Abstract
Purpose
Currently available diagnostic techniques can be unreliable in the diagnosis of delayed fracture healing in certain clinical situations, which can lead to increased complication rates and costs to the health care system. This study sought to determine the utility of positron emission tomography (PET) scanning with 18F-fluoride ion, which localizes in regions of high osteoblastic activity, and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), an indicator of cellular glucose metabolism, in assessing bone healing in a rat femur fracture model.
Methods
Fractures were created in the femurs of immunocompetent rats. Animals in group I had a fracture produced via a manual three-point bending technique. Group II animals underwent a femoral osteotomy with placement of a 2-mm silastic spacer at the fracture site. Fracture healing was assessed with plain radiographs, 18F-fluoride, and 18F-FDG PET scans at 1, 2, 3, and 4-week time points after surgery. Femoral specimens were harvested for histologic analysis and manual testing of torsional and bending strength 4 weeks after surgery.
Results
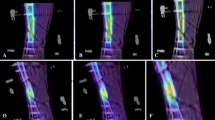
All fractures in group I revealed abundant callus formation and bone healing, while none of the nonunion femurs were healed via assessment with manual palpation, radiographic, and histologic evaluation at the 4-week time point. 18F-fluoride PET images of group I femurs at successive 1-week intervals revealed progressively increased signal uptake at the union site during fracture repair. In contrast, minimal tracer uptake was seen at the fracture sites in group II at all time points after surgery. Data analysis revealed statistically significant differences in mean signal intensity between groups I and II at each weekly interval. No significant differences between the two groups were seen using 18F-FDG PET imaging at any time point.
Conclusion
This study suggests that 18F-fluoride PET imaging, which is an indicator of osteoblastic activity in vivo, can identify fracture nonunions at an early time point and may have a role in the assessment of longitudinal fracture healing. PET scans using 18F-FDG were not helpful in differentiating metabolic activity between successful and delayed bone healing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heppenstall RB. The present role of bone graft surgery in treating nonunion. Orthop Clin North Am 1984;15:113–23.
Jupiter JB, First K, Gallico GG 3rd, May JW. The role of external fixation in the treatment of posttraumatic osteomyelitis. J Orthop Trauma 1988;2:79–93.
Hulth A. Current concepts of fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1989;49:265–84.
Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Forriol F. Nonunion: general principles and experimental data. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;419:4–12.
Zlowodzki M, Obremskey WT, Thomison JB, Kregor PJ. Functional outcome after treatment of lower-extremity nonunions. J Trauma 2005;58:312–7.
Bowen CV, Botsford DJ, Hudak PL, Evans PJ. Microsurgical treatment of septic nonunion of the tibia. Quality of life results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1996;332:52–61.
Sprague S, Bhandari M. An economic evaluation of early versus delayed operative treatment in patients with closed tibial shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2002;122:315–23.
Bhandari M, Adili A, Leone J, Lachowski RJ, Kwok DC. Early versus delayed operative management of closed tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;368:230–9.
Heckman JD, Sarasohn-Kahn J. The economics of treating tibia fractures. The cost of delayed unions. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 1997;56:63–72.
Ikeda K, Tomita K, Hashimoto F, Morikawa S. Long-term follow-up of vascularized bone grafts for the reconstruction of tibial nonunion: evaluation with computed tomographic scanning. J Trauma 1992;32:693–7.
Savolaine ER, Ebraheim N. Assessment of femoral neck nonunion with multiplanar computed tomography reconstruction. Orthopedics 2000;23:713–5.
Shefelbine SJ, Simon U, Claes L, Gold A, Gabet Y, Bab I, et al. Prediction of fracture callus mechanical properties using micro-CT images and voxel-based finite element analysis. Bone 2005;36:480–8.
Belsole RJ, Hilbelink DR, Llewellyn JA, Dale M, Greene TL, Rayhack JM. Computed analyses of the pathomechanics of scaphoid waist nonunions. J Hand Surg [Am] 1991;16:899–906.
Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Ney DR, Brooker AF Jr, Magid D. Nonunion of acetabular fractures: evaluation with interactive multiplanar CT. J Orthop Trauma 1989;3:33–40.
Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Magid D, Scott WW Jr, Brooker AF, Siegelman SS. Fracture nonunion: CT assessment with multiplanar reconstruction. Radiology 1988;167:483–8.
Bhattacharyya T, Bouchard KA, Phadke A, Meigs JB, Kassarjian A, Salamipour H. The accuracy of computed tomography for the diagnosis of tibial nonunion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2006;88:692–7.
Moed BR, Kim EC, van Holsbeeck M, Schaffler MB, Subramanian S, Bouffard JA, et al. Ultrasound for the early diagnosis of tibial fracture healing after static interlocked nailing without reaming: histologic correlation using a canine model. J Orthop Trauma 1998;12:200–5.
Moed BR, Subramanian S, van Holsbeeck M, Watson JT, Cramer KE, Karges DE, et al. Ultrasound for the early diagnosis of tibial fracture healing after static interlocked nailing without reaming: clinical results. J Orthop Trauma 1998;12:206–13.
Moed BR, Watson JT, Goldschmidt P, van Holsbeeck M. Ultrasound for the early diagnosis of fracture healing after interlocking nailing of the tibia without reaming. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;310:137–44.
Derbyshire ND, Simpson AH. A role for ultrasound in limb lengthening. Br J Radiol 1992;65:576–80.
Young JW, Kostrubiak IS, Resnik CS, Paley D. Sonographic evaluation of bone production at the distraction site in Ilizarov limb-lengthening procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1990;154:125–8.
Hirata T, Konishiike T, Kawai A, Sato T, Inoue H. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head perfusion in femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001;393:294–301.
Dailiana ZH, Zachos V, Varitimidis S, Papanagiotou P, Karantanas A, Malizos KN. Scaphoid nonunions treated with vascularised bone grafts: MRI assessment. Eur J Radiol 2004;50:217–24.
De Schrijver F, De Smet L. Isolated fracture of the capitate: the value of MRI in diagnosis and follow up. Acta Orthop Belg 2002;68:310–5.
Lee C, Dorcil J, Radomisli TE. Nonunion of the spine: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;419:71–5.
Kuschner SH, Lane CS, Brien WW, Gellman H. Scaphoid fractures and scaphoid nonunion. Diagnosis and treatment. Orthop Rev 1994;23:861–71.
Rayan GM. Occult wrist pain due to capitate nonunion. South Med J 1994;87:402–4.
Schelstraete K, Daneels F, Obrie E. Technetium-99m-diphosphonate, gallium-67 and labeled leukocyte scanning techniques in tibial nonunion. Acta Orthop Belg 1992;58 Suppl 1:168–72.
O'Reilly RJ, Cook DJ, Gaffney RD, Angel KR, Paterson DC. Can serial scintigraphic studies detect delayed fracture union in man? Clin Orthop Relat Res 1981;160:227–32.
Ebraheim NA, Savolaine ER, Patel A, Skie M, Jackson WT. Assessment of tibial fracture union by 35–45 degrees internal oblique radiographs. J Orthop Trauma 1991;5:349–50.
Sorensen J, Ullmark G, Langstrom B, Nilsson O. Rapid bone and blood flow formation in impacted morselized allografts: positron emission tomography (PET) studies on allografts in 5 femoral component revisions of total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand 2003;74:633–43.
Blau M, Nagler W, Bender MA. Fluorine-18: a new isotope for bone scanning. J Nucl Med 1962;3:332–4.
Narita N, Kato K, Nakagaki H, Ohno N, Kameyama Y, Weatherell JA. Distribution of fluoride concentration in the rat’s bone. Calcif Tissue Int 1990;46:200–4.
Toegel S, Hoffmann O, Wadsak W, Ettlinger D, Mien LK, Wiesner K, et al. Uptake of bone-seekers is solely associated with mineralisation! A study with 99mTc-MDP, 153Sm-EDTMP and 18F-fluoride on osteoblasts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:491–4.
Blau M, Ganatra R, Bender MA. 18F-fluoride for bone imaging. Semin Nucl Med 1972;2:31–7.
Reeve J, Arlot M, Wootton R, Edouard C, Tellez M, Hesp R, et al. Skeletal blood flow, iliac histomorphometry, and strontium kinetics in osteoporosis: a relationship between blood flow and corrected apposition rate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1988;66:1124–31.
Hawkins RA, Choi Y, Huang SC, Hoh CK, Dahlbom M, Schiepers C, et al. Evaluation of the skeletal kinetics of fluorine-18-fluoride ion with PET. J Nucl Med 1992;33:633–42.
Schiepers C, Nuyts J, Bormans G, Dequeker J, Bouillon R, Mortelmans L, et al. Fluoride kinetics of the axial skeleton measured in vivo with fluorine-18-fluoride PET. J Nucl Med 1997;38:1970–6.
Cook GJ, Fogelman I. The role of positron emission tomography in the management of bone metastases. Cancer 2000;88(12 Suppl):2927–33.
Blake GM, Park-Holohan SJ, Cook GJ, Fogelman I. Quantitative studies of bone with the use of 18F-fluoride and 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate. Semin Nucl Med 2001;31:28–49.
Schwartz Z, Shani J, Soskolne WA, Touma H, Amir D, Sela J. Uptake and biodistribution of technetium-99m-MD32P during rat tibial bone repair. J Nucl Med 1993;34:104–8.
Berger F, Lee YP, Loening AM, Chatziioannou A, Freedland SJ, Leahy R, et al. Whole-body skeletal imaging in mice utilizing microPET: optimization of reproducibility and applications in animal models of bone disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:1225–36.
Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Flusser G, Zuriel L, Kollender Y, Lerman H, et al. Assessment of malignant skeletal disease: initial experience with 18F-fluoride PET/CT and comparison between 18F-fluoride PET and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med 2004;45:272–8.
Frost ML, Fogelman I, Blake GM, Marsden PK, Cook G Jr. Dissociation between global markers of bone formation and direct measurement of spinal bone formation in osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 2004;19:1797–804.
Cook GJ, Blake GM, Marsden PK, Cronin B, Fogelman I. Quantification of skeletal kinetic indices in Paget’s disease using dynamic 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography. J Bone Miner Res 2002;17:854–9.
Pakos EE, Fotopoulos AD, Ioannidis JP. 18F-FDG PET for evaluation of bone marrow infiltration in staging of lymphoma: a meta-analysis. J Nucl Med 2005;46:958–63.
Hsu W, Feeley B, Krenek L, Gamradt S, Stout D, Chatziioannou A, et al. The characterization of osteolytic and osteoblastic lesions in a prostate cancer mouse model with the use of 18F-FDG and 18F-fluoride PET/CT scans. In: Transactions of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2005. Washington DC.
Lee FY, Yu J, Chang SS, Fawwaz R, Parisien MV. Diagnostic value and limitations of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for cartilaginous tumors of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86-A:2677–85.
Mumme T, Reinartz P, Alfer J, Muller-Rath R, Buell U, Wirtz DC. Diagnostic values of positron emission tomography versus triple-phase bone scan in hip arthroplasty loosening. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2005;125:322–9.
Strauss LG, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Koczan D, Bernd L, Haberkorn U, Ewerbeck V, et al. 18F-FDG kinetics and gene expression in giant cell tumors. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1528–35.
Eary JF, O'Sullivan F, Powitan Y, Chandhury KR, Vernon C, Bruckner JD, et al. Sarcoma tumor FDG uptake measured by PET and patient outcome: a retrospective analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:1149–54.
Hawkins DS, Schuetze SM, Butrynski JE, Rajendran JG, Vernon CB, Conrad EU 3rd, et al. [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography predicts outcome for Ewing sarcoma family of tumors. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:8828–34.
O'Sullivan F, Roy S, O'Sullivan J, Vernon C, Eary J. Incorporation of tumor shape into an assessment of spatial heterogeneity for human sarcomas imaged with FDG-PET. Biostatistics 2005;6:293–301.
Schuetze SM, Rubin BP, Vernon C, Hawkins DS, Bruckner JD, Conrad EU 3rd, et al. Use of positron emission tomography in localized extremity soft tissue sarcoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer 2005;103:339–48.
Shields AF, Mankoff DA, Link JM, Graham MM, Eary JF, Kozawa SM, et al. Carbon-11-thymidine and FDG to measure therapy response. J Nucl Med 1998;39:1757–62.
Blokhuis TJ, Patka P, Bakker FC, Haarman HJ, van Lingen A, Roos JC, et al. Quantitative assessment of fracture healing using positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:329–30.
Piert M, Zittel TT, Becker GA, Jahn M, Stahlschmidt A, Maier G, et al. Assessment of porcine bone metabolism by dynamic 18F-fluoride ion PET: correlation with bone histomorphometry. J Nucl Med 2001;42:1091–100.
Messa C, Goodman WG, Hoh CK, Choi Y, Nissenson AR, Salusky IB, et al. Bone metabolic activity measured with positron emission tomography and [18F]fluoride ion in renal osteodystrophy: correlation with bone histomorphometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993;77:949–55.
Peterson B, Zhang J, Iglesias R, Kabo M, Hedrick M, Benhaim P, et al. Healing of critically sized femoral defects, using genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue. Tissue Eng 2005;11:120–9.
Wieland B, Bida G, Padgett H, Go H. Current status of CTI target systems for the production of PET radiochemicals. Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Targetry and Target Chemistry; 1989.
Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Stocklin G. Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med 1986;27:235–8.
Stout D, Chow P, Gustilo A, Grubwieser S, Chatziioannou A. Multimodality isolated bed system for mouse imaging experiments. Molecular Imaging and Biology 2003;5:128–29.
Tai YC, Ruangma A, Rowland D, Siegel S, Newport DF, Chow PL, et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET focus: a third-generation microPET scanner dedicated to animal imaging. J Nucl Med 2005;46:455–63.
Chatziioannou A, Qi J, Moore A, Annala A, Nguyen K, Leahy R, et al. Comparison of 3-D maximum a posteriori and filtered backprojection algorithms for high-resolution animal imaging with microPET. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2000;19:507–12.
Loening AM, Gambhir SS. AMIDE: a free software tool for multimodality medical image analysis. Mol Imaging 2003;2:131–7.
Whelan DB, Bhandari M, McKee MD, Guyatt GH, Kreder HJ, Stephen D, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver variation in the assessment of the healing of tibial fractures after intramedullary fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2002;84:15–8.
Kokubu T, Hak DJ, Hazelwood SJ, Reddi AH. Development of an atrophic nonunion model and comparison to a closed healing fracture in rat femur. J Orthop Res 2003;21:503–10.
Einhorn TA, Majeska RJ, Mohaideen A, Kagel EM, Bouxsein ML, Turek TJ, et al. A single percutaneous injection of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates fracture repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A:1425–35.
Frost ML, Cook GJ, Blake GM, Marsden PK, Benatar NA, Fogelman I. A prospective study of risedronate on regional bone metabolism and blood flow at the lumbar spine measured by 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography. J Bone Miner Res 2003;18:2215–22.
Brenner W, Vernon C, Conrad EU, Eary JF. Assessment of the metabolic activity of bone grafts with 18F-fluoride PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:1291–8.
dos Santos Neto FL, Volpon JB. Experimental nonunion in dogs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1984;187:260–71.
Volpon JB. Nonunion using a canine model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1994;113:312–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, W.K., Feeley, B.T., Krenek, L. et al. The use of 18F-fluoride and 18F-FDG PET scans to assess fracture healing in a rat femur model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34, 1291–1301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0280-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0280-6