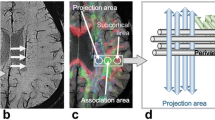
Abstract
Purpose
Accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common form of dementia, remains difficult. In order to assess whether fully automated stereotactic surface projection (3D-SSP) presentation contributes to the diagnosis of AD by single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), we investigated the diagnostic accuracy of transaxial display with and without 3D-SSP analysis as well as the correlation between cerebral perfusion in different cortical areas and the mini mental score (MMS).
Methods
Seventy-two patients referred because of cognitive impairment were included in the study. According to the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke (NINCDS) and the Alzheimer’s disease and Related Disorders Association (ADRDA) criteria, 27 patients were diagnosed as having probable AD while 45 were classified as non-AD patients. 3D-SSP was used to quantify the regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) acquired from SPECT imaging.
Results
Compared with the transaxial section presentation alone, 3D-SSP presentation improved the area under the receiver operating curve (p<0.05) as well as intra-observer (k=0.73 vs 0.88) and inter-observer (k=0.50 vs 0.84) reproducibility. Upon normalisation of regional to thalamic activity, multiple regression analysis revealed a strong correlation between the MMS and rCBF in the right parietal cortex (p=0.002).
Conclusion
Addition of 3D-SSP to the transaxial section display of ECD-SPECT studies improves the reproducibility and the diagnostic performance in respect of AD in patients with cognitive impairment and provides a valid tool for assessment of the severity of cortical perfusion abnormalities in such patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Small GW, Rabins PV, Barry PP, Buckholtz NS, DeKosky ST, Ferris SH, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer disease and related disorders. Consensus statement of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the American Geriatrics Society. J Am Med Assoc 1997;278:1363–71.
Lautenschlager N, Foley EJ, Haupt M, Zimmer R, Farrer LA, Kurz A. A systematic genetic-epidemiologic family study of patients with Alzheimer disease—experience with the MIRAGE study in Germany. Z Gerontol 1994;27:341–5.
Hebert LE, Beckett LA, Scherr PA, Evans DA. Annual incidence of Alzheimer disease in the United States projected to the years 2000 through 2050. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2001;15:169–73.
Messa C, Perani D, Lucignani G, Zenorini A, Zito F, Rizzo G, et al. High-resolution technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT in patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease: comparison with fluorine-18-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 1994;35:210–6.
Mielke R, Pietrzyk U, Jacobs A, Fink GR, Ichimiya A, Kessler J, et al. HMPAO SPET and FDG PET in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia: comparison of perfusion and metabolic pattern. Eur J Nucl Med 1994;21:1052–60.
Ishii K, Sasaki M, Sakamoto S, Yamaji S, Kitagaki H, Mori E. Tc-99m ethyl cysteinate dimer SPECT and 2-[F-18]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose PET in Alzheimer’s disease. Comparison of perfusion and metabolic patterns. Clin Nucl Med 1999;24:572–5.
Masterman DL, Mendez MF, Fairbanks LA, Cummings JL. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of technetium 99-HMPAO SPECT in discriminating Alzheimer’s disease from other dementias. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 1997;10:15–21.
Bartenstein P, Minoshima S, Hirsch C, Buch K, Willoch F, Mosch D, Schad D, Schwaiger M, Kurz A. Quantitative assessment of cerebral blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease by SPECT. J Nucl Med 1997;38:1095–101.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;34:939–44.
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Koeppe RA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 1995;36:1238–48.
Metz CE. ROC methodology in radiologic imaging. Invest Radiol 1986;21:720–33.
Jobst KA, Barnetson LP, Shepstone BJ. Accurate prediction of histologically confirmed Alzheimer’s disease and the differential diagnosis of dementia: the use of NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-III-R criteria, SPECT, X-ray CT, and Apo E4 in medial temporal lobe dementias. Oxford Project to Investigate Memory and Aging. Int Psychogeriatr 1998;10:271–302.
Lim A, Tsuang D, Kukull W, Nochlin D, Leverenz J, McCormick W, et al. Clinico-neuropathological correlation of Alzheimer’s disease in a community-based case series. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999;47:564–9.
Lopez OL, Litvan I, Catt KE, Stowe R, Klunk W, Kaufer DI, et al. Accuracy of four clinical diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative dementias. Neurology 1999;53:1292–9.
Hogervorst E, Bandelow S, Combrinck M, Irani S, Smith A. The validity and reliability of 6 sets of clinical criteria to classify Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in cases confirmed post-mortem: added value of a decision tree approach. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2003;16:170–80.
Sjobeck M, Englund E. Alzheimer’s disease and the cerebellum: a morphologic study on neuronal and glial changes. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2001;12:211–8.
Pickut BA, Dierckx RA, Dobbeleir A, Audenaert K, Van Laere K, Vervaet A, De Deyn PP. Validation of the cerebellum as a reference region for SPECT quantification in patients suffering from dementia of the Alzheimer type. Psychiatry Res 1999;90:103–12.
Heiss WD, Kessler J, Szelies B, Grond M, Fink G, Herholz K. Positron emission tomography in the differential diagnosis of organic dementias. J Neural Transm Suppl 1991;33:13–9.
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. Preserved pontine glucose metabolism in Alzheimer disease: a reference region for functional brain image (PET) analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1995;19:541–7.
Blesa R, Mohr E, Miletich RS, Hildebrand K, Sampson M, Chase TN. Cerebral metabolic changes in Alzheimer’s disease: neurobehavioral patterns. Dementia 1996;7:239–45.
Piert M, Koeppe RA, Giordani B, Berent S, Kuhl DE. Diminished glucose transport and phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease determined by dynamic FDG-PET. J Nucl Med 1996;37:201–8.
Rodriguez G, Vitali P, Calvini P, Bordoni C, Girtler N, Taddei G, et al. Hippocampal perfusion in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatry Res 2000;100:65–74.
Karbe H, Kertesz A, Davis J, Kemp BJ, Prato FS, Nicholson RL. Quantification of functional deficit in Alzheimer’s disease using a computer-assisted mapping program for 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT. Neuroradiology 1994;36:1–6.
Martin AJ, Friston KJ, Colebatch JG, Frackowiak RS. Decreases in regional cerebral blood flow with normal aging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991;11:684–9.
Soonawala D, Amin T, Ebmeier KP, Steele JD, Dougall NJ, Best J, et al. Statistical parametric mapping of 99mTc-HMPAO-SPECT images for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: normalizing to cerebellar tracer uptake. Neuroimage 2002;17:1193–202.
Ishii K, Willoch F, Minoshima S, Drzezga A, Ficaro EP, Cross DJ, Kuhl DE, Schwaiger M. Statistical brain mapping of 18F-FDG PET in Alzheimer’s disease: validation of anatomic standardization for atrophied brains. J Nucl Med 2001;42:548–57.
DeKosky ST, Shih WJ, Schmitt FA, Coupal J, Kirkpatrick C. Assessing utility of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan in Alzheimer disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 1990;4:14–23.
Elgh E, Sundstrom T, Nasman B, Ahlstrom R, Nyberg L. Memory functions and rCBF 99mTc-HMPAO SPET: developing diagnostics in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:1140–8.
Colloby SJ, Fenwick JD, Williams ED, Paling SM, Lobotesis K, Ballard C, et al. A comparison of 99mTc-HMPAO SPET changes in dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease using statistical parametric mapping. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:615–22.
Imran MB, Kawashima R, Awata S, Sato K, Kinomura S, Ono S, et al. Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT in the evaluation of Alzheimer’s disease: correlation between neuropsychiatric evaluation and CBF images. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;66:228–32.
Hirsch C, Bartenstein P, Minoshima S, Mosch D, Willoch F, Buch K, et al. Reduction of regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: evaluation of an observer-independent analytic approach. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 1997;8:98–104.
Jagust WJ, Haan MN, Reed BR, Eberling JL. Brain perfusion imaging predicts survival in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1998;51:1009–13.
Ishii K, Mori T, Hirono N, Mori E. Glucose metabolic dysfunction in subjects with a clinical dementia rating of 0.5. J Neurol Sci 2003;15:71–4.
Friedland RP, Budinger TF, Ganz E, Yano Y, Mathis CA, Koss B, et al. Regional cerebral metabolic alterations in dementia of the Alzheimer type: positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1983;7:590–8.
Hoffman JM, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Hanson M, Crain B, Hulette C, Earl N, Coleman RE. FDG PET imaging in patients with pathologically verified dementia. J Nucl Med 2000;41:1920–8.
Nagata K, Maruya H, Yuya H, Terashi H, Mito Y, Kato H, et al. Can PET data differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from vascular dementia? Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000;903:252–61.
Steinling M, Defebvre L, Duhamel A, Lecouffe P, Lavenu I, Pasquier F, Charpentier P. Is there a typical pattern of brain SPECT imaging in Alzheimer’s disease? Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2001;12:371–8.
Kalaria R. Similarities between Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 2002;203–4:29–34.
Bartels SJ, Horn SD, Smout RJ, Dums AR, Flaherty E, Jones JK, et al. Agitation and depression in frail nursing home elderly patients with dementia: treatment characteristics and service use. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2003;11:231–8.
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Kragh-Sorensen P. Prevalence and characteristics of dementia in Parkinson disease: an 8-year prospective study. Arch Neurol 2003;60:387–92.
Hanyu H, Asano T, Kogure D, Abe S, Iwamoto T, Takasaki M. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using brain SPECT with three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2001;41:582–7.
Small GW, Komo S, La Rue A, Saxena S, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, et al. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease by combining apolipoprotein E and neuroimaging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1996;802:70–8.
Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Yun LS, Chen K, Bandy D, Minoshima S, et al. Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer’s disease in persons homozygous for the epsilon 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N Engl J Med 1996;334:752–8.
Kennedy AM, Frackowiak RS, Newman SK, Bloomfield PM, Seaward J, Roques P, et al. Deficits in cerebral glucose metabolism demonstrated by positron emission tomography in individuals at risk of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 1995;186:17–20.
Minoshima S, Giordani B, Berent S, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 1997;42:85–94.
Herholz K, Schopphoff H, Schmidt M, Mielke R, Eschner W, Scheidhauer K, et al. Direct comparison of spatially normalized PET and SPECT scans in Alzheimer’s disease. J Nucl Med 2002;43:21–6.
van Dyck CH, Lin CH, Smith EO, Wisniewski G, Cellar J, Robinson R, et al. Comparison of technetium-99m-HMPAO and technetium-99m-ECD cerebral SPECT images in Alzheimer’s disease. J Nucl Med 1996;37:1749–55.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Mont-Godinne University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, BNT., Minoshima, S., George, J. et al. Diagnosis of suspected Alzheimer’s disease is improved by automated analysis of regional cerebral blood flow. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31, 1487–1494 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-004-1597-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-004-1597-7