Abstract.
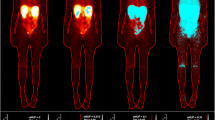
Pre-therapeutic metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scans can be performed using labelling with either iodine-123 or iodine-131. 123I-MIBG scans provide better image quality and count statistics, while 131I-MIBG allows registration of tracer kinetics over a longer period. The aim of this study was to determine how much information about the 131I-MIBG therapy total body dose according to the MIRD formalism can be gathered from 123I-MIBG pre-therapy scans. Thirty-eight 131I-MIBG therapies administered to a total of 15 patients suffering from neuroblastoma (n=6), carcinoid tumours (n=5), phaeochromocytoma (n=3) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (n=1) were included. The mean administered activity was 5.3 GBq (SD 2.4 GBq). Three biplanar 123I-MIBG total body scans were taken only once before a series of therapies while three biplanar 131I-MIBG scans were taken after each therapy. Attenuation correction was performed taking into account the difference in attenuation between 123I and 131I. Using the MIRD formalism, the total body dose to the patient was calculated on the basis of: (1) a single exponential fit drawn through the data from the 123I-MIBG pre-therapy scans, (2) a bi-exponential fit through the combined data of 123I-MIBG pre-therapy and 131I-MIBG post-therapy scans. The mean total body dose calculated in our study was significantly higher for patients suffering from neuroblastoma (mean±SD 0.37±0.21 mGy/MBq) than for patients suffering from phaeochromocytoma (0.08±0.02 mGy/MBq), carcinoid tumours (0.07±0.01 mGy/MBq) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (0.09 mGy/MBq). The correlation coefficient between the dose calculated on the basis of the 123I-MIBG pre-therapy scans and the subsequent 131I-MIBG therapy was 0.93 when a correction factor of 1.26 was taken into account. When considering all following therapies, the correlation was 0.85 and the correction factor, 1.20. Our results show that it is feasible to use data from pre-therapy 123I-MIBG scans to calculate the total body dose of the subsequent 131I-MIBG therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monsieurs, M., Brans, B., Bacher, K. et al. Patient dosimetry for 131I-MIBG therapy for neuroendocrine tumours based on 123I-MIBG scans. Eur J Nucl Med 29, 1581–1587 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-002-0973-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-002-0973-4