Acton reviews the promise of dynamic imaging using an infusion of tracer for the study of transient tumor response to photodynamic and other therapies, as reported in original articles in this issue.
Page 1067
Sharkey surveys challenges and obstacles to clinical implementation of radioimmunotherapy in solid tumors and previews an article in this issue that proposes avenues for advancement.
Page 1070
Nie and colleagues describe and evaluate 3 semiautomatic computer-aided diagnostic schemes for distinguishing between benign and malignant pulmonary nodules with information provided by combined PET/CT and by PET or CT alone.
Page 1075

Quan and colleagues report on a new image acquisition and processing technique to produce PET/CT images rendered in 3-dimensional volumes that can be reviewed in various formats to create virtual “fly-through” and external “fly-around” navigation.
Page 1081
Kim and colleagues use 18F-FDG PET to investigate regional brain metabolic impairment in children with Prader–Willi syndrome, a genetic disorder that is the most common cause of human syndromic obesity.
Page 1088
Yin and colleagues apply 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT to identify brain areas that control urinary continence in healthy men and discuss the potential clinical implications of their findings for the appropriate treatment of urinary incontinence.
Page 1093

Kashihara and colleagues observe and quantify myocardial uptake of 123I-MIBG in patients with pure autonomic failure, a condition with pathologic features similar to those in idiopathic Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies.
Page 1099
Römer and colleagues report on the utility of SPECT-guided CT in a population of cancer patients to clarify assessments of spinal, thoracic, or pelvic foci of increased bone metabolism that had been classified as indeterminate on SPECT.
Page 1102
Berman and colleagues provide a comprehensive educational review of the range of noninvasive imaging techniques for risk stratification in patients with suspected or known chronic coronary artery disease and propose a conceptual approach to the selection of tests.
Page 1107
Bérard and colleagues assess the potential for dynamic, small-animal PET in monitoring transient metabolic processes and investigating the mechanisms of action of new photosensitizing drugs in photodynamic therapy of cancer.
Page 1119
Tijink and colleagues research the potential of radioimmunotherapy with a human monoclonal antibody immunoprotein, either alone or in combination with cetuximab, for treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a mouse model.
Page 1127
Tseng and colleagues describe a novel approach to tumor-selective targeting and quantitative in vivo PET assessment of gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy and discuss the implications for more accurate treatment planning and monitoring.
Page 1136
Lantry and colleagues report on both in vitro and small animal studies of a new radiolabeled bombesin analog for imaging and systemic radiotherapy with improved pharmacokinetics and better retention of radioactivity in the tumor.
Page 1144

Bettio and colleagues investigate the synthesis, radiolabeling, and in vitro and in vivo activities of a new 18F-labeled folic acid derivative and discuss its promise in PET imaging of folate receptor–positive tumors.
Page 1153
Wang and colleagues evaluate the efficacy of multimodality imaging with several radiotracers for the prediction and monitoring of early responses in tumors to prodrug activation gene therapy with herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir.
Page 1161
Cai and colleagues introduce a new method of labeling RGD peptides through a thiol-reactive synthon and discuss the potential for radiolabeling of other thiolated biomolecules for PET integrin expression imaging of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.
Page 1172
Kesner and colleagues develop and test semiautomated methods of coregistering a digital mouse phantom image with a small-animal PET image and apply those methods to the calculation of activity distributions in a mouse model.
Page 1181

Sitek and colleagues report on the development of a physical and computer-generated hybrid phantom that allows the creation of multiple noise realizations of tomographic datasets of dynamic uptake without the need for separate acquisitions for each set of parameters.
Page 1187
Chareonthaitawee and colleagues examine the short-term reproducibility of 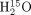 and 13NH3 myocardial blood flow in a swine model of chronic coronary artery disease.
and 13NH3 myocardial blood flow in a swine model of chronic coronary artery disease.
Page 1193

Pandit-Taskar and colleagues analyze retrospective study data to determine whether lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel lymph node mapping of breast masses in the pregnant woman presents an unacceptable risk to the fetus.
Page 1202
Gulec and colleagues summarize the principles of 90Y-microsphere dosimetry and provide the mathematic derivations of the equations used in the MIRD schema.
Page 1209
Sander and colleagues demonstrate noninvasive molecular imaging of lentiviral-marked cells by PET and discuss the implications of this capability for future monitoring of gene therapy.
Page 1212

Suleiman and colleagues report on a review and analysis of available Radioactive Drug Research Committee data from a 30-y period and identify changes that might make regulations governing such committees more consistent with current scientific knowledge and health policy.
Page 1220
Delbeke and colleagues provide new consensus procedure guidelines to assist physicians in recommending, performing, interpreting, and reporting the results of SPECT/CT for imaging of adult and pediatric patients.
Page 1227
ON THE COVER
The possibility of generating 3-dimensional PET/CT images, such as illustrated here, has been demonstrated. Previously, these detailed anatomic renderings were achievable with conventional imaging but not with PET. Despite some limitations of the initial pilot study, the findings are exciting and provide the impetus for future validation studies in controlled experiments. Additionally, the technique appears to show potential for guiding surgical procedures and for adding important diagnostic information that may herald new applications for PET/CT.

SEE PAGE 1085







