Table of Contents
Cover image
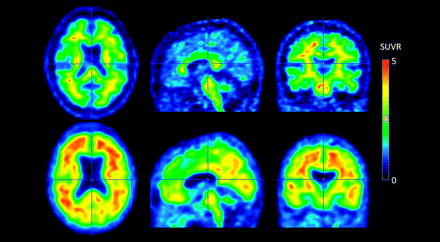
The biodistribution and dosimetry of 18F-flutemetamol, a newly developed radioligand to visualize and quantify amyloid burden, have been characterized. Here, PET slices through the brain of a healthy subject (top) and a patient with Alzheimer disease (bottom) show the distribution of uptake. Specific uptake is present in gray matter in patients, and aspecific uptake is seen in white matter, pons, and thalamus. Variability in dosimetry between subjects was relatively low.
See page 818.



