPECT in hyperalgesic fibromyalgia. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:130–4.
Guedj E, Cammilleri S, Colavolpe C, Taieb D, de Laforte C, Niboyet J, et al. Predictive value of brain perfusion SPECT for ketamine response in hyperalgesic fibromyalgia. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007; 34(8):1274–79.
Giesecke T, Gracely RH, Grant MA, Nachemson A, Petzke F, Williams DA, et al. Evidence of augmented central pain processing in idiopathic chronic low back pain. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:613–23.
Adiguzel O, Kaptanoglu E, Turgut B, Nacitarhan V. The possible effect of clinical recovery on regional cerebral blood flow deficits in fibromyalgia: a prospective study with semiquantitative SPECT. South Med J 2004;97:651–5.
Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhao ZQ. Anterior cingulate cortex contributes to the descending facilitatory modulation of pain via dorsal reticular nucleus. Eur J Neurosci 2005;22:1141–8.
Lee BH, Park SH, Won R, Park YG, Sohn JH. Antiallodynic effects produced by stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 2000;291:29–32 (Sep 8).
Langsjo JW, Salmi E, Kaisti KK, Aalto S, Hinkka S, Aantaa R, et al. Effects of subanesthetic ketamine on regional cerebral glucose metabolism in humans. Anesthesiology 2004;100:1065–71.
Gracely RH, Petzke F, Wolf JM, Clauw DJ. Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence of augmented pain processing in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:1333–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guedj, E., Cammilleri, S., Colavolpe, C. et al. Follow-up of pain processing recovery after ketamine in hyperalgesic fibromyalgia patients using brain perfusion ECD-SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34, 2115–2119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0589-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0589-9