Uren reviews the relatively brief history and current clinical significance of the sentinel lymph node biopsy technique and looks to the literature for answers to key questions about the efficacy and safety of this increasingly important approach.
Page 191
Reilly surveys the development of pretargeting strategies using monoclonal antibodies and, previewing an article in this issue of JNM, outlines the promise and challenges of pretargeting using bispecific antibodies and radiolabeled haptens.
Page 196

Meyer and colleagues assess the application of voxelwise graphical analysis to the generation of high-quality parametric images of total volume of distribution of the novel PET tracer 18F-CPFPX in imaging of cerebral adenosine receptors.
Page 200
Kim and colleagues research the reproducibility and reliability of 11C-DASB parametric imaging of binding potential and relative blood flow for PET studies of serotonin transporters in humans.
Page 208
Ciarmiello and colleagues report on findings, including PET data, indicating that white-matter volume loss may precede gray-matter atrophy long before onset of clinical symptoms of Huntington's disease and that this loss may be associated with neuronal dysfunction in early disease.
Page 215
Ezziddin and colleagues explore predisposing factors for uptake of both 111In-pentetreotide and 123I/131I-MIBG in scintigraphy of patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic endocrine tumors, with special reference to new World Health Organization tumor classifications.
Page 223
Rossi and colleagues present findings from an observational multicenter trial of a standardized sentinel lymph node biopsy protocol in patients with primary cutaneous melanoma.
Page 234
Fang and colleagues investigate correlations between serum interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels and response to 89SrCl2 as palliative therapy in patients with painful bone metastases.
Page 242
Kraeber-Bodéré and colleagues report on the results of a phase I study of the safety, targeting, and antitumor efficacy of pretargeted radioimmunotherapy using an anti-carcinoembryonic antigen bispecific antibody and a radiolabeled hapten in patients with nonmedullary or medullary thyroid carcinoma.
Page 247

Pauleit and colleagues compare the diagnostic capabilities of 18F-FET and 18F-FDG PET in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, including the ability to differentiate between tumor and inflammation.
Page 256
Kwee and colleagues assess 18F-fluorocholine uptake in malignant and benign areas of the prostate at 2 time points to determine the suitability of delayed or dual-phase 18F-fluorocholine PET for localizing malignancy.
Page 262
Padmanabhan and colleagues evaluate radionuclide and optical methods to measure changes in human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene expression in tumor cells before and after 5-fluorouracil treatment.
Page 270

Zenz and colleagues study the incidence and clinical picture of bone marrow transplantation nephropathy in patients receiving a radiolabeled anti-CD66 antibody before allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
Page 278
Even-Sapir and colleagues report on the comparative abilities of 99mTc-MDP planar bone scintigraphy, SPECT, 18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT in the detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer.
Page 287
Allen-Auerbach and colleagues investigate the incidence of missed pulmonary micronodules on PET/CT studies acquired during shallow breathing and discuss the implications of their findings for comprehensive cancer staging.
Page 298
Heiss and Herholz present an in-depth review of brain receptor imaging and highlight ligands and receptors that are already in clinical use and are likely to influence new drug development and enhance highly specific neurologic imaging.
Page 302

Slifstein and colleagues perform whole-body radiation dosimetry of 11C-raclopride in healthy humans to derive the maximum allowable single-study dose under U.S. federal regulations and compare this to the dose range currently used in PET research studies.
Page 313
Garcia and colleagues describe a novel system developed to assist physicians in detecting renal obstruction in patients undergoing pre- and postfurosemide 99mTc-MAG3 scanning.
Page 320
Kim and colleagues report on a factor analysis technique for extracting blood input function and myocardial time–activity curve from dynamic small-animal PET images of the rodent heart as a method for overcoming imaging problems caused by cardiac motion.
Page 330
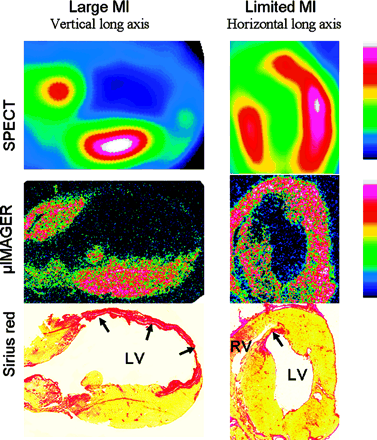
Maskali and colleagues assess a novel gated SPECT imaging technique for predicting and quantifying variable left ventricular remodeling in a rat infarct model.
Page 337
Tipre and colleagues explore in vivo inhibition of defluorination of 18F-FCWAY in a rat model to improve use of the tracer in PET assessment of brain regional 5-HT1A receptor densities.
Page 345

Gunn and colleagues investigate whether somatostatin receptor (sst) gene expression is upregulated in vitro by exposure of sst-expressing cells to low- or high-dose octreotide therapy over varying times.
Page 354
Liu and colleagues detail initial studies of the mechanism of intracellular antisense targeting through measurements of in situ transcription, immunofluorescence, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, 32P-labeled uridine-5′-triphosphate incorporation, accumulations of 99mTc-labeled DNAs, and messenger RNA transcription.
Page 360
ON THE COVER
In this illustration of the possible effect of different numbers of radiotracer injections (X) on the outcome of lymphoscintigraphy, arrows represent lymphatic flow. A single injection (left) might enter only central lymphatic vessels, missing those potentially containing malignant cells. Moreover, the large volume of tracer used might cause nonsentinel nodes to be detected. Multiple injections (right) might enter peripheral lymphatic vessels and thus detect sentinel nodes containing metastatic melanoma cells. Moreover, the small volume of tracer used might help to avoid detection of second-tier nodes.








