Clinical multimodality imaging: Pichler and colleagues offer a focus on PET/MRI instrumentation as the next generation of clinical molecular imaging, including technical evolution and the range of potential applications.
Page 333

Monte Carlo method: Bolch provides a brief history and perspective on nuclear medicine uses of the Monte Carlo method, a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random samplings to compute physical quantities.
Page 337
18F-FLT PET with CTLA4 blockade: Ribas and colleagues evaluate the role of whole-body molecular imaging in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving tremelimumab, a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4–blocking antibody.
Page 340

18F-FDG uptake in normal breast: Mavi and colleagues investigate whether and how age, menopausal state, and tissue density are related to 18F-FDG uptake in normal glandular breast tissue.
Page 347

Predictive PET in NETs: Campana and colleagues explore the use of standardized uptake values from 68Ga-DOTANOC PET imaging as accurate noninvasive markers for disease prognosis in patients with neuroendocrine tumors.
Page 353
PET and surgical staging in cervical cancer: Kang and colleagues report on a metaanalysis of the diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET in detecting paraaortic lymph node metastasis in patients with cervical cancer.
Page 360
Arterial wall toxicity in NHL RIT: Hobbs and colleagues look at absorbed doses to the arterial wall in patients undergoing radioimmunotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma to assess the potential for delayed toxicity.
Page 368

Paraaortic sentinel node localization: Vermeeren and colleagues describe and evaluate preoperative SPECT/CT for lymphatic mapping and a portable γ-camera for intraoperative radioguidance in patients with paraaortic sentinel nodes.
Page 376

Salvage therapy with 177Lu-octreotate: van Essen and colleagues detail the effects of additional therapy with this radiolabeled somatostatin analog in patients with progressive gastroenteropancreatic or bronchial neuroendocrine tumors who had benefited from previous therapeutic cycles.
Page 383
99mTc(CO)3(NTA) renal tracer: Taylor and colleagues compare the pharmacokinetics of this tricarbonyl core agent with those of 131I-ortho-iodohippuran, the clinical gold standard for measurement of effective renal plasma flow, in healthy volunteers.
Page 391
90Y-DOTATOC treatment of glioblastoma: Heute and colleagues report on the use of this somatostatin receptor radiopharmaceutical in the treatment of patients with high-grade malignant gliomas.
Page 397

Cost-effectiveness of PET and PET/CT: Buck and colleagues provide an educational overview and evaluation of methodologies for cost-effectiveness studies of PET and PET/CT in oncology.
Page 401
Endocardial versus epicardial cell injection: Mitchell and colleagues compare the cell retention and clearance kinetics of subepicardial and subendocardial techniques for stem cell delivery to recently infarcted myocardium.
Page 413

Enhanced melanoma uptake: Guo and colleagues examine the effect of the ring size of the radiolabeled lactam bridge–cyclized α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone peptide on its melanoma-targeting properties and discuss the implications for imaging and treatment.
Page 418

Targeting prostate cancer cells: He and colleagues evaluate the tumor-targeting capabilities of a radiolabeled internalizing human antibody fragment to provide high contrast in a mouse model of human prostate carcinoma.
Page 427
Knottin peptide-based ultrasound agent: Willmann and colleagues describe a new class of targeting ligands for contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of tumor angiogenesis using microbubbles conjugated to integrin-binding knottin peptides.
Page 433
Benzamide PET of melanoma: Denoyer and colleagues evaluate the novel melanin probe 118F-MEL050 for PET imaging of primary and metastatic melanoma using murine models.
Page 441
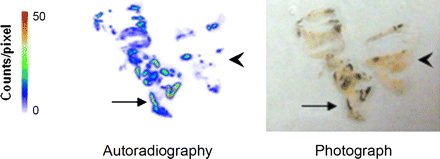
68Ge calibration methodology: Zimmerman and Cessna describe a technique for calibrating 68Ge radioactivity content in a commercially available source for activity calibrators in a way that is traceable to the national standard and extend this approach to 18F calibration.
Page 448
Labeling octreotide with 18F: Laverman and colleagues present a 2-step, 1-pot method for rapid and efficient labeling of peptides with 18F.
Page 454

Monte Carlo cellular dosimetry: Cai and colleagues compare Monte Carlo N-particle 111In self- and cross-doses to breast cancer cell nuclei with doses calculated by other methods and determine whether Monte Carlo results can predict cell survival.
Page 462
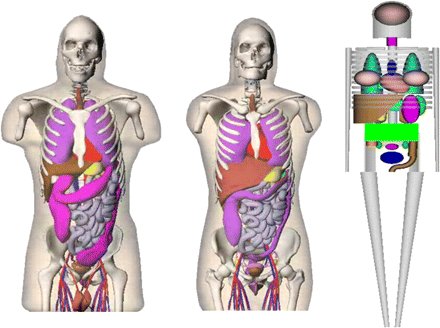
Animal models for dose assessment: Keenan and colleagues describe a series of anatomically realistic mouse and rat whole-body phantoms and use these models to facilitate dose calculations in various rodent species.
Page 471
111In-NLS-trastuzumab radiosensitization: Costantini and colleagues elucidate the mechanisms by which methotrexate radiosensitizes HER2-positive human breast cancer cells to the 111In-trastuzumab modified with nuclear-localization sequence peptides and determine the potential sensitizing effects of paclitaxel and doxorubicin when combined with this radiopharmaceutical.
Page 477

Improving anti-CD66 mAb RIT: Kletting and colleagues review the development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model capable of describing biodistribution and extrapolating between different doses of anti-CD66 monoclonal antibody in radioimmunotherapy.
Page 484
ON THE COVER
Monte Carlo N-particle simulation has been shown to compare well with 2 analytic methods in the calculation of subcellular S values. The radii of cells and nuclei have a profound effect on S values and may vary considerably. The cell and nucleus diameters of 6 commonly used breast cancer cell lines have been measured and reported for the first time.
See page 467.








