Belhocine reviews recent reports on the role of 18F-FDG PET imaging as a reliable means of monitoring after therapy for cervical cancer.
Schäfers and colleagues use gated SPECT to assess functional remodeling after partial left ventriculectomy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.

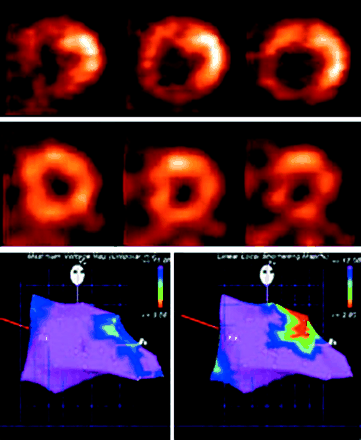
Graf and colleagues compare nonfluoroscopic electroanatomic mapping with SPECT perfusion and PET metabolic imaging in the assessment of myocardial viability in patients with coronary artery disease.
Fricke and colleagues report on a method to improve coregistration and reduce artifacts resulting from miasalignment in attenuation-corrected myocardial perfusion SPECT.
Koepfli and colleagues use PET to explore the effects of long-term β-receptor blocker treatment on myocardial blood flow and coronary vasodilatory capacity in patients with coronary artery disease.
Lai and colleagues devise a prognostic scoring system based on clinical, treatment, and laboratory factors to indicate which patients could benefit most from 18F-FDG PET restaging for salvage therapy in recurrent cervical cancer.
Keidar and colleagues compare 18F-FDG PET/CT with side-by-side PET and CT in suspected recurrent lung cancer and evaluate the relative effects on patient management.
Signore and colleagues report on 99mTc-interleukin 2 scintigraphy as a means of measuring tumor infiltration to identify patients with suspected melanoma who may benefit from immunotherapy.
Spence and colleagues look at possible diagnostic benefits in delaying the interval between 18F-FDG administration and PET data acquisition in imaging gliomas.
Nguyen and colleagues assess the long-term benefits of radionuclide therapy with 111In-pentetreotide and 131I-MIBG in patients with advanced-stage gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors uncontrolled by other therapies.
Shu-Hang and colleagues evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of 18F-FDG PET in detection of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma in patients after questionable MRI findings.
Cobben and colleagues investigate the utility of 18F-FLT PET in staging and restaging of disease in patients with non–small cell lung cancer.
Schechter and colleagues report on the dosimetric properties of 99mTc-ethylene dicysteine C225 as a novel diagnostic agent in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and as a possible screening agent to select candidates for C225 therapy.
Lorberboym and colleagues assess functional imaging with 123I-FP-CIT in patients with cerebrovascular disease to identify those who will most benefit from treatment for vascular parkinsonism.
Schwarz and colleagues provide data on the decline in dopamine transporter binding in Parkinson’s disease and present evidence for a new model of disease progression.
Bennink and colleagues report on the use of 99mTc-HMPAO white blood cell scintigraphy as a reliable, noninvasive tool both in predicting therapeutic re-sponse and in follow-ups of patients with ulcerative colitis.
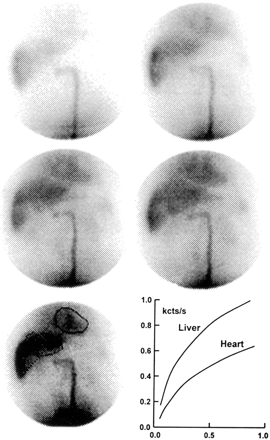
Vajro and colleagues assess the clinical utility of 99mTc-pertechnetate per-rectal portal scintigraphy as a minimally invasive tool for better assessment and follow-up of portal hypertension in children with chronic cholestasis.
Krausz and colleagues report changes in regional cerebral blood flow in patients both before and after treatment for mild hypothyroidism.
Capello and colleagues investigate the increased therapeutic potential of linking RGD peptides to somatostatin analogs and discuss possible clinical applications.
Meine and colleagues review the role of nuclear medicine in the combined assessment of myocardial perfusion and left ventricular function, including the ability of new modalities to enhance the diagnosis and prognosis of coronary artery disease.
Wessels and colleagues analyze reported marrow dosimetry results from radioimmunotherapy trials and propose a standard, benchmark method for marrow dosimetry for radiolabeled antibodies.
Mawlawi and colleagues describe the 2- and 3D performance characteristics and whole-body imaging suitability of a newly developed PET/CT scanner using the National Electrical Manufacturers Association NU94 and NU01 standards.
Anton and colleagues report on an in vitro demonstration of the usefulness of a vector coexpressing HSV1-tk and VEGF for noninvasive imaging of expression of a therapeutic transgene.
Eerd and colleagues test the imaging characteristics of 111In-labeled LTB4 antagonist DPC11870 in New Zealand White rabbits with experimental pulmonary aspergillosis infection.
Sugiyama and colleagues report on investigations in a mouse model on the feasibility of 18F-FLT as a PET tracer for imaging tumor proliferation and monitoring response to therapy.
van Montfrans and colleagues evaluate a scintigraphic technique to assess lymphocyte homing to the colon in experimental colitis in a rat model.
Suzuki and colleagues image endogenous gene expression in brain cancer using peptide nucleic acid antisense agents modified to enable crossing of biologic membrane barriers and access to intracellular target mRNA molecules.
Chen and colleagues introduce and evaluate an improved peptide tracer for microPET imaging in brain tumor models and outline its potential applications in both imaging and therapy.
Schaffland and colleagues research 131I-labeling of rituximab using 2 different radioiodination degrees as part of a search for optimal conditions for radioimmunotherapy of lymphoma.
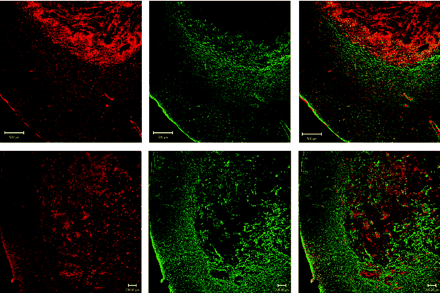
ON THE COVER
This patient was judged as showing positive findings on 99mTc-scintigraphy. Despite the small size of the tumor (green arrow), regional lymph nodes are detectable (red arrow), reflecting an active immune response inside the primary and metastatic tumors. The target-to-background radioactivity ratio is 1.44. CD25 staining shows a mild positivity for neoplastic cells and a strong, diffuse positivity for lymphocytes.