Lewis reviews past research and current promise of the sodium/iodide symporter in reporter gene imaging and therapy and previews an article on the same topic in this issue.
Page 1
DeNardo comments on the scientific significance of a study in this issue on the use of 2 biologic agents to achieve targeted molecular therapeutic synergy by coactivation or blockade of cancer cell signaling pathways.
Page 4
Van Den Bossche and colleagues assess the ability of sequential 99mTc-depreotide scintigraphy to provide accurate and very early prediction of responses to endocrine therapy in patients with advanced breast cancer.
Page 6

Kalff and colleagues evaluate prognostic information obtained from postchemoradiation 18F-FDG PET imaging in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer undergoing radical surgery with curative intent.
Page 14
Lodge and colleagues compare the performance of 2- and 3-dimensional acquisition in whole-body 18F-FDG PET imaging using a lutetium oxyorthosilicate–based tomograph in patients undergoing oncology management evaluations.
Page 23
Metser and colleagues report on the utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT, with data from both the PET and the unenhanced CT portions of the study, in distinguishing benign from malignant adrenal lesions in patients with cancer.
Page 32
Buchert and colleagues detail the use of 11C-(+)McN5652 PET to assess age-related declines in available brain serotonin transporter in young, healthy individuals and the implications of these results for age-dependent correction in SPECT and PET studies.
Page 38
Fujimura and colleagues investigate the binding of the PET ligand 18F-FEDAA1106 to peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in healthy men and present a method for quantitative analysis of findings.
Page 43
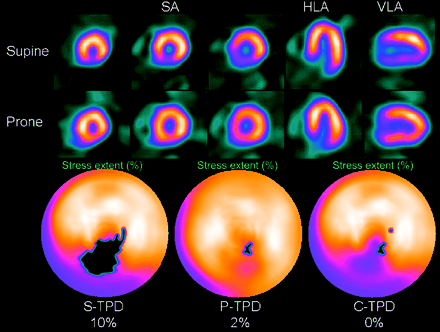
Nishina and colleagues report on the comparative diagnostic value of prone imaging alone and combined acquisition in myocardial perfusion SPECT assessment for coronary artery disease in a large series of patient studies.
Page 51
Sdringola and colleagues use dipyridamole PET to compare changes in perfusion defects throughout the coronary vascular tree and in worst flow-limiting stenoses as predictors of coronary events in long-term follow-up and relate these changes to treatment regimens.
Page 59
Schinkel and colleagues research the utility of 18F-FDG SPECT imaging in predicting improvement of left ventricular function and heart failure symptoms after coronary revascularization in patients with diabetes mellitus and ischemic dysfunction.
Page 68
Berman and colleagues review current applications and interactions of noninvasive imaging approaches—including nuclear cardiology, cardiac CT, and cardiac magnetic resonance—in assessment of patients with suspected coronary artery disease.
Page 74
Matsumoto and colleagues describe a new dedicated PET unit that offers 3-dimensional continuous-emission and spiral-transmission scanning and evaluate its performance using the National Electrical Manufacturers Association NU 2-2001 standard.
Page 83
Beyer and colleagues investigate the effect of CT truncation in whole-body PET/CT imaging of large patients and describe the efficacy of an extended field-of-view correction technique.
Page 91

Cropley and colleagues estimate radiation-absorbed doses of the dopamine D1 receptor radioligand 11C-NNC 112 in humans, using dynamic whole-body PET imaging in healthy volunteers.
Page 100

Ferrari and colleagues calculate values for dosimetry of locoregional brain treatments with several 90Y-labeled compounds and report initial safety and efficacy results in 12 patients treated with 90Y-DOTATOC.
Page 105
Zhang and colleagues report on quantitative PET imaging of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression with the dimeric RGD peptide 18F-FRGD2 and evaluate its promise in antiangiogenic therapy assessment and drug development.
Page 113
Capello and colleagues evaluate the biodistributions of novel peptide compounds RGD-111In-DTPA-octreotate and 125I-RGD-octreotate in rats and investigate the caspase-3 activation of the unlabeled compound RGD-DTPA-octreotate in vitro.
Page 122
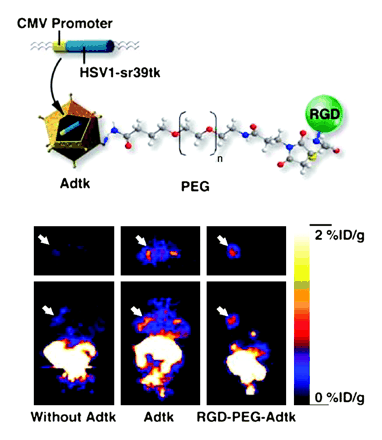
Xiong and colleagues describe chemical modification of an adenovirus targeting integrin αvβ3–expressing tumors and outline methods for PET monitoring of in vivo transfectivity of vectors in this promising gene delivery approach.
Page 130
Förster and colleagues detail the results of 4 different methods designed to reduce kidney uptake of radiolabeled DOTA-biotin for multistep immune targeting approaches in radioimmunotherapy.
Page 140

van Waarde and colleagues compare the biodistribution and tumor selectivity of 4 PET tracers (2 σ-receptor ligands and 2 11C-labeled compounds) with those of 18F-FLT and 18F-FDG in a rat model.
Page 150
Aruva and colleagues report on the synthesis of a novel 99mTc-pentapeptide with high affinity for α-chain-fibrin and assess its efficacy in imaging experimental deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in a swine model.
Page 155

Rimoldi and colleagues research the feasibility and accuracy of quantifying subendocardial and subepicardial myocardial blood flow and relative coronary flow reserves using 15O-labeled water and 3-dimensional–only PET in a swine model.
Page 163
DeGrado and colleagues report on validation studies of 18F-FTP as a metabolically trapped fatty acid oxidation probe in an isolated perfused rat heart model, examining effects of both hypoxia and changes in exogenous fatty acid availability.
Page 173
Vadysirisack and colleagues investigate whether posttranslational processing and cell-surface trafficking of the sodium/iodide (NIS) symporter affect mediated radioiodide uptake in cells expressing exogenous NIS and discuss the implications for monitoring gene therapy.
Page 182
ON THE COVER
A replication-deficient Ad vector carrying HSV1-39tk packed as a reporter gene on CMV promoter has successfully been modified using bifunctional PEG. The natural tropism of the virus was ablated even at a low rate of modification. The addition of cyclic RGD peptide enhanced transduction in cells expressing integrin αvβ3. This enhancement depended on binding of the peptide to integrin and was independent of viral receptors. Trans duction in nontarget tissues was markedly decreased after intravenous delivery of the modified vector, suggesting that PEGylation may help reduce in vivo sequestration of the vector.