Blood-to-Cell Clearance of 18F-FDG and 11C-MG as Measure of Hepatic Blood Perfusion in Pigs
| 18F-FDG (n = 6) | 11C-MG (n = 6) | |||
| Parameter | Correlation between  and Q, r and Q, r | Relative deviation of  from Q from Q | Correlation between  and Q, r and Q, r | Relative deviation of  from Q from Q |
Measured 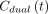 , 60-min; 2-tissue compartmental model for 18F-FDG, 1-tissue compartmental model for 11C-MG , 60-min; 2-tissue compartmental model for 18F-FDG, 1-tissue compartmental model for 11C-MG | 0.60 (P = 0.14) | 0.08 ± 0.09 (P = 0.43) | 0.26 (P = 0.61) | 0.11 ± 0.10 (P = 0.28) |
Measured  , 3-min; 1-tissue compartmental model for both 18F-FDG and 11C-MG , 3-min; 1-tissue compartmental model for both 18F-FDG and 11C-MG | 0.88 (P = 0.02) | 0.10 ± 0.04 (P = 0.08) | 0.58 (P = 0.23) | 0.32 ± 0.08 (P = 0.01) |
Model-derived  , 3-min; 1-tissue compartmental model for both 18F-FDG and 11C-MG , 3-min; 1-tissue compartmental model for both 18F-FDG and 11C-MG | 0.94 (P = 0.01) | 0.19 ± 0.11 (P = 0.13) | 0.77 (P = 0.07) | 0.27 ± 0.12 (P = 0.07) |
 = PET-estimated blood-to-cell clearance of tracer (mL of blood/mL of liver tissue/min); Q = blood perfusion of liver tissue measured by ultrasound transit-time flow meters (mL of blood/mL of liver tissue/min);
= PET-estimated blood-to-cell clearance of tracer (mL of blood/mL of liver tissue/min); Q = blood perfusion of liver tissue measured by ultrasound transit-time flow meters (mL of blood/mL of liver tissue/min);  = measured dual-input time–activity curve (kBq/mL of blood);
= measured dual-input time–activity curve (kBq/mL of blood);  = estimated dual-input time–activity curve (kBq/mL of blood); r = Pearson correlation coefficient for correlation between individual pairs of
= estimated dual-input time–activity curve (kBq/mL of blood); r = Pearson correlation coefficient for correlation between individual pairs of  and Q. P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant correlation. Relative deviation of
and Q. P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant correlation. Relative deviation of  from Q is presented as mean ± SEM (mean deviations with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significantly different from zero; 1-sample t test).
from Q is presented as mean ± SEM (mean deviations with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significantly different from zero; 1-sample t test).




