18F-DOPA PET applications: Nanni and colleagues provide an overview of the use of 18F-DOPA in PET and PET/CT imaging for neurologic and oncologic indications and preview a related article in this issue of JNM.
Page 1577
Qualitative and quantitative PET in lymphoma: Weber looks at the success of 18F-FDG PET in assessment of tumor response to chemotherapy for Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and considers the advantages of adding quantitative parameters to visual assessment.
Page 1580
Limitations of CT in PET/CT: Gollub and colleagues explore the technical causes and diagnostic significance of missed findings in the unenhanced CT portion of PET/CT scans.
Page 1583
PET response evaluation for NSCLC: de Geus-Oei and colleagues assess the value of 18F-FDG PET in predicting chemotherapy response in patients with non–small cell lung cancer and compare 2 methods for quantifying changes in glucose metabolism in such studies.
Page 1592
Carbidopa 18F-DOPA PET in paraganglioma: Timmers and colleagues investigate the sensitivity of 18F-DOPA PET in the detection of paraganglioma and its metastatic lesions and evaluate whether tracer uptake by tumors is enhanced by carbidopa.
Page 1599

Interval sentinel lymph nodes and melanoma: Matter and colleagues review the incidence, lymphatic anatomy, and metastatic risk of interval sentinel nodes, as well as the role of preoperative lymphoscintigraphy in reviewing all known lymphatic areas.
Page 1607

PET staging of nasopharyngeal cancer: Liu and colleagues provide evidence that 18F-FDG PET can replace multimodality conventional work-ups in primary staging of patients with nonkeratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Page 1614

Dental effects of radioiodine therapy: Walter and colleagues investigate the long-term incidence of dental problems after high-dose 131I therapy for differentiated thyroid cancer and describe associated risk factors.
Page 1620
Early SUV assessment in lymphoma: Lin and colleagues assess the prognostic value of standardized uptake values in early 18F-FDG PET imaging in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and compare their results with those from routine visual analysis.
Page 1626

Nicotinic receptor availability in nonsmokers: Cosgrove and colleagues use SPECT and MRI to examine the availability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in healthy men and women and assess whether menstrual phase in women affects these findings.
Page 1633
Perspectives on dementia: Inui and colleagues assess a combined SPECT approach using 123I-IMP for brain perfusion imaging, 123I-MIBG for cardiac sympathetic nerve function, and 99mTc-sestamibi for myocardial function in patients with probable or possible dementia with Lewy bodies.
Page 1641

18F-FDOPA kinetics in brain tumors: Schiepers and colleagues investigate the action of this amino acid analog using PET in patients with brain tumors to derive a useful clinical model of uptake for different types of neoplasms.
Page 1651
Variable cardiac uptake in oncology PET: Inglese and colleagues analyze global and regional 18F-FDG cardiac images in fasted cancer patients free from cardiac disease and offer a word of caution on the diagnosis of myocardial scar in such patients.
Page 1662

Early tetrofosmin imaging: Rossi and colleagues, representing the multicenter Myoview Imaging Optimization study, assess whether early myocardial tetrofosmin SPECT imaging is feasible and as accurate as standard delayed imaging in detecting coronary artery disease in patients with anginal symptoms.
Page 1670
Nicorandil therapy in acute MI: Kasama and colleagues use 123I-MIBG scintigraphy to explore the long-term effects of this adenosine triphosphate–sensitive potassium channel opener in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Page 1676
Bystander and low–dose rate effects: Sgouros and colleagues provide an educational overview of the history, key experiments, and current understanding of these radiation-induced effects and pose questions about their relevance in radionuclide therapy.
Page 1683
Weak sources in PET: Goertzen and colleagues evaluate the potential effects of intrinsic radioactivity in lutetium oxyorthosilicate–based small-animal PET imaging and offer advice on strategies for visualizing weak sources in these scanners.
Page 1692

PET in breast cell proliferation: Tian and colleagues report on PET imaging and quantitation with a dual-specificity probe that molecularly targets both CCND1 mRNA and insulinlike growth factor 1 receptor in early breast cancer.
Page 1699

Dynamic tracking of cell therapy: Doyle and colleagues study the feasibility of dynamic 3D-PET/CT tracking of 18F-FDG–labeled circulating progenitor cell therapy during intracoronary injection in a swine model of acute myocardial infarction.
Page 1708

Uptake of tracers into brown fat: Baba and colleagues determine whether multiple clinically useful radiotracers accumulate in brown adipose tissue and assess the uptake of these tracers in rats kept in normal and cold environments.
Page 1715

PET and methamphetamine effects: Fowler and colleagues measure the pharmacokinetics of two 11C-labeled methamphetamine enantiomers in the baboon brain and peripheral organs to assess the saturability and pharmacologic specificity of binding.
Page 1724

HED retention in noncardiac tissues: Thackeray and colleagues explore the retention of 11C-meta-hydroxyephedrine in brown adipose tissue, lung, pancreas, skeletal muscle, and kidney and discuss the potential for novel PET studies of sympathetic nervous system integrity in these tissues.
Page 1733
68Ge/Ga generator postprocessing: Zhernosekov and colleagues describe an efficient method for processing generator-derived 68Ga eluates, including the labeling and purification of biomolecules, for radiopharmaceuticals for routine applications.
Page 1741
ON THE COVER
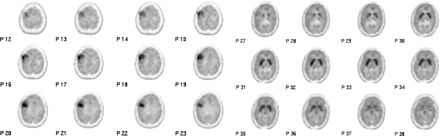
Mean parametric images illustrating 123I-5-IA-85380 activity in 10 men and 19 women in VT′ (regional activity divided by total plasma parent between 6 and 8 h) and VT (regional activity divided by free plasma parent between 6 and 8 h). Across brain regions, the main VT′ component was significantly greater in women than in men, but the main VT component did not significantly differ between the sexes.

See page 1637.







