Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of multiple cycles of 177Lu-DOTA-Evans blue (EB)-TATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) at escalating doses in neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). Methods: Thirty-two NET patients were randomly divided into 3 groups and treated with escalating doses. Group A received 1.17 ± 0.09 GBq/cycle; group B, 1.89 ± 0.53 GBq/cycle; and group C, 3.97 ± 0.84 GBq/cycle. The treatment was planned for up to 3 cycles. Treatment-related adverse events were graded according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 5.0. Treatment response was evaluated according to the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer criteria and modified PERCIST. Results: Administration of PRRT was well tolerated, without life-threatening adverse events (CTCAE grade 4). CTCAE grade 3 hematotoxicity was recorded in 1 patient (16.6%) in group B (thrombocytopenia) and 3 patients (21.4%) in group C (thrombocytopenia in 3, anemia in 1). CTCAE grade 3 hepatotoxicity (elevated aspartate aminotransferase) was recorded in 1 patient in group A (8.3%) and 1 patient in group C (7.1%). No nephrotoxicity was observed. According to the criteria of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer, the overall disease response rates were similar in groups A, B, and C (50.0%, 50.0%, and 42.9%, respectively), and the overall disease control rates were higher in groups B (83.3%) and C (71.5%) than in group A (66.7%). According to modified PERCIST, a lower disease response rate but a similar disease control rate were found. When a comparable baseline SUVmax ranging from 15 to 40 was selected, the percentage change in SUVmax increased slightly in group A (2.1% ± 40.8%) but decreased significantly in groups B and C (−38.7% ± 10.0% and −14.7% ± 20.0%, respectively) after the first PRRT (P = 0.001) and decreased in all 3 groups after the third PRRT (groups A, B, and C: −6.9% ± 42.3%, −49.2% ± 30.9%, −11.9% ± 37.9%, respectively; P = 0.044). Conclusion: Dose escalations of up to 3.97 GBq/cycle seem to be well tolerated for 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE. 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE doses of 1.89 and 3.97 GBq/cycle were effective in tumor control and more effective than 1.17 GBq/cycle.
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a heterogeneous group of tumors originating from the diffuse neuroendocrine system. Data from the registries of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program showed that the incidence of NETs increased 6.4-fold from 1973 to 2012 (1). However, because of the rarity, tumor heterogeneity, nonspecific clinical behavior, and slow growth of NETs, their diagnosis can be delayed even up to 7 y (2,3). Thus, at the time of diagnosis, over 50% of NET cases are at an advanced stage when surgery is no longer advised (4).
NETs are characterized by abundant expression of somatostatin receptor 2, providing an important target for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT). 177Lu-DOTATATE is the most commonly used radiopharmaceutical for PRRT. Although 177Lu-DOTATATE has been approved in Europe and the United States for the treatment of NETs, optimization of the therapeutic efficacy is still ongoing. Evans blue (EB) dye binds reversibly to serum albumin (5,6), which is an excellent candidate carrier to prolong the half-life of rapidly clearing 177Lu-DOTATATE.
177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE is based on a modification of 177Lu-DOTATATE with EB to greatly extend the circulation half-life (7,8). Preclinical studies showed that compared with the similar radioactive dose of 177Lu-DOTATATE, 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE had an approximately 4-fold higher tumor dose and more effective tumor control (7,9). Application in humans also showed about an 8-fold higher tumor dose for 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE than for 177Lu-DOTATATE, but the dose was also 3.2-fold higher in the kidneys and 18.2-fold higher in the bone marrow (10). The results were encouraging even after 1 cycle of PRRT in NET patients (11). In this study, we aimed to further evaluate the safety and efficacy of multiple cycles of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE with escalating doses in the treatment of NETs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
This study was registered at Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03478358) and approved by the Institute Review Board of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Peking Union Medical College. From August 2017 to June 2019, 32 patients with histologically confirmed NETs were recruited for this prospective study. All subjects gave written informed consent. The inclusion criteria were the same as described for our previously published study (11).
The patients were randomly divided into 3 groups using sequentially numbered, opaque sealed envelopes. Group A (7 men and 5 women; mean age, 53 ± 13 y) was treated with 1.17 ± 0.09 GBq (31.6 ± 2.4 mCi) of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE per cycle; group B (4 men and 2 women; mean age, 55 ± 10 y), with 1.89 ± 1.53 GBq (51.1 ± 14.3 mCi); and group C (7 men and 7 women; mean age, 50 ± 10 y), with 3.97 ± 0.84 GBq (107.3 ± 22.7 mCi). A flowchart of the groups is shown in Figure 1.
Participants’ flow chart of groups A–C. PD = progressive disease.
Treatment Regimen and Follow-up
Preparation of DOTA-EB-TATE and labeling of 177Lu were performed as described previously (11,12). The treatments were planned for up to 3 cycles, to be repeated at 8- to 12-wk intervals.
Hematologic parameters, liver function, and kidney function were tested at baseline, 1 wk, and 4 wk after each cycle of treatment. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT was performed at baseline, some days before the second and third cycles of treatment, and 2–3 mo after the last cycle.
Safety and Symptom Evaluation
Treatment-related adverse events were recorded for 8–12 wk after PRRT administration. Hemotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity were graded according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 5.0.
Functional performance was assessed by the criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group at baseline and 8–12 wk after the last cycle of PRRT.
68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT Response Evaluation
The response on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT was evaluated with reference to the criteria of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) and modified PERCIST. All images were evaluated by the same physician, who was masked to the clinical data.
Statistical Analysis
The percentage change in tumor SUVmax was obtained by dividing the change in SUVmax by the baseline SUVmax. Data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 23.0, SPSS; IBM). A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Quantitative data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistics were compared among groups using 1-way ANOVA or nonparametric testing.
RESULTS
Patients
The median number of cycles of PRRT in the 3 groups was 3. In group A, the median cumulative administered activity was 3.5 GBq (range, 2.2–3.7 GBq); all 12 patients received the first and second cycles of PRRT, and 9 (75.0%) received the third cycle. In group B, the median cumulative administered activity was 5.7 GBq (range, 1.9–6.0 GBq); all 6 patients received the first cycle of PRRT, and 5 (83.3%) received the second and third cycles. In group C, the median cumulative administered activity was 10.5 GBq (range, 4.1–14.3 GBq); all 14 patients received the first cycle of PRRT, 13 (92.3%) received the second cycle, and 8 (57.1%) received the third cycle. Baseline characteristics are in Table 1; there were no significant differences among the groups.
Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
Safety Evaluation
Generally, patients tolerated PRRT well, with no immediate adverse effects such as irritating pain, allergy, or fever during administration and no life-threatening adverse events (CTCAE grade 4) during the observation period. Only 1 patient, in group C, had nausea (at a tolerable level) and vomiting several hours after administration, but this patient recovered within 2 wk after every cycle of PRRT. All scheduled laboratory tests were obtained.
Hematotoxicity
No life-threatening CTCAE grade 4 hematotoxicity was observed. In group A, no CTCAE grade 3 hematotoxicity was observed. In group B, CTCAE grade 3 hematotoxicity (thrombocytopenia) was observed in 1 patient (16.6%), who had been diagnosed with grade 2 myelosuppression 2 y previously due to previous radiotherapy. In group C, 3 (21.4%) patients had CTCAE grade 3 hematotoxicity (thrombocytopenia in 3 patients, anemia in 1 patient). Among these 3 patients, platelet counts, which are reported to be preferentially affected after the third cycle of 177Lu-PRRT (13), dropped greatly after the first cycle. All 3 patients had prior exposure to multiple courses of alkylating therapy or sulfatinib/everolimus, which are important predisposing factors toward hematotoxicity (Supplemental Table 1; supplemental materials are available at http://jnm.snmjournals.org) (14).
The changes in white blood cell (WBC) count, hemoglobin, and platelets between baseline and 4 wk after each cycle of treatment are listed in Supplemental Table 2. Significant differences in the percentage change in hemoglobin among the groups were observed in the second and third cycles of PRRT (P < 0.001 and P = 0.015, respectively), with hemoglobin significantly increased in group A (second cycle: 1.8% ± 9.2%, P < 0.001; third cycle: 7.1% ± 12.6%, P = 0.004) and group B (second cycle: 5.3% ± 10.8%, P = 0.001; third cycle: 1.1% ± 11.1%, P = 0.011) when compared with group C (second cycle: −14.1% ± 7.8%; third cycle: −17.2% ± 14.4%). No significant change was observed in WBCs or platelets.
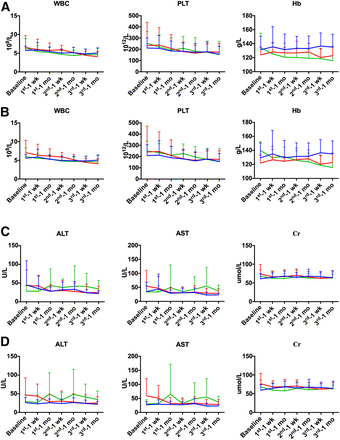
The mean WBC count, platelets, and hemoglobin at baseline, 1 wk, and 4 wk after each cycle of PRRT are shown in Figure 2A. Generally, the mean WBC count, platelets, and hemoglobin fluctuated within the reference ranges and were consistent among all patients and among patients who received 3 cycles of PRRT. Platelets were primarily affected, followed by WBC count and hemoglobin—predominantly after the second PRRT. WBC count and platelets were relatively stable in the 3 groups. Hemoglobin dropped more in group C than in groups A and B.
Changes in WBC, hemoglobin, platelets, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and creatinine at baseline and at 1 and 4 wk after each cycle of PRRT in all patients (A and C) and in patients who completed 3 cycles of PRRT (B and D). Blue line = group A; red line = group B; green line = group C.
Hepatotoxicity
No life-threatening CTCAE grade 4 hepatotoxicity was observed. CTCAE grade 3 hepatotoxicity was recorded for only 1 patient in group A (8.3%) and 1 patient in group C (7.1%). Regarding the patient in group A, disease-related liver dysfunction could not be excluded. This patient had liver dysfunction of unknown cause 6 mo before PRRT and 3 mo later, after cessation of the last cycle of PRRT. Regarding the patient in group C, who had normal baseline liver function, this patient had transient simultaneous rises in serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and bilirubin but recovered before the second cycle of PRRT. This reaction was probably a transient one caused not by radiotoxicity but by squeezing of normal liver tissue by edema and tumor necrosis (Supplemental Table 1).
No significant change in alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase between baseline and 4 wk after each cycle of treatment was observed (Supplemental Table 2). The mean counts for alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase at baseline, 1 wk, and 4 wk after each cycle of PRRT are shown in Figure 2B. Within the reference ranges, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase fluctuated the most and were generally elevated in group C but generally decreased in groups A and B.
Nephrotoxicity
No CTCAE grade 2, 3, or 4 nephrotoxicity was observed (Supplemental Table 1). Significant differences in the percentage change in creatinine among the 3 groups was observed in the first and second cycles of PRRT (P = 0.040, P = 0.033), with decreased creatinine in group B (first cycle: −6.6% ± 16.7%, P = 0.035; second cycle: −10.2% ± 16.6%, P = 0.016) and group C (first cycle: −6.4% ± 19.0%, P = 0.010; second cycle: −6.3 ± 11.0, P = 0.011), as opposed to increased creatine in group A (first cycle: 13.8% ± 21.0%; second cycle: 11.5% ± 18.6%) (Supplemental Table 2).
Response Evaluation
Functional Performance Evaluation
Performance status according to the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group remained stable after therapy. The only exceptions were 2 patients in group C who went from a grade of 2 to a grade of 3.
68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT Response
One patient in group C died after the second PRRT because of disease progression. According to the EORTC criteria, the overall disease response rate was similar among groups 1, 2, and 3 (50.0%, 50.0%, and 42.9%, respectively). The overall disease control rate was higher in groups B (83.3%) and C (71.5%) than in group A (66.7%). According to modified PERCIST, a lower disease response rate but similar disease control rate were found (Supplemental Table 3). Examples of treatment efficacy (partial response) on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT are shown in Figure 3.
Representative images of partial remission in group A (A), group B (B), and group C (C).
For all selected, qualified lesions, the percentage change in SUVmax differed significantly among the 3 groups (P = 0.044) after the third PRRT, with a significant decrease in groups B and C (−37.7% ± 34.2% and −7.6% ± 65.8%, respectively) but an increase in group A (8.1% ± 53.3).
For lesions with a comparable baseline SUVmax, ranging from 15 to 40, the percentage change in SUVmax increased in group A after the first PRRT (2.1% ± 40.8%) but significantly decreased in groups B and C (−38.7% ± 10.0% and −14.7% ± 20.0%, respectively) (P = 0.001). After the third PRRT, the percentage change in SUVmax decreased in all groups (−6.9% ± 42.3%, −49.2% ± 30.9%, and −11.9% ± 37.9% in groups A, B, and C, respectively) (P = 0.044) (Supplemental Table 4). Similar results were observed in patients who received 3 cycles of PRRT (Supplemental Table 5).
Groups B and C had a significantly decreased SUVmax after the first to third PRRTs when compared with baseline tumor SUVmax in patients who received 3 cycles of PRRT (P < 0.05). However, no significant decrease was observed in group A (P > 0.05), indicating poorer tumor control than in groups B and C (Supplemental Table 6).
DISCUSSION
Bone marrow is one of the dose-limiting organs in PRRT. On the basis of a 2-Gy dose limit, the highest feasible dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE would be 34.3 GBq (radiation exposure, 0.0582 ± 0.0137 mSv/MBq (10)). However, the validity of a 2-Gy limit for 177Lu-PRRT was questioned. Bergsma et al. (15) found that patients receiving 4 cycles of 7.4 GBq would already have reached the 2-Gy dose limit. However, salvage PRRT, defined as rechallenge with one or more 177Lu-DOTATATE therapy cycles after 4 initial PRRT cycles, did not increase the risk of hematotoxicity (16–18). Therefore, the maximal dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE based on bone marrow tolerance might be more than 34.3 GBq.
Hematotoxicity is one of the concerning adverse events in PRRT. In this study, CTCAE grade 3 thrombocytopenia was observed in 1 (16.6%) patient in group B, who was diagnosed with grade 2 myelosuppression previously. In group C, 3 (21.4%) patients had CTCAE grade 3 thrombocytopenia. Notably, platelet counts have been reported to be preferentially affected after 3 cycles of 177Lu-PRRT (13). However, in this study, platelet counts dropped greatly after the first cycle of PRRT in these 3 patients with CTCAE grade 3 thrombocytopenia. Their prior exposure to multiple courses of alkylating therapy and sulfatinib/everolimus was an important predisposing factor toward hematotoxicity (14). The CTCAE grade 3/4 hematotoxicity rate of 177Lu-DOTATATE/TOC has been reported to be 3.1%–12.5% (13,15,16,19–24), which is similar to what we observed in group B. However, in a study performed by Brieau et al. (25), the CTCAE grade 3/4 hematotoxicity rate was 30% (thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia in 25%, 15%, and 10%, respectively) among 20 patients who had received prior multiple cycles of chemotherapy. In our study, most patients also had received several therapies before PRRT, including chemotherapy, because PRRT was previously not available in China. 177Lu-PRRT commonly introduces thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia (14), but no CTCAE grade 3/4 neutropenia or anemia was observed in our study, except for 1 of the 3 patients with CTCAE grade 3 thrombocytopenia, who also had grade 3 anemia at baseline but remained stable after PRRT. Thus, 3.97 GBq of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE per cycle may not pose a higher risk of hematotoxicity as long as we consider the importance of risk factors.
What’s more, patients with extensive bone marrow involvement may tolerate 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE well. In our study, 1 patient with extensive bone marrow metastasis in group A (Fig. 3A) had relatively good bone marrow function at baseline (normal WBC count and platelets but grade 2 anemia) after treatment with surgery, octreotide acetate (Sandostatin LAR; Novartis), and a mammalian-target-of-rapamycin inhibitor (everolimus). However, no leukopenia or thrombocytopenia was observed after 3 cycles of PRRT. In addition, the hemoglobin level remained stable after the first PRRT and improved after the second (grade 1 anemia) and third (grade 0 anemia) PRRTs. Similar findings have been found in other studies (26,27).
The maximum tolerated dose to the kidneys for PRRT was 23–29 Gy (28–30). To not exceed an absorbed dose of 23 Gy, the highest feasible dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE would be 20.0 GBq (radiation exposure, 1.15 ± 0.92 mSv/MBq) (10). However, this limited dose to the kidneys may not be directly translatable to PRRT with the long-acting somatostatin analog 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE, since it is characterized by a sustained but lower radiation dose rate, which is different from that of 177Lu-DOTATATE. Therefore, the maximal dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE based on kidney tolerance might be more than 20 GBq. The fact that we observed no CTCAE grade 2–4 nephrotoxicity during any cycle of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE or on follow-up suggests that 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE is well tolerated and produces no nephrotoxicity during multiple cycles of PRRT with a cumulative radioactivity of up to 11 GBq.
A recent metaanalysis demonstrated that the pooled disease response rate and disease control rate were approximately 25.0%–42.0% and 75.0%–83.0%, respectively, on the basis of RECIST or the Southwest Oncology Group criteria (31). Similar results were shown in the other 2 metaanalyses (32,33). In our study, the disease response rates in groups A, B, and C were 50.0%, 50.0%, and 42.9%, respectively, and the disease control rates were 66.7%, 83.3%, and 71.5%, respectively. 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE of 1.17 GBq/cycle seems to be as effective as the standard PRRT of 5.55–7.4 GBq/cycle. Although a pooled study showed poor agreement on tumor response between RECIST and the EORTC criteria (34), Aras et al. (35) found significant agreement among the Southwest Oncology Group criteria, RECIST, the EORTC criteria, and PERCIST. For early therapeutic response assessment in solid tumors, the EORTC criteria appear to be more sensitive and accurate than RECIST (36).
In this study, a 1.89 GBq/cycle dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE had almost no side effects and produced a better tumor response than 1.17 GBq/cycle. However, 3.97 GBq/cycle was still considered safe, except for patients who had prior exposure to chemotherapy with alkylating agents. Furthermore, a significant increase in hemoglobin was observed in the second and third PRRTs in groups A and B, but there was a decrease in group C. Correspondingly, the disease control rate in group C was 92.9% after the first cycle but dropped sharply to 69.3% and 62.5% after the second and third cycles, respectively. We do not yet know the reason for the sharp decline in therapeutic effect during the second and third PRRTs in group C. Some sources in the literature have suggested that a low hemoglobin concentration may be one factor (37,38). Thus, with careful patient selection and adequate monitoring, a 3.97-GBq or higher dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE is expected to achieve a better tumor response. Predictive blood biomarkers such as the PRRT Predictive Quotient and the NETest would probably be helpful in predicting efficacy and in monitoring disease (39).
There are several limitations to this study. First, the number of patients in each group was limited and uneven. Second, there was no analysis of overall survival or long-term toxicity; such an analysis will be conducted in the future. Finally, only 3 dose escalations were performed, and the maximum tolerated dose has not been determined. Further study with more patients and more dose escalations is warranted.
CONCLUSION
NET patients tolerated 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE well, with acceptable hematotoxicity. A 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE dose of 1.89 GBq/cycle appears to produce a good tumor response with almost no side effects. However, with careful patient selection and adequate monitoring, a 3.97-GBq or higher dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE may still be safe and is expected to produce an even better tumor response.
DISCLOSURE
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 81871392 and 81701742), the Chinese Academy of Medical Science Major Collaborative Innovation Project (2019-I2M-1-001), the Chinese Academy of Medical Science Clinical and Translational Medicine Research Foundation (grant 2019XK320032), the Capital Health Development Scientific Research Project (2018-1-4011), and National University of Singapore start-up fund (Nos. R-180-000-017-133, R-180-000-017-731, and R-180-000-017-733). No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Are multiple cycles of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE with escalating doses safe and effective in the treatment of advanced NET, and what is the optimal dose?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: In this prospective pilot study, 32 NET patients were randomly divided into 3 escalating dose groups. The patients seemed to tolerate 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE well, even up to 3.97 GBq/cycle. The overall disease control rate, as well as the percentage decrease in tumor SUVmax, were highest with a 1.89-GBq dose, followed by 3.97 and 1.17 GBq.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: A 1.89-GBq dose of 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE per cycle appears to produce a good tumor response with almost no side effects. With careful patient selection and monitoring, a 3.97-GBq or higher dose is expected to achieve an even better tumor response.
Footnotes
Published online Aug. 21, 2020.
- © 2021 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication April 29, 2020.
- Accepted for publication July 3, 2020.