18F-FDOPA and neuroendocrine tumors: Minn and colleagues provide an overview of the use of this tracer in PET and PET/CT imaging of neuroendocrine tumors, pancreatic β-cell hyperplasia, and other disorders and discuss future applications in diagnosis and therapy.
Page 1915
Improving lung scintigraphy: Parker previews 2 articles on lung scintigraphy in this issue of JNM and reviews the current status of the procedure in the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism.
Page 1919
Nonrigid registration of chest PET/CT: Grgic and colleagues apply intraindividual analysis to determine whether a nonrigid registration algorithm can improve fusion quality of 18F-FDG PET and CT thoracic images and describe optimal breathing protocols.
Page 1921
Tracers in pulmonary NET tumors: Kayani and colleagues compare the performance of 68Ga-DOTATATE, a novel selective somatostatin receptor 2 ligand, and 18F-FDG in detection of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors.
Page 1927

Fitted input function to estimate MRglc: Vriens and colleagues report on and validate a mathematic function to describe the arterial plasma time–activity concentration curve for quantification of glucose metabolic rate and therapy response monitoring with dynamic 18F-FDG PET.
Page 1933
18F-FDG PET in HNSCC follow-up: Krabbe and colleagues assess the role and timing of serial 18F-FDG PET scans as surveillance for early locoregional recurrence, distant metastases, and second primary tumors after treatment for advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Page 1940

18F-FDG and 62Cu-ATSM in lung cancer: Lohith and colleagues delineate intratumoral uptake and tracer distribution of 62Cu-ATSM, a hypoxic imaging tracer, and 18F-FDG in patients with lung cancer of pathohistologically different types.
Page 1948

Cerebral P-gp inhibition by tariquidar: Wagner and colleagues use PET with (R)-11C-verapamil, a permeability glucoprotein (P-gp) substrate, to measure P-gp function at the human blood–brain barrier after administration of tariquidar, a potent P-gp inhibitor.
Page 1954

11C-MET PET and glioma progression: Ullrich and colleagues investigate the potential of 11C-MET PET to detect tumor progression in patients with gliomas and assess changes in tracer uptake and molecular immunohistochemical markers during progression.
Page 1962

Ischemia in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Chung and colleagues use 99mTc-ECD brain perfusion SPECT to characterize cerebral hypoperfusion in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Page 1969

Reference tissue models in BBB disruption: Folkersma and colleagues assess and validate a simplified reference tissue model for analyzing dynamic (R)-11C-PK11195 scans in traumatic brain injury, where blood–brain barrier disruptions are likely.
Page 1975
Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: Djaberi and colleague explore the diagnostic challenge presented by diabetic patients with myocardial perfusion defects but no evidence of obstructive epicardial coronary disease.
Page 1980
V/Q SPECT and low-dose CT vs. MDCT in PE: Gutte and colleagues compare the diagnostic abilities of ventilation–perfusion (V/Q) SPECT, V/Q SPECT with low-dose CT, and pulmonary multidetector CT angiography with a combined SPECT/MDCT scanner in pulmonary embolism.
Page 1987
Cerebral blood flow in diabetes: Káplár and colleagues look for differences in global or regional cerebral blood flow resulting from microvascular damage in types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus.
Page 1993

SPECT for pulmonary embolism: Stein and colleagues provide an educational overview on the current status and accuracy of SPECT in acute pulmonary embolism and discuss its role in the context of increased use of CT angiography.
Page 1999
Pretargeted RIT of pancreatic cancer: Karacay and colleagues report on a novel pretargeting procedure for therapeutic delivery of 90Y-labeled PAM4 IgG, a monoclonal antibody that recognizes a unique epitope associated with a mucin in pancreatic cancer.
Page 2008
177Lu-AMBA in GRP-R prostate cancer: Maddalena and colleagues evaluate the tumor binding and imaging potential of this radiolabeled bombesin derivative in low gastrin-releasing peptide receptor models of prostate cancer and determine how reduced expression affects radiotherapeutic efficacy.
Page 2017
Systemic radionuclide therapy and gliomas: Samnick and colleagues test the therapeutic potential of 131I-IPA, a tumor-specific amino acid derivative, combined with external-beam photon radiotherapy in glioma-bearing rats.
Page 2025
RIT with 125I-mAbs: Santoro and colleagues assess the in vivo biologic efficiency of internalizing and noninternalizing 125I-labeled monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of small solid tumors.
Page 2033
18F-labeled phosphoramidate: Lapi and colleagues report on studies exploring phosphoramidates as novel small-molecule prostate-specific membrane antigen inhibitors to develop more effective prostate cancer imaging agents with improved specificity and clearance properties.
Page 2042
Mutant TK/GFP fusion reporter: Hsieh and colleagues construct a mutant thymidine kinase/green fluorescent protein reporter gene with low cytotoxicity and high temporal resolution for real-time optical and PET monitoring of transcription induction and other biochemical changes.
Page 2049

Imaging VEGF receptors in abscesses: Levashova and colleagues determine whether labeled forms of single-chain vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can be used to image VEGF receptors in an animal model of sterile soft-tissue inflammation.
Page 2058
PET radioligand for H3 receptors: Plisson and colleagues synthesize and evaluate the potential utility of 11C-GSK189254, a histamine H3 receptor antagonist, for PET imaging of these receptors.
Page 2064
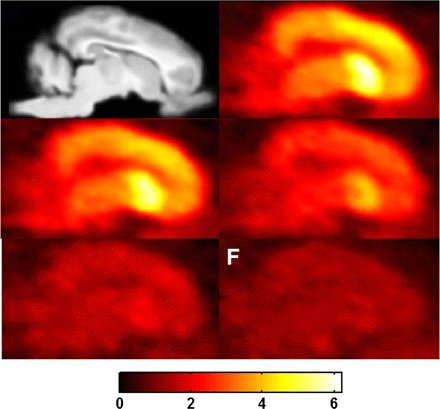
Therapy and 111In-vinorelbine liposomes: Chow and colleagues investigate the therapeutic effectiveness of specific amounts of these PEGylated liposomes by varying radiation dosage and concentrations of chemotherapeutic agents in animal tumor growth suppression studies.
Page 2073

Radiolabeled divalent gastrin peptide: Sosabowski and colleagues expand on previous studies of 111In-labeled divalent gastric peptides with potential for radionuclide therapy in tumors overexpressing gastrin/cholecystokinin subtype 2 receptors.
Page 2082
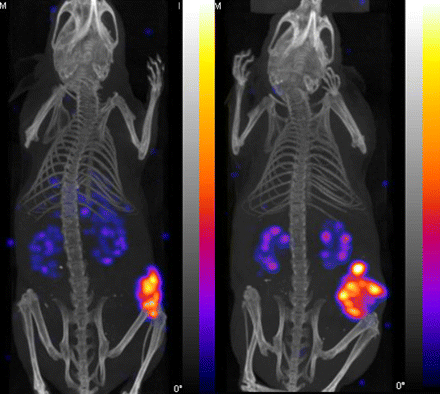
ON THE COVER
Both ventilation–perfusion SPECT and multidetector CT angiography have high accuracy in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, but only limited data comparing the two are available. A prospective study using a hybrid scanner has concluded that ventilation–perfusion SPECT in combination with unenhanced low-dose CT has excellent diagnostic performance and should probably be considered first-line imaging in the work-up of most cases of pulmonary embolism.
See page 1990.








