Abstract
1351
Objectives Over-expression of HER2/neu, c-erb-B2 membrane-bound receptor tyrosine kinase (HER2) is often associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and a poor prognosis. Trastuzumab (brand name Herceptin), a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting HER2, has increased therapeutic efficacy as a monotherapy or in combination with other chemotherapeutics. Current standard of care involves assessing HER2 expression on biopsied or resected tumor tissue by IHC, or for gene amplification using FISH. The ability to effectively image HER2 expression in tumor lesions throughout the entire body prior to implementing HER2 directed therapy could improve patient selection and potentially evaluate overall response to therapy. Imaging research in this area has resulted in several promising novel radiotracers. Our first-in-human results (preliminary dosimetry, biodistribution, and determination of accuracy of imaging HER2 lesions), were obtained using the novel radiotracer 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab in patients with breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and bladder malignancies. The incorporation of CHX-A”, a 3rd generation acyclic bifunctional chelating agent (used in >10 clinical trials with an excellent safety profile), in our radiotracer provides the advantage of flexibility for chelating a wide variety of radiometals to antibodies while maintaining specificity. Prior in-vitro and murine in-vivo studies showed high receptor specificity/tumor retention of 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab.
Methods 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab was prepared on-site using a kit as previously published resulting in a mean purity of 99.1%, SD 0.6 and mean mass of 136.6 μm, SD 35.6. 13 patients were enrolled with target lesion 蠅1.5cm and known HER2 status: 10 breast cancer, 2 NSCLC and 1 bladder cancer. After bolus IV injection of ~5mCi (mean 4.6, SD 0.54) of 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab, 11 patients underwent either whole body planar gamma camera imaging at multiple timepoints(6), SPECT or SPECT/CT-torso imaging(3), or both(2). Visual interpretation defined imaging HER2 status which was correspondingly compared with pre-enrollment biopsy-based HER2 designation in each subject.
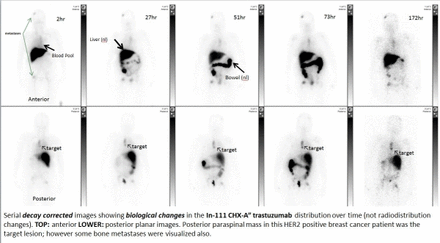
Results Imaging results with 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab correlated with clinical HER2 attribution in all breast and lung cancer patients (Figure below shows a concordant HER2 positive patient imaging series), but was discordant (imaging false positive) in the single bladder cancer patient. The radio-biodistribution(which was previous presented as a poster 2011) obtained from 6 patients planar series yielded dosimetry estimates (using OLINDA1.1) showing the liver to accumulate the highest dose at 2.4 rads/mCi, followed by the lower large intestines, gall bladder and upper large intestines (1.2, 0.76, and 0.75 rads/mCi, respectively), suggestive of biliary excretion. The measured effective dose(ED) and Effective Dose Equivalent(EDE) are 0.47 and 0.42 rem/mCi respectively. The decay corrected serial tumor uptake showed low variability after 24-72h, suggesting this as a suitable imaging window. No serious adverse events attributable to the agent were encountered. One subject reported a Grade 1 taste disturbance.
Conclusions Our data shows dosimetry similar to various other clinical nuclear medicine procedures, low intra-patient biodistribution variations, and high correspondence between visible 111In-CHX-A” trastuzumab tumor uptake and biopsy-based HER2 designation 91%--one false positive on imaging in this small population. The relative ease of synthesis, high chemical purity and the imaging results presented, the completion of this 1st in human study lays the groundwork for future larger clinical studies, potentially resulting in a useful diagnostic and/or therapeutic clinical radiopharmaceutical.