Abstract
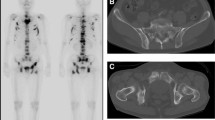
A 16-year-old male patient was evaluated with Tc-99m Diethylenetriamine-pentaacetic acid (DTPA) and Tc-99m 2–3 Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy for renal failure secondary to renal calculi. The uptake in the renal cortex was significantly decreased both on DMSA and DTPA studies. Uptake calculation on DMSA scintigraphy in the kidneys disclosed values of less than 5 %. The activity in the liver and bone was significantly increased. A bone scan performed with Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate (MDP) revealed increased bone uptake with decreased soft tissue activity. Findings on bone scan were compatible with super scan, most likely due to renal osteodystrophy. This case illustrates the altered biodistribution of Tc-99m DMSA and a shift of the radiopharmaceutical to the bone marrow which is mot likely related to colloid formation due to changes in mineral balance in patients with renal failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin TH, Khentigan A, Winchell HS: A Tc-99m-chelate substitute for organoradiomercurial renal agents.J Nucl Med 15: 34–35, 1974
Ikeda I, Inoue O, Kurato K: Chemical and biological studies on Tc-99m DMS-I: Formation of complexes by four different methods.Int J Nucl Bio 4: 56, 1977
Kowalsky RJ, Perry JR: Radiopharmaceuticals in Nuclear Medicine, Appleton and Lange, pp 329–333, 1987
Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ: Essentials of Nuclear Medicine Imaging, WB Saunders Company, pp 237–239, 1991
Kawamura J, Hosokawa S, Fujita T, et al: Validity of Tc-99m-dimercaptosuccinic acid renal uptake for an assessment of individual kidney function.J Urol 119: 305–309, 1978
Kawamura J, Hosokawa S, Yoshida O: Renal function studies using Tc-99m-Dimercaptosuccinic acid.Clin Nucl Med 4: 39–47, 1979
Yee CA, Lee HB, Blaufox MD: Tc-99m DMSA renal uptake: Influence of biochemical and physiologic factors.J Nucl Med 22: 1054–1058, 1981
Moretti JL, Rapir JR, Saccavini JC, et al: 2-3 Dimercaptosuccinic acid chelates: Their structure and biological behavior. In: Raynoaud C (ed.):Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Proceedings of the Third World Congress of Nuclear Medicine and Biology. Paris, Pergamon Press, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çaglar, M., Naldöken, S. Increased bone marrow uptake on Tc-99m DMSA scintigraphy in a patient with renal osteodystrophy. Ann Nucl Med 7, 281–283 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164712
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164712