Abstract
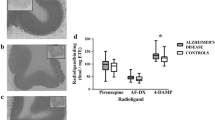
Postmortem cerebral neocortical and hippocampal samples were taken from patients who died with dementia of the Alzheimer type (DAT) and individuals without diagnoses of neurological or psychiatric disease (control). Nicotinic binding was assayed with 20 nM [3H]acetylcholine ([3H]ACh) in the presence of atropine, or with 4 nM (-)-[3H]Nic). Binding of both ligands was lower in the following regions from DAT vs. control brains (P≤0.05): superior, middle and inferior temproal gyri, orbital frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus, pre- and postcentral gyri, inferior parietal lobule, and hippocampal endplate. Values of the correlation coefficient (r's) for binding of the nicotinic cholinergic ligands in these regions ranged from 0.70 to 0.93 (P's<0.05), suggesting that [3H]ACh and (-)-[3H]Nic labeled the same sites in human brain. There was no difference in nicotinic binding in the presubiculum, comparing DAT and control samples (P>0.05). Here too, correlations between binding of the two ligands were statistically significant in control and DAT groups (r's=0.92,P's<0.05). Nicotinic binding measured with [3H]ACh, but not (-)-[3H]Nic, was significantly lower in the H2 (field of Rose) and H1-subiculum areas of DAT samples compared to control. Correlations between binding of the two ligands in these regions ranged from 0.21 to 0.34 for the two groups (P's>0.05). The findings support a loss of neocortical and hippocampal nicotininc cholinergic binding sites in DAT. Further study is necessary to better characterize the regional losses of nicotinic binding in DAT and to resolve the differences in binding measured by [3H]ACh and (-)-[3H]Nic in the H1-subiculum and H2 (field of Rose) regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKhann, G., Drachman, D., Folstein, M., Katzman, R., Price, D., and Stadlan, E. 1984. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services task force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 34:939–944.
Perry, E. K., Gibson, P. H., Blessed, G., Perry, R., and Tomlinson, B. E. 1977. Neurotransmitter enzyme abonormalities in senile dementia: Choline acetyltransferase and glutamic acid decarboxylase activities in necropsy brain tissue. J. Neurol. Sci. 34:247–265.
Terry, R., and Davies, P. 1980. Dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 3:77–95.
Terry, E. 1980. The cholinergic system in old age and Alzheimer's disease. Age and Ageing 9:1–8.
Price, D., Whitehouse, P., Struble, R., Clark, A., Coyle, A., DeLong, M., and Hedreen, J. 1982. Basal forebrain cholinergic systems in Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Neurosci. Commentaries 1:84–92.
Rinne J., Laakso, K., Lonnberg, P., Molsa, P., Paljarvi, L., Rinne, J., Sako, E., and Rinne, U. 1985. Brain muscarinic receptors in senile dementia. Brain Res 336:19–25.
Rossor, M. 1982. Dementia. Lancet II:1200–1204.
Perry, E. and Perry, R. 1980. The cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease. Pages 135–183,in Roberts P. (ed.), Biochemistry of Dementia. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Wilcock, F. G., Esiri, M., Bowen, D., and Smith, C. 1982. Alzheimer's disease: Correlation of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity with the severity of dementia and histologial abnormalities. J. Neurol. Sci. 57:407–417.
Ball, M., Merskey, H., Fisman, M., Fyfe, I., Fox, H., Cape, R., Waller, S., and London, E. 1983. Hippocampal morphometry in Alzheimer dementia: Implications for neurochemical hypothesis. Pages 45–57,in Katzman, R. (ed.), Banbury Report 15: Biological Aspects of Alzheimer's Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories, Long Island, N.Y.
Bowen, D., White, P., Spillane, J., Goodhardt, M., Curzon, G., Iwangoff, P., Meier-Ruge, W., and Davison, A. 1979. Accelerated aging or selective neuronal loss as an important cause of dementia. Lancet I:11–14.
Perry, E. K., Tomlinson, B. E., Blessed, G., Bergmann, K., Gibson, P. H., and Perry, R. H. 1978. Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br. Med. J. II:1457–1459.
Caulfield, M., Straughan, D., Cross, A., Crow, T., and Birdsall, N. 1982. Cortical muscarinic receptor subtypes and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet II:1277.
Davies, P. and Verth, A. 1977. Regional distribution of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in normal and Alzheimer's type dementia brains. Brain Res. 138:385–392.
Gottfries, C-G., Adolfsson, R., Aquilonius, S-M. Carlsson, A., Eckernas, S-A., Nordberg, A., Oreland, L., Svennerholm, L., Wiberg, A., and Winblad, B. 1983. Biochemical changes in dementia disorders of Alzheimer type. Neurobiol. Aging 4:261–271.
Lang, W. and Henke, H. 1983. Cholinergic receptor binding and autoradiography in brains of non-neurological and senile dementia of the Alzheimer-type patients. Brain Res. 267:271–280.
Nordberg, A., Larsson, C., Adolfsson, R., Alafuzoff, I., and Winblad, B. 1983. Muscarinic receptor compensation in hippocampus of Alzheimer patients. J. Neural Transm. 56:13–19.
Palacios, J. 1982. Autoradiographic localization of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the hippocampus of patients with senile dementia. Brain Res. 243:173–175.
Waller, S., Ball, M., Reynolds, M., and London, E. 1986. Muscarinic binding and choline acetyltransferase in postmortem brains of demented patients. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 13S:528–532.
Araujo, D. M., Lapchak, P. A., Robitaille, Y., Gauthier, S., and Quirion, R. 1988. Differential alteration of various cholinergic markers in cortical and subcortical regions of human brain in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 50:1914–1923.
Holman, B. L., Gibson, R. E., Hill, T. C., Eckelman, W. C., Albert, M., and Reba, R. C. 1985. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in Alzheimer's disease:In vivo imaging with iodine 125-labeled 3-quinuclidinyl-4-iodobenzilate with emission tomography. JAMA 254:3063–3066.
Mash, D., Flynn, D., and Potter, L. 1985. Loss of M2 muscarinic receptors in the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease and experimental cholinergic denervation. Science 228:1115–1117.
Nordberg, A., Alafuzoff, I., and Winblad, B. 1986. Muscarinic receptor subtypes in hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease and mixed dementia type. Neurosci. Letters 70:160–164.
Reisine, T., Yamamura, H., Bird, E., Spokes, E., and Enna, S. 1978. Pre- and postsynaptic neurochemical alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 159:477–481.
Rinne, J., Rinne, J., Laakso, K., Paljarvi, L., and Rinne, U. 1984. Reduction in muscarinic receptor binding in limbic areas of Alzheimer's brain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 47:651–652.
Jenni-Eirmann, S., vonHahn, H. P., Honegger, C. G., and Ulrich, J. 1984. Studies on neurotransmitter binding in senile dementia. Gerontology 30:350–358.
Nordberg, A., Adem, A., Nilsson, L., and Winblad, B. 1987. Cholinergic deficits in CNS and peripheral non-neuronal tissue in Alzheimer's dementia. Pages 858–868,in Dowdall M. (ed.), Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cholinergic Function. Ellis Howard Publishers, Sussex, England.
Kellar, K. J., Whitehouse, P. J., Martino-Barrows, A. M., Marcus, K., and Price, D. L. 1987. Muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic binding sites in Alzheimer's disease cerebral cortex. Brain Research 436:62–68.
Nordberg, A. and Winblad, B. 1986. Reduced number of [3H]nicotine and [3H]acetylcholine binding sites in the frontal cortex of Alzheimer brains. Neurosci. Letters 72:115–119.
Shimohama, S., Taniguchi, T., Fujiwara, M., and Kameyama, M. 1986. Changes in nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in Alzheimer-type dementia. J. Neurochem. 46:288–293.
Whitehouse, P. J., Martino, A. M., Antuono, P. G., Lowenstein, P. R., Coyle, J. T., Price, D. L., and Kellar, K. J. 1986. Nicotinic acetylcholine binding sites in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Research 371:146–151.
Whitehouse, P. J., Martino, A. M., Wagster, M. V., Price, D. L., Mayeux, R., Atack, J. R., and Kellar, K. J. 1988. Reductions in [3H]nicotinic acetylcholine binding in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease: An autoradiographic study. Neurology 38:720–723.
Khachaturian, Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 42:1097–1105.
Ball, M. J., Griffin-Brooks, S., MacGregor, J., Nagy, B., Ojalvo-Rose, E., and Fewster, P. H. 1988. Neuropathological definition of Alzheimer's disease: Multivariate analyses in the morphometric distinction between Alzheimer dementia and normal aging. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disorders 2:29–37.
Ball, M. J. 1978. Histotopography of cellular changes in Alzheimer's disease. Pages 89–104,in Nandy K. (ed.), Senile dementia: A biomedical approach. Elsevier Science Publishers, New York.
Schwartz, R. D. and Kellar, K. J. 1983. Nicotinic cholinergic receptor binding sites in the brain: Regulationin vivo. Science 220:214–216.
Schwartz, R. D., McGee, Jr., E., and Kellar, K. J. 1982. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors labeled by [3H]acetylcholine in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 22:56–62.
Davies, P. and Feisullin, S. 1981. Postmortem stability of α-bungarotoxin binding sites in mouse and human brain. Brain Res. 216:449–454.
Morley, B. J., Kemp, G. E., and Salvaterra, P. 1979. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites in the CNS. Life Sci. 24:859–872.
Oswald, R. E. and Freeman, J. A. 1981. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding and central nervous system nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuroscience 6:1–14.
Clarke, P. B. S., Schwartz, R. D., Paul, S. M. Pert, C. B., and Pert, A. 1985. Nicotinic binding in rat brain. Autoradiographic comparison of [3H]acetylcholine, [3H]nicotine and [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin. J. Neurosci. 5:1307–1315.
Larsson, C. and Nordberg, A. 1985. Comparative analysis of nicotine-like receptor-ligand interactions in rodent brain homogenate. J. Neurochem. 45:24–31.
Marks, M. J. and Collins, A. C. 1982. Characterization of nicotinic binding in mouse brain and comparison with the binding of alpha-bungarotoxin and quinuclidinyl benzilate. Mol. Pharmacol. 22:554–564.
Abood, D. M. and Grassi, S. 1986. [3H]Methylcarbamylcholine, a new radioligand for studying brain nicotinic receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 35:4199–4202.
Larsson, C., Nilsson, L., Halén, A. and Nordberg, A. 1986. Subchronic treatment of rats with nicotine: Effects on tolerance and on [3H]acetylcholine and [3H]nicotine binding in the brain. Drug Alc. Depend. 17:37–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
London, E.D., Ball, M.J. & Waller, S.B. Nicotinic binding sites in cerebral cortex and hippocampus in alzheimer's dementia. Neurochem Res 14, 745–750 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964952
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964952