Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) with respect to lymph node (LN) metastasis in patients with advanced gastric cancer, and to ascertain the factors that affect this accuracy.
Methods
Seventy-three patients with advanced gastric cancer, verified in all cases by endoscopic biopsy, were enrolled in this prospective study. We conducted FDG PET and other routine preoperative studies, including abdominal computed tomography (CT). Patients underwent either curative-intent gastrectomy and lymphadenectomy (n=67) or exploratory laparotomy. The Japanese system for the classification of gastric cancer was used for LN assessment.
Results
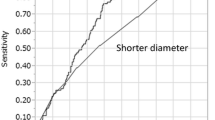
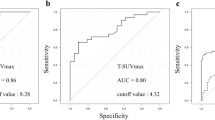
FDG PET was able to detect primary lesions in 70 of the 73 cases. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value of FDG PET for LN metastasis were 40%, 95%, 91% and 56%, respectively. Signet-ring cell carcinoma was associated with the lowest sensitivity (15%), whereas other cell types could be detected with moderate sensitivity (30–71%) and high specificity (93–100%). According to multiple logistic regression, the standardised uptake value for primary tumours was the only independent variable to be significantly related to sensitivity for LN metastasis (p=0.02, odds ratio=1.14). CT was superior to PET in terms of sensitivity (p<0.0001), and PET was superior to CT in terms of specificity (p<0.0001) and PPV (p=0.05).
Conclusion
FDG PET exhibits good specificity for LN staging of gastric cancer, and FDG uptake in the primary tumour is significantly related to the accuracy of FDG PET. Despite some clear limitations, FDG PET proved useful in the LN staging of FDG-avid gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakamura K, Morisaki T, Sugitani A, Ogawa T, Uchiyama A, Kinukawa N, et al. An early gastric carcinoma treatment strategy based on analysis of lymph node metastasis. Cancer 1999;85:1500-5
Yokota T, Ishiyama S, SaitoT, Teshima S, Narushima Y, Murata K, et al. Lymph node metastasis as a significant prognostic factor in gastric cancer: a multiple logistic regression analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol 2004;39:380–4
Kim HJ, Karpeh MS. Surgical approaches and outcomes in the treatment of gastric cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 2002;12:162–9
Fraser I, Nash R, James DC. Computed tomography in gastric cancer. Br J Surg 1985;72:249–50
Andaker L, Morales O, Hojer H, Backstrand B, Borch K, Larsson J. Evaluation of preoperative computed tomography in gastric malignancy. Surgery 1991;109:132–5
Ziegler K, Sanft C, Zimmer T, Zeitz M, Felsenberg D, Stein H, et al. Comparison of computed tomography, endosonography, and intraoperative assessment in TN staging of gastric carcinoma. Gut 1993;34:604–10
Nattermann C, Dancygier H. Endosonography in diagnosis and staging of malignant tumors of the stomach. A prospective comparative study between endosonography, computerized tomography and conventional ultrasonography. Z Gastroenterol 1993;31:719–26
Wakelin SJ, Deans C, Crofts TJ, Allan PL, Plevris JN, Paterson-Brown S. A comparison of computerised tomography, laparoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound in the preoperative staging of oesophago-gastric carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 2002;41:161–7
Pauwels EK, Sturm EJ, Bombardieri E, Cleton FJ, Stokkel MP. Positron-emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. Part I. Biochemical uptake mechanism and its implication for clinical studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2000;126:549–59
Ak I, Stokkel MP, Pauwels EK. Positron emission tomography with 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in oncology. Part II. The clinical value in detecting and staging primary tumours. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2000;126:560–74
Gambhir SS, Czernin J, Schwimmer J, Silverman DH, Coleman RE, Phelps ME. A tabulated summary of the FDG PET literature. J Nucl Med 2001;42(Suppl):1S–93S
Kole AC, Plukker JT, Nieweg OE, Vaalburg W. Positron emission tomography for staging oesophageal and gastroesophageal malignancy. Br J Cancer 1998;78:521–27
Mcateer D, Wallis F, Couper G, Norton M, Welch A, Bruce D, et al. Evaluation of 18F-FDG positron emission tomography in gastric and oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Radiol 1999;72:525–9
Lerut T, Flamen P, Ectors N, Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Hiele M. Histopathologic validation of LN staging with FDG-PET scan in cancer of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: a prospective study based on primary surgery with extensive lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg 2000;232:743–52
Stahl A, Ott K, Weber WA, Becker K, Link T, Siewert JR. FDG PET imaging of locally advanced gastric carcinomas: correlation with endoscopic and histopathological findings. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:288–95
De Potter T, Flamen P, Van Cutsem E, Penninckx F, Filez L, Bormans G. Whole-body PET with FDG for the diagnosis of recurrent gastric cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:525–29
Kim B, Lee J, Yang W, Lee J, Cheon G, Choi C, et al. Findings of F-18 FDG whole body PET in patients with stomach cancer. Korean J Nucl Med 2001;35:301–12
Mochiki E, Kuwano H, Katoh H, Asao T, Oriuchi N, Endo K. Evaluation of 18F-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography for gastric cancer. World J Surg 2004;28:247–53
Yeung HW, Macapinlac H, Karpeh M, Finn RD, Larson SM. Accuracy of FDG-PET in gastric cancer. Preliminary experience. Clin Positron Imaging 1998;1:213–21
von Schulthess GK. Clinical PET and PET/CT Imaging in body oncology. In: von Schulthess GK (ed) Clinical molecular anatomic imaging. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott; 2003, p 249
Kim S, Chung JK, Kim BT, Kim SJ, Jeong JM, Lee DS, et al. Relationship between gastrointestinal F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation and gastrointestinal symptoms in whole-body PET. Clin Positron Imaging 1999;2(5):273–9
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma–2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer 1998;1:10–24
Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA. Tumors of the stomach. In: WHO classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics. Tumors of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press; 2000:38–52
Fukagawa T, Sasako M, Mann GB, Sano T, Katai H, Maruyama K, et al. Immunohistochemically detected micrometastases of the lymph nodes in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer 2001;92:753–60
Vesselle H, Schmidt RA, Pugsley JM, Li M, Kohlmyer SG, Vallires E, et al. Lung cancer proliferation correlates with [F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by positron emission tomography. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:3837–44
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Cancer Center (0221080). The authors thank Mr. Woo Jae Won, Mr. Young Seok Kim, Mr. Yong Geun Kim and Mr Sang Hyuk Yoon for their excellent technical and generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Seok-Ki Kim and Keon Wook Kang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SK., Kang, K.W., Lee, J.S. et al. Assessment of lymph node metastases using 18F-FDG PET in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33, 148–155 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1887-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1887-8