Abstract
Objective: The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) disposition of yohimbine (YO) and 11-hydroxy-yohimbine (11-OH-YO), after oral administration of a single dose of YO (0.65 mg · kg−1) were studied in young and older healthy subjects and in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD).
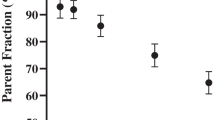
Results: Plasma disposition of YO displayed large variability; no significant differences among subject groups were observed. In contrast, 11-OH-YO Cmax and AUC were significantly lower in the older normal subjects than in the young normal or AD subjects. A strong positive correlation between CSF and plasma YO concentrations was observed. A weak positive correlation between CSF and plasma concentrations of 11-OH-YO was also observed. CSF to plasma concentration ratios for yohimbine and 11-OH-YO were low (approximately 2%).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 September 1995 / Accepted in revised form: 4 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corre, P., Peskind, E., Chevanne, F. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma disposition of yohimbine and 11-hydroxy-yohimbine in young and older healthy subjects, and Alzheimer's disease patients. E J Clin Pharmacol 52, 135–138 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050262
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050262