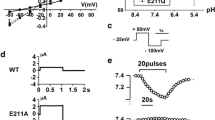
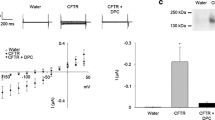
Abstract
ClC-5 chloride channels and epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) are present in many cell types including airway and retinal epithelia. Since ENaC activity is known to be affected by chloride transport, we co-injected Xenopus oocytes with cRNAs encoding ENaC and ClC-5 to investigate whether channel currents are impacted by heterologous co-expression of these proteins. ClC-5 currents were not detectably affected by co-expression with ENaC, whereas amiloride-sensitive ENaC currents were significantly lower compared to control oocytes expressing ENaC alone. Co-expression of ENaC with cRNA sequences encoding non-conducting fragments of ClC-5 revealed that the amino acid sequence region between positions 347 and 647 was sufficient for inhibition of ENaC currents. Co-expression of ENaC and another transport protein, the sodium dicarboxylate co-transporter (NaDC-1), did not affect ENaC currents. To test whether the inhibitory effects of ClC-5 were specific for ENaC, ClC-5 was also co-expressed with CFTR. CFTR currents were also inhibited by co-expression with ClC-5, whereas ClC-5 currents were unaffected. Western blot analysis of biotinylated oocyte surface membranes revealed that the co-expression of ClC-5 with ENaC, CFTR, or NaDC-1 decreased the abundance of these proteins at the surface membrane. We conclude that overexpression of ClC-5, specifically amino acids 347–647, can alter the normal translation or trafficking of ENaC and other ion transport proteins by a mechanism that is independent of the chloride conductance of ClC-5.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Accardi C. Miller (2004) ArticleTitleSecondary active transport mediated by a prokaryotic homologue of CLC Cl- channels Nature 427 803B–807B Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02314
S. Blaug R. Quinn J. Quong S. Jalickee S.S. Miller (2003) ArticleTitleRetinal pigment epithelial function: a role for CFTR? Doc Ophthalmol. 106 43–50
M. Briel R. Greger K. Kunzelmann (1998) ArticleTitleCl− transport by cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) contributes to the inhibition of epithelial Na+ channels (ENaCs) in Xenopus oocytes expressing CFTR and ENaC J. Physiol. 508 825–836 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.825bp.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjtlShurc%3D Occurrence Handle9518736
C.M. Canessa L. Schild G. Buell B. Thorens I. Gautschl J.D. Horisberger B.C. Rossier (1994) ArticleTitleAmiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits Nature 367 463–467 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXitlymsL4%3D Occurrence Handle8107805
H. Chabot M.F. Vives A. Dagenais C. Grygorczyk Y. Berthiaume R. Grygorczyk (1999) ArticleTitleDownregulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by CFTR co-expressed in Xenopus oocytes is independent of Cl− conductance J. Membrane Biol. 169 175–188 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002329900529 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvF2ru7w%3D
J. Chillaron R. Estevez I. Samarzija S. Waldegger X. Testar F. Lang A. Zorzano A. Busch M. Palacin (1997) ArticleTitleAn intracellular trafficking defect in type I cystinuria rBAT mutants M467T and M467K J. Biol. Chem. 272 9543–9549 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.272.14.9543 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXisVGqtrs%3D Occurrence Handle9083097
O. Devuyst P. Christie P.J. Courtoy R. Beauwens R.V. Thakker (1999) ArticleTitleIntra-renal and subcellular distribution of the human chloride channel, ClC-5, reveals a pathophysiological basis for Dent’s disease Hum. Mol. Genet. 8 247–257 Occurrence Handle10.1093/hmg/8.2.247 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXht12itrY%3D Occurrence Handle9931332
R. Dutzler E.B. Campbell M. Cadene B.T. Chait R. MacKinnon (2002) ArticleTitleX-ray structure of a ClC chloride channel at 3.0 AÅ reveals the molecular basis of anion selectivity Nature 415 287–294 Occurrence Handle10.1038/415287a Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XptlWksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11796999
R.D. Edmonds I.V. Silva W.B. Guggino R.B. Butler P.L. Zeitlin C.J. Blaisdell (2002) ArticleTitleClC-5: Ontogeny of an alternative chloride channel in respiratory epithelia Am. J. Physiol. 282 L501–L507 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xit1Ght70%3D
R. Estevez T.J. Jentsch (2002) ArticleTitleClC chloride channels: correlating structure with function Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12 531–539 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-440X(02)00358-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvF2rurw%3D Occurrence Handle12163078
P. Fong G. Cooper (2003) ArticleTitleRelationship between intracellular pH and chloride in Xenopus oocytes expressing the chloride channel CIC-0 Amer. J. Physiol. 284 C331–C338
T. Friedrich T. Breiderhoff T.J. Jentsch (1999) ArticleTitleMutational analysis demonstrates that ClC-4 and ClC-5 directly mediate plasma membrane currents J. Biol. Chem. 274 896–902 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.274.2.896 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtFyisw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9873029
W. Günther A. Luchow F. Cluzeaud A. Vandewalle T.J. Jentsch (1998) ArticleTitleClC-5, the chloride channel mutated in Dent’s disease, colocalizes with the proton pump in endocytotically active kidney cells Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 8075–8080 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.95.14.8075 Occurrence Handle9653142
R. Grygorczyk H. Chabot D.H. Malinowska J. Cuppoletti (2001) ArticleTitleDownregulation of ENaC by ClC-2 chloride channel in Xenopus oocytes Pediatr. Pulmonol. Suppl. 22 84
J.D. Horisberger (2003) ArticleTitleENaC-CFTR interactions: the role of electrical coupling of ion fluxes explored in an epithelial cell model Pfluegers Arch. 445 522–528 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXis1GnsbY%3D
C. Isnard-Bagnis N. Da Silva V. Beaulieu A.S. Yu D. Brown S. Breton (2003) ArticleTitleDetection of ClC-3 and ClC-5 in epididymal epithelium: immunofluorescence and RT-PCR after LCM Am J. Physiol. 284 C220–C232 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXntVSjtw%3D%3D
R. Iyer T.M. Iverson A. Accardi C. Miller (2002) ArticleTitleA biological role for prokaryotic ClC chloride channels Nature 419 715–718 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvVyrtr0%3D Occurrence Handle12384697
H.L. Ji M.L. Chalfant B. Jovov J.P. Lockhart S.B. Parker C.M. Fuller B.A. Stanton D.J. Benos (2000) ArticleTitleThe cytosolic termini of the βγ- and γ-ENaC subunits are involved in the functional interactions between cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and epithelial sodium channel J. Biol. Chem. 275 27947–27956 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmsVKksL0%3D Occurrence Handle10821834
Q. Jiang J. Li R. Dubroff Y.J. Ahn J.K. Foskett J. Englehardt T.R. Kleyman (2000) ArticleTitleEpithelial sodium channels regulate cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channels in Xenopus oocytes J. Biol. Chem. 275 13266–13274 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.275.18.13266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtFyksLw%3D Occurrence Handle10788432
B. Jovov K.L. Marrs D.J. Benos E.M. Schwiebert (1999) ArticleTitleExpression of ClC chloride channels in human airway epithelia Pediatr. Pulmonol. Suppl. 19 191
A.A. Konstas J.P. Koch C. Korbmache (2003) ArticleTitlecAMP-dependent activation of CFTR inhibits the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) without affecting its surface expression Pfuegers Arch 455 513–521
J. König R. Schreiber T. Voelcker M. Mall K. Kunzelmann (2001) ArticleTitleThe cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) inhibits ENaC through an increase in the intracellular Cl− conductance EMBO Rep. 2 1047–1051 Occurrence Handle10.1093/embo-reports/kve232 Occurrence Handle11606421
K. Kunzelmann (2003) ArticleTitleENac is inhibited by an increase in the intracellular Cl− concentration mediated through activation of Cl− channels Pfluegers Arch. 445 504–512 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXis1Gnsbg%3D
S. Lindenthal S. Schmieder J. Ehrenfeld N.K. Wills (1997) ArticleTitleCloning and functional expression of a ClC chloride channel from the renal cell line A6 Am. J. Physiol. 275 C1176–C1185
S.E. Lloyd S.H. Pearce S.E. Fisher K. Steinmeyer B. Schwappach S.J. Scheinman B. Harding A. Bolino M. Devoto P. Goodyer S.P. Rigden O. Wrong T.J. Jentsch I.W. Craig R.V. Thakker (1996) ArticleTitleA common molecular basis for three inherited kidney stone diseases Nature 379 445–449 Occurrence Handle10.1038/379445a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XovVagsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8559248
V.A. Luyckx P.O. Goda D.B. Mount T. Nishio A. Hall SC. Hebert T.G. Hammond A.S. Yu (1998) ArticleTitleIntrarenal and subcellular localization of rat ClC5 Am. J. Physiol. 275 F761–F769 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnsF2ktbo%3D Occurrence Handle9815133
M. Mall B.R. Grubb J.R. Harkema W.K. O’Neal R.C. Boucher (2004) ArticleTitleIncreased airway epithelial Na+ absorption produces cystic fibrosis-like lung disease in mice Nat. Med. 10 487–493 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm1028 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjsF2jtL8%3D Occurrence Handle15077107
P.B. McCray SuffixJr. J.D. Bettencourt J. Bastacky (1992) ArticleTitleDeveloping bronchopulmonary epithelium of the human fetus secretes fluid Am. J. Physiol. 262 L270–L279 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XitFWks74%3D Occurrence Handle1372486
M. Mirshahi C. Nicolas S. Mirshahi N. Golestaneh F. d’Hermies M.K. Agarwal (1999) ArticleTitleImmunochemical analysis of the sodium channel in rodent and human eye Exp. Eye. Res 69 21–32 Occurrence Handle10.1006/exer.1999.0675 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvVOns7g%3D Occurrence Handle10375446
L. Mo H.L. Hellmich P. Fong T. Wood J. Embesi N.K. Wills (1999) ArticleTitleComparison of amphibian and human ClC-5: Similarity of functional properties and inhibition by external pH J. Membrance Biol. 168 253–264 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002329900514 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXisFWnsrc%3D
L. Mo W. Xiong T. Qian H. Sun N.K. Wills (2004) ArticleTitleCo-expression of complementary fragments of ClC-5 and restoration of chloride channel function in a Dent’s disease mutation Am. J. Physiol. 286 C79–C89 Occurrence Handle10.1152/ajpcell.00009.2003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXot1Whuw%3D%3D
G. Nagel T. Szellas J.R. Riordan T. Friedrich K. Hartung (2001) ArticleTitleNon-specific activation of the epithelium sodium channel by the CFTR chloride channel EMBO Rep. 2 249–254 Occurrence Handle10.1093/embo-reports/kve045 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXks1aktbc%3D Occurrence Handle11266369
A.M. Pajor N. Sun H.G. Valmonte (1998) ArticleTitleMutational analysis of histidine residues in the rabbit Na+ dicarboxylate co-transporter NaDC-1 Biochem. J. 331 257–264 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXisVWkt7k%3D Occurrence Handle9512488
N. Piwon W. Gunther M. Schwake M.R. Bosl T.J. Jentsch (2000) ArticleTitleClC-5 Cl−-channel disruption impairs endocytosis in a mouse model for Dent’s disease Nature. 408 369–373 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35042597 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosVertLY%3D Occurrence Handle11099045
P.M. Reddy M.M. Quinton (2003) ArticleTitleFunctional interaction of CFTR and ENaC in sweat glands Pfluegers Arch. 455 499–503
H. Sakamoto Y. Sado L. Naito T.H. Kwon S. Inoue K. Endo M. Kawasaki S. Uchida S. Nielsen S. Sasaki F. Marumo (1999) ArticleTitleCellular and subcellular immunolocalization of ClC-5 channel in mouse kidney: colocalization with H+ -ATPase Am. J. Physiol. 277 F957–F965 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXps1Ok Occurrence Handle10600943
E.M. Schwiebert D.J. Benos M.E. Egan M.J. Stutts W.B. Guggino (1999) ArticleTitleCFTR is a conductance regulator as well as a chloride channel Physiol. Rev. 79 S145–S166 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhs1Orsrw%3D Occurrence Handle9922379
J.N. Snouwaert K.K. Brigman A.M. Latour N.N. Malouf R.C. Boucher O. Smithies B.H. Koller (1992) ArticleTitleAn animal model for cystic fibrosis made by gene targeting Science 257 1073–1088 Occurrence Handle1509258
W. Stühmer (1998) ArticleTitleElectrophysiologic recordings from Xenopus oocytes Methods Enzymol 293 280–300 Occurrence Handle9711614
J. Sturgess J. Imrie (1982) ArticleTitleQuantitative evaluation of the development of tracheal submucosal glands in infants with cystic fibrosis and control infants Am. J. Patholl. 106 303–311 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2C2MjksVc%3D
A. Vandewalle F. Cluzeaud K.C. Peng M. Bens A. Luchow W. Günther T.J. Jentsch (2001) ArticleTitleTissue distribution and subcellular localization of the ClC-5 chloride channel in rat intestinal cells Am. J. Physiol. 280 C373–C381 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtVWqu74%3D
S.S. Wang O. Devuyst P.J. Courtoy X.T. Wang H. Wang Y. Wang R.V. Thakker S. Guggino W.B. Guggino (2000) ArticleTitleMice lacking renal chloride channel, ClC-5, are a model for Dent’s disease, a nephrolithiasis disorder associated with defective receptor-mediated endocytosis Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 2937–2945 Occurrence Handle10.1093/hmg/9.20.2937 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjt1Sr Occurrence Handle11115837
T. Weng B.F. Godley G. Jin N. Mangini E.G. Kennedy A.S. Yu N.K. Wills (2002) ArticleTitleOxidant and antioxidant modulation of chloride channels expressed in human retinal pigment epithelium Am. J. Physiol. 283 C839–C849 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XntFOntbY%3D
T. Weng L. Mo H.L. Hellmich A.S.L. Yu T. Wood N.K. Wills (2001) ArticleTitleExpression and regulation of C1C-5 chloride channels: effects of antisense and oxidants Am. J. Physiol. 280 C1511–C1520 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksFKnu70%3D
N.K. Wills T. Weng L. Mo H.L. Hellmich A. Yu S. Buchheit B.F. Godley (2000) ArticleTitleChloride channel expression in cultured human RPE cells: response to oxidative stress Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41 4247–4255 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FmtlOhug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11095622
X. Yao A. Pajor (2000) ArticleTitleThe transport properties of the human renal Na+-dicarboxylated cotransporter under voltage clamp conditions Am. J. Physiol. 279 F54–F64 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltlyqt78%3D
X. Yao A. Pajor (2002) ArticleTitleArginine-349 and aspartate-373 of the Na+/dicarboxylate cotransporter are conformationally sensitive residues Biochemistry 41 1083–1090 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi0156761 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptlWns7Y%3D Occurrence Handle11790133
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr. Thomas Jentsch for donation of human ClC-5, Drs. Bernard Rossier, and Alex Puoti for Xenopus ENaC subunits, Dr. Cecilia Canessa for rat ENaC constructs, and Dr. Mouhamed Awayda for HA-tagged αENaC cDNA. Thanks also to Hong Sun for technical support. We are grateful to Dr. Ana Pajor for providing the rabbit Na+/dicarboxylate cotransporter NaDC-1, anti-NaDC-1 antibody, and related advice and assistance, and for reading a preliminary version of this manuscript. This work was supported by the John Sealy Memorial Endowment for Biomedical Research and NIH grant # DK53352 to N.W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, L., Wills, N. ClC-5 Chloride Channel Alters Expression of the Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC). J Membrane Biol 202, 21–37 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0717-4
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0717-4