Visual Abstract
Abstract
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–targeting PET imaging is becoming the reference standard for prostate cancer staging, especially in advanced disease. Yet, the implications of PSMA PET–derived whole-body tumor volume for overall survival are poorly elucidated to date. This might be because semiautomated quantification of whole-body tumor volume as a PSMA PET biomarker is an unmet clinical challenge. Therefore, in the present study we propose and evaluate a software that enables the semiautomated quantification of PSMA PET biomarkers such as whole-body tumor volume. Methods: The proposed quantification is implemented as a research prototype. PSMA-accumulating foci were automatically segmented by a percental threshold (50% of local SUVmax). Neural networks were trained to segment organs in PET/CT acquisitions (training CTs: 8,632, validation CTs: 53). Thereby, PSMA foci within organs of physiologic PSMA uptake were semiautomatically excluded from the analysis. Pretherapeutic PSMA PET/CTs of 40 consecutive patients treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 were evaluated in this analysis. The whole-body tumor volume (PSMATV50), SUVmax, SUVmean, and other whole-body imaging biomarkers were calculated for each patient. Semiautomatically derived results were compared with manual readings in a subcohort (by 1 nuclear medicine physician). Additionally, an interobserver evaluation of the semiautomated approach was performed in a subcohort (by 2 nuclear medicine physicians). Results: Manually and semiautomatically derived PSMA metrics were highly correlated (PSMATV50: R2 = 1.000, P < 0.001; SUVmax: R2 = 0.988, P < 0.001). The interobserver agreement of the semiautomated workflow was also high (PSMATV50: R2 = 1.000, P < 0.001, interclass correlation coefficient = 1.000; SUVmax: R2 = 0.988, P < 0.001, interclass correlation coefficient = 0.997). PSMATV50 (ml) was a significant predictor of overall survival (hazard ratio: 1.004; 95% confidence interval: 1.001–1.006, P = 0.002) and remained so in a multivariate regression including other biomarkers (hazard ratio: 1.004; 95% confidence interval: 1.001–1.006 P = 0.004). Conclusion: PSMATV50 is a promising PSMA PET biomarker that is reproducible and easily quantified by the proposed semiautomated software. Moreover, PSMATV50 is a significant predictor of overall survival in patients with advanced prostate cancer who receive 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy.
Prostate cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer-related death in men (1). The precise detection of prostate cancer metastases is of great importance for therapy monitoring and treatment intensification (2). Moreover, metastases are often responsible for prostate cancer–related morbidity and mortality (3,4). Thus, the quantification of the whole-body tumor volume is clinically relevant, and we conjecture that it could ultimately predict overall survival (OS) of patients.
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–targeting PET has emerged to become the reference standard examination for the diagnostic workup of patients with prostate cancer (5,6). PSMA is a cell surface marker of prostate cancers cells and is targeted by various ligands for both diagnostic and therapeutic approaches (7,8). However, despite their name, PSMA-ligands such as PSMA-11 show strong accumulation without pathologic implications in many organs, for example, the liver, kidneys, salivary glands, and others (9,10). Therefore, physiologic PSMA accumulations have to be discarded when quantifying image biomarkers.
Image biomarkers have been proposed for various molecular imaging modalities such as scintigraphy or PET (11,12). For example, the bone scan index can be quantified automatically using skeletal scintigraphy and has proven to predict the survival of patients with prostate cancer (13). However, skeletal scintigraphy neglects soft-tissue metastases, which are of great clinical importance. Yet, only manual or rudimentary automated approaches have been proposed for quantifying the whole-body tumor volume in PSMA PET/CT (14,15). Although several studies demonstrated that the change of PSMA PET/CT–derived tumor volume correlates with therapy response, the predictive potential is still poorly elucidated (14,16–19). Importantly, there is no clear evidence that PSMA PET–derived biomarkers can predict the survival of patients with prostate cancer. Finally, most software tools for the automated quantification of PSMA PET biomarkers use a global SUV threshold for the segmentation of prostate cancer foci (14,15). This procedure may neglect partial-volume effects that hamper a sound tumor volume quantification (20–22). Additionally, global thresholding violates the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) recommendation for molecular volume quantification, which suggests percental thresholding (e.g., 50% of maximal lesion SUV should be used for segmentation of the very same lesion) (23).
In this article, we propose and evaluate a novel semiautomated software, which quantifies the whole-body tumor volume in PSMA PET/CT. Percental thresholding is used in analogy to EANM guidelines for 18F-FDG. Moreover, a neural network is used, which semiautomatically excludes many physiologic PSMA foci from the quantification. Finally, we estimate the survival of patients with advanced prostate cancer who are receiving systemic therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
To enable the automated organ segmentation, a total number of 8,685 CT scans were labeled by a team of experienced annotators mentored and reviewed by a radiologist. Data were rigorously split for training (n = 8,632) and validation (n = 53 CTs) of the neural networks dedicated to organ segmentation. All data involved in organ segmentation development were independent from the PSMA PET/CTs.
For the analysis of PSMA PET/CT biomarkers, a total number of 40 consecutive patients with metastasized castration-resistant prostate cancer were included in this study. Patients were treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 in the department of nuclear medicine in Münster from December 2014 to December 2016. PSMA PET/CTs were acquired before the start of therapy. OS time until death or censoring was recorded. Blood parameters were obtained immediately before the administration of the first therapy. Detailed patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The retrospective analysis was approved by the local ethics committee (no. 2016-585-f-S, Ethikkommission der Ärztekammer Westfalen-Lippe and der Westfälischen Wilhelms-Universität Münster).
Patient Characteristics
PET Acquisition
A Biograph mCT (Siemens Healthineers) was used for PET/CT acquisitions. The PSMA-11 precursor was provided by ABX (ABX GmbH). A GalliaPharm Gallium generator was used (Eckert & Ziegler). Intravenous administration of 68Ga-PSMA-11 was body-weight–dependent (2 MBq/kg of body weight). PET/CT images (vertex to proximal tibia) were acquired 60 min after tracer administration. Image reconstruction was done in analogy to previous publications (11). Patients were asked to void their bladder before imaging. Either low-dose or contrast-enhanced CT acquisitions were obtained directly before PET acquisition.
Semiautomated Software
A novel software was developed for the semiautomated analysis of PSMA PET/CT acquisitions to quantify the whole-body tumor volume in a 3-step approach (Fig. 1 shows the overall workflow). To this end, all pathologic PSMA-avid foci have to be delimited. This has been implemented in the research prototype software MI Whole Body Analysis Suite (MIWBAS, version 1.0; Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.).
Overall workflow. (A–D) Maximum-intensity projections of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET. Automatically selected and segmented foci are overlaid in red. Proposed software segments all PSMA foci (step 1; A), delineates organs of physiologic tracer uptake (step 2; B), and finally semi automatically excludes PSMA foci within these organs (step 3; C and D). Automated exclusion of physiologic organs removed kidneys (exemplary green arrow in B). However, bladder and a salivary gland were missed and thus manually excluded from analysis (green arrow in C). Final segmentation is shown by panel D.
Step 1: Automated PSMA Foci Segmentation
A patient-specific global threshold (thresholdPSMA) was defined to select voxel clusters with increased PSMA expression:
where SUVmean and SUVSD denote mean and SD of a spheric liver region of interest (ROI) (15 mm radius). This equation was adopted from the qPSMA approach of Gafita et al. (15). The liver reference ROI, which is needed to obtain SUVmean and SUVSD, was automatically positioned (24). To this end, the center of the right liver lobe was automatically determined. Manual adjustments of ROI positioning were only necessary in the case of liver metastases. We use this threshold for the entire PET acquisition to select voxel clusters (i.e., for bone foci and soft-tissue foci). A convolution of the PSMA PET with a 1-mL sphere was performed to obtain SUVpeak, which was used only for the selection of voxel clusters in analogy to PERCIST (25).
First, voxels with a SUVpeak exceeding the thresholdPSMA were selected in the whole-body PSMA PET acquisition to form voxel clusters (i.e., group of adjacent voxels). Small voxel clusters falling below a volume of 0.5 mL were discarded. Second, each voxel cluster was segmented based on the local SUVmax of the given cluster, which may enlarge or shrink the cluster size. To this end, all voxels of the cluster exceeding 50% of the local SUVmax were regarded as portions of the cluster. This procedure is done iteratively, starting with the voxel cluster with the highest SUVmax. Thereby, voxel clusters are successively transformed to candidate foci, which may resemble physiologic or pathologic PSMA accumulation (Fig. 2). The assignment of these foci to anatomic locations is described in step 2 and the removal of physiologic PSMA uptake in step 3.
Segmentation concepts. 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT of patient with partly necrotic and thus low PSMA-accumulating lymph node metastases (arrows). Segmentation of PSMA foci is done by fixed global threshold alone (A) or by the consecutive application of same global threshold followed by local percental threshold (50% of SUVmax) for each focus (B). Global thresholding is erroneously selecting necrotic tumor parts as well as vital metastases. Moreover, global thresholding is producing a large confluent ROI, which includes both kidneys, a bone metastasis and parts of the liver (A). Corrections would require voxelwise manipulations. In contrast, additional application of percental thresholds (50% of SUVmax) result in multiple ROIs (indicated by separate colors), which are not confluent and exclude necrotic tumor parts (B). Moreover, physiologic uptake can easily be discarded by semiautomated deletion of ROIs in organs with physiologic uptake.
Step 2: Automated Organ Segmentation
The anatomic position of each candidate focus was automatically determined to exclude foci of organs with physiologic tracer uptake and to quantify the tumor volume with respect to certain organs. The following organs were therefore chosen for automated segmentation: liver, kidneys, bladder, heart, lungs, brain, and skeleton. The algorithm segmented these organs with a generative adversarial network (GAN) in a 3-step inference using CT data: first, a set of 126 anatomic landmarks, including vessel bifurcations, bony structures, and organ center and boundary points, was detected in the CT (26). Preliminary ROIs of each individual organ based on the detected landmarks were extracted and fed to a dedicated organ segmentation network for refinement. The preliminary ROIs were substantially smaller than the CT volume, which improved the consistency by focusing on regional variations rather than variations in the overall image and increased efficiency by reducing computational load. For the skeleton, the ROI was the entire CT volume (27). Second, a dedicated deep image-to-image network (DI2IN) was used for the final segmentation of each organ (28). It consisted of a convolutional encoder–decoder architecture combined with multilevel feature concatenation. For training, an adversarial network was selectively used to regularize the training process of DI2IN by discriminating the output of DI2IN from the ground truth in a patch-by-patch manner using binary cross-entropy. For validation, the segmentation quality was measured as a dice similarity coefficient (DSC) between the segmentation and the ground truth of the validation set in resampled resolutions, where DSC is a volumetric overlap metric between 2 mask volumes, for example, A and B: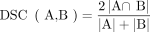
Third, each organ segmentation mask was transferred to the PET data.
Step 3: Semiautomated Determination of Image Biomarkers
Candidate foci within organs with physiologic PSMA accumulation (liver, spleen, bladder, kidneys) are automatically excluded. Candidate foci within other organs with physiologic PSMA uptake such as small bowl, salivary and tear glands, ganglia, and others had to be manually discarded. If physiologic foci were erroneously missed by the software, they were manually removed. Thereby, only foci with pathologic PSMA uptake remained in the analysis (i.e., pathologic foci).
Biomarkers were calculated for soft tissue, the skeleton, and the whole patient: The volumes of segmented lesions were summed to obtain the whole-body tumor volume (PSMATV50). In analogy to total lesion glycolysis, PSMATL was quantified as product of PSMATV50 and SUVmean. Additionally, the highest SUVmax and SUVpeak as well as averaged SUVmean were quantified.
Manual PSMA PET Measurements and Interobserver Agreement
First, manual reads of PSMA PET/CTs were performed (by a reader with >2 y of clinical PET experience) using syngo.MM Oncology software (Siemens Healthineers) to quantify PSMATV50, SUVmean, SUVpeak, and SUVmax (the VOI Isocontour segmentation tool was used, involving manually identifying a spheric region in which 50% of SUVmax was used for segmentation). Second, an interobserver study was performed (by readers with >5 y PET experience) independently using the semiautomated software. A subcohort of 20 randomly selected patients was used for both purposes due to logistic reasons.
Additionally, the whole-body tumor volume was quantified without 50% percental thresholding for comparison and denoted PSMATV. To this end, manual segmentation of pathologic PSMA foci was done in the subgroup using the global thresholdPSMA. Refinement of the threshold was only done in the case of confluent lesions or other visual saliences (e.g., necrotic tumor parts that were erroneously segmented).
Statistical Analysis
SPSS 24 (IBM) was used for paired t tests, log-rank test, Cox regression, interclass correlation coefficient (ICC), Spearman ρ or Pearson correlational analysis and plotting. MATLAB R2018b (The MathWorks) and Excel 2010 (version 14.0; Microsoft) were used for data management. Values are presented as mean together with the 95% confidence interval (95% CI). Mean absolute agreement ICC was calculated using a 2-way mixed-effect model. P values less than 0.05 were regarded as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Organ Segmentation
The automatic organ segmentation demonstrated a mean DSC value of at least 0.86 for every organ. The skeleton segmentation performed accurately, with a mean DSC value over 0.92 (95% CI, 0.894–0.944). Details are given in Table 2.
Numbers of Training and Validation Data for Each Organ and DSC Over Validation Set
Manual Measurement of PSMA Biomarkers
Manual and semiautomatically quantified whole-body tumor volume did not significantly differ and showed high correlation (162.8 vs. 173.3 mL, P = 0.107; R2 = 0.996, P < 0.001). The same was true for SUVmax (58.0 vs. 53.3, P = 0.229; R2 = 0.790, P < 0.001), SUVpeak (35.1 vs. 35.6, P = 0.541; R2 = 0.964, P < 0.001), and SUVmean (16.1 vs. 15.9, P = 0.779; R2 = 0.943, P < 0.001). Statistically significant difference was observed for PSMATL between manual and semiautomated reads (2,422.2 vs. 2,649.1, P = 0.031; R2 = 0.990, P < 0.001).
PSMA PET/CT reading using the semiautomated software was on average 3.3 times faster than using the manual approach and can be accomplished in approximately 2 min (average time per patient, 119.6 vs. 397.3 s, P = 0.02, n = 10).
Interobserver Agreement of PSMA Biomarkers
Whole-body PSMATV50 was highly correlated (R2 = 1.000; P < 0.001) between reader 1 and 2 (for soft-tissue PSMATV50: R2 = 1.000, P < 0.001; for skeletal PSMATV50: R2 = 1.000, P < 0.001). The same was true for SUVmax (R2 = 0.988, P < 0.001), SUVmean (R2 = 0.953, P < 0.001), and PSMALA (R2 = 0.998, P < 0.001). ICCs of PSMATV50, PSMATL, SUVmax, and SUVmean were 1.000 (95% CI: 1.000–1.000), 1.000 (95% CI: 0.999–1.000), 0.997 (95% CI: 0.991–0.999), and 0.988 (95% CI: 0.969–0.995). Details are provided in Figure 3.
Evaluation of proposed software. Semiautomatically derived whole-body PSMATV50 is highly correlated with volume of all manually segmented lesions (A). The same is true for the whole-body PSMATL (B). Bland–Altmann plot of interobserver agreement is shown in C. Subcohort (n = 20) was used for these analyses.
PSMA Biomarkers and OS
In a first approach, univariate Cox regression was performed for PSMA biomarkers and blood tumor markers. Significant predictors of OS were PSMATV50 (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.004; P = 0.002) and alkaline phosphatase (HR: 1.001; P = 0.047). PSMATV50 measured in deciliter had an HR of 1.45. In a second approach, significant predictors were included in a multivariate analysis, in which only PSMATV50 remained a significant predictor of OS (HR: 1.004, P = 0.004; 95% CI: 1.001–1.006). Detailed results of uni- and multivariate Cox regressions are presented in Table 3 and Figure 4.
Cox Regressions of Survival and Biomarkers
OS stratified by whole-body tumor volume, which was measured by proposed software. All patients (n = 40) were stratified by whole-body PSMATV50 quartiles (A and B) or PSMATV quartiles (C and D).
Median OS according to PSMATV50 quartiles were (in descending order of tumor volume): 5.3, 7.9, 11.4, and 21.3 mo. There was no significant difference comparing OS of patients with regard to the PSMATV50 median (21.3 vs. 6.7 mo, P = 0.058). However, OS was significantly longer in quartile 1 of PSMATV50 than in quartile 4 (21.3 vs. 5.3 mo, P < 0.031).
PSMATV50 Versus PSMATV
Tumor volume measured as PSMATV was significantly greater than PSMATV50 (661.0 vs. 213.0 mL, P < 0.001). However, there was a correlation between PSMATV and PSMATV50 (R2 = 0.473; P < 0.001). PSMATV could not significantly predict OS (HR: 1.001, P = 0.062; 95% CI: 1.000–1.001) in univariate Cox regression. Likewise, there was no significant difference regarding OS between quartile 4 and quartile 1 of PSMATV (7 vs. 7.5 mo, P = 0.235).
PSMA Biomarkers and Blood Parameters
There were moderate correlations between whole-body PSMATV50 and blood levels of prostate-specific antigen (> = 0.553; P < 0.001) or skeletal PSMATV50 and alkaline phosphatase (> = 0.525; P = 0.001; Fig. 5).
Correlation of imaging and blood biomarkers. There was moderate correlation between whole-body PSMATV and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels (A). Same was true for skeletal PSMATV and alkaline phosphatase levels (B). Values were plotted after log10 transformation.
DISCUSSION
The semiautomated quantification of PSMA PET biomarkers such as the whole-body tumor volume by the proposed software was significantly faster than manual PET/CT readings and can be achieved on average in 2 min, and the correlation between manual and semiautomated reading was excellent. In contrast to previously proposed approaches, percental thresholding was used and no time-consuming refinement of image segmentation masks is needed. Moreover, the semiautomatically quantified tumor volume (PSMATV50) could significantly predict the OS of patients with advanced prostate cancer.
Imaging-derived biomarkers, such as whole-body tumor volume, are excellent predictors of survival in patients with various metastasized diseases (29,30). For prostate cancer, the quantification of the fraction of metastatically affected bones in planar bone scintigraphy could accurately stratify patients according to symptomatic progression and OS in a prospective phase III trial (30). Several approaches have been proposed to semiautomatically quantify tumor volumes in PSMA PET/CT (11,14,15,31). It was shown previously that the change of whole-body tumor volume correlated with the overall response (14,16). Yet, the relevance of PSMA PET imaging biomarkers as predictors of survival in patients with prostate cancer is poorly elucidated. The present work demonstrated that PSMATV50 is a significant predictor of survival in patients with advanced prostate cancer who undergo 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy. An increase of 100 mL in whole-body tumor volume (PSMATV50) is associated with a 1.4-fold-higher risk of death. Interestingly, PSMATL did not significantly predict OS, thus strengthening the assumption that PSMA SUV does not predict response to systemic therapy and clarifying the need for novel PET biomarkers such as PSMATV50.
Organs of physiologic PSMA-ligand excretion have to be excluded when quantifying whole-body tumor volume or other biomarkers. To this end, various approaches have been proposed to assist the reader in removing physiologic accumulations (14,15). A GAN is used by the proposed software for automated organ segmentation. The CT component is used by the neural network to extract anatomic landmarks and segmentations, which are transferred to the PET component by rigid transformation. The DSC, which measures the accuracy segmentation, is higher for the proposed software (mean: 0.926) than for the software qPSMA (77.4–85.6) when analyzing the skeleton mask (18).
In contrast to other semiautomated software packages, the proposed software uses percental thresholding of PSMA foci: for each focus, 50% of the SUVmax is automatically used for confinement. This is in line with EANM guidelines for 18F-FDG PET, which recommend percental thresholding using 41% or 50% of the SUVmax for volumetric analyses (23). The use of percental thresholding is advantageous both in technical and in physical regard. The technical advantage of percental thresholding is that adjacent metastases are separated, and the whole-body tumor burden is dismembered in separate lesions. Thereby, each focus can automatically be assigned to an anatomic location. Foci assigned to organs with known physiologic excretion can thus be removed using heuristic rules (e.g., kidney, ureter, etc.). Moreover, the user is not requested to exclude missed physiologic foci by the manual adjustment of masks, but rather by deletion of the individual focus. Thus, the need of user interaction is reduced to a minimum, in contrast to global thresholding, which results in large confluent ROIs combining physiologic and pathologic foci (15). The physical benefit of percental thresholding is that the lesion size can be quantified accurately. In contrast, segmenting lesions by a global threshold is prone to overestimating the volume because of positron range and partial-volume effects, which induce image blur (22). Therefore, percental thresholding is a prerequisite for correct volumetric analyses.
Despite the 2-fold advantage of percental thresholding, there was a high correlation between whole-body tumor volume between PSMATV and PSMATV50. However, PSMATV50 was significantly smaller than PSMATV. Interestingly, PSMATV could not significantly predict OS, indicating that percental thresholding should be implemented in modern assisted reading software.
The present study faces some limitations. Only a relatively small number of patients were included, possibly hampering the generalizability to a larger population. Additionally, all enrolled patients received 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy after the quantification of PSMA biomarkers. 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy is targeting the same molecule that is visualized by PSMA PET. The survival prediction might therefore be biased. Moreover, one could argue that a decrease of the local SUVmax in response to therapy would cause PSMATV50 to paradoxically increase. However, solitary changes only of SUVmax seem unrealistic. Rather, not only SUVmax but also the uptake of the entire lesion should concordantly decrease in response to therapy in this scenario. Therefore, PSMATV50 would decrease and thus correctly assess therapy response. Yet, future studies should evaluate PSMATV50 as biomarker for therapy response.
The physiologic uptake of PSMA tracer varies; especially, 18F-PSMA-1007 has a fundamentally different physiologic uptake because of liver-dominant excretion (32). The liver reference ROI might be unsuitable to provide a patient-specific thresholdPSMA for foci selection in 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT acquisitions. Therefore, future studies should evaluate blood-pool activity as reference for ligand agnostic definitions of thresholdPSMA.
The metastatic extent of the cohort was heterogeneous, and confidence intervals of regression were relatively large. Additionally, liver metastasis with small tumor volume might still have heavily influenced OS, possibly distorting the relationship of tumor volume to OS. Future studies should evaluate the predictive potential of PSMATV50 in larger homogeneous patient cohorts that receive anticancer therapies distinct from 177Lu-PSMA-617.
CONCLUSION
The quantification of PSMA PET/CT biomarkers using the proposed software is feasible and achieves excellent interobserver agreement. Semiautomated PET reading is faster than manual analysis. Moreover, semiautomatically derived PSMATV50 biomarker is a significant predictor of OS in patients with advanced prostate cancer, whereas PSMATV is not. Future studies elucidating the predictive potential of PSMATV50 seem warranted.
DISCLOSURE
Kambiz Rahbar received consultant fees from ABX and Bayer Healthcare and lectureship fees from AAA, SIRTEX, AMGEN, and Janssen Cielag. Vijay Shah, Zhoubing Xu, Guillaume Chabin, Sasa Grbic, and Bruce Spottiswoode are full-time employees of Siemens Medical Solutions, USA, Inc. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Can PSMA PET–based tumor volume be quantified by a semiautomated software and be used as a prognostic biomarker of OS?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: Semiautomated PET reading is feasible, has high interobserver agreement, and is faster than manual analysis. Semiautomatically derived tumor volume is a significant predictor of OS, whereas blood tumor markers are not.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Semiautomatically derived tumor volume is a significant predictor of OS in patients with advanced prostate cancer.
Footnotes
Published online Apr. 24, 2020.
- © 2020 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication January 14, 2020.
- Accepted for publication March 25, 2020.













