Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of applying a previously described dose strategy based on 99mTc-pertechnetate thyroid uptake under thyrotropin suppression (TcTUs) to radioiodine therapy for unifocal thyroid autonomy.
Methods
A total of 425 consecutive patients (302 females, 123 males; age 63.1±10.3 years) with unifocal thyroid autonomy were treated at three different centres with 131I, using Marinelli’s formula for calculation of three different absorbed dose schedules: 100–300 Gy to the total thyroid volume according to the pre-treatment TcTUs (n=146), 300 Gy to the nodule volume (n=137) and 400 Gy to the nodule volume (n=142).
Results
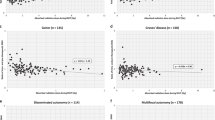
Successful elimination of functional thyroid autonomy with either euthyroidism or hypothyroidism occurred at a mean of 12 months after radioiodine therapy in 94.5% of patients receiving 100–300 Gy to the thyroid volume, in 89.8% of patients receiving 300 Gy to the nodule volume and in 94.4% receiving 400 Gy to the nodule volume. Reduction in thyroid volume was highest for the 100–300 Gy per thyroid and 400 Gy per nodule strategies (36±19% and 38±20%, respectively) and significantly lower for the 300 Gy per nodule strategy (28±16%; p<0.01).
Conclusion
A dose strategy based on the TcTUs can be used independently of the scintigraphic pattern of functional autonomous tissue in the thyroid.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reinhardt MJ, Joe A, von Mallek D, Zimmerlin M, Manka-Waluch A, Palmedo H, et al. Dose selection for radioiodine therapy of borderline hyperthyroid patients with multifocal and disseminated autonomy on the basis of 99mTc-pertechnetate thyroid uptake. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:480–485
Bähre M, Hilgers R, Lindemann C, Emrich D. Physiological aspects of the thyroid trapping function and its suppression in iodine deficiency using 99mTc pertechnetate. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1987;115:175–182
Emrich D, Erlenmaier U, Pohl M, Luig H. Determination of the autonomously functioning volume of the thyroid. Eur J Nucl Med 1993;20:410–414
Miller JM, Horn RC, Block MA. The autonomous functioning thyroid nodule in the evolution of nodular goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1967;27:1264–1274
Ramelli F, Studer H, Bruggisser D. Pathogenesis of thyroid nodules in multinodular goiter. Am J Pathol 1982;109:215–223
Studer H, Ramelli F. Simple goiter and its variants: euthyroid and hyperthyroid multinodular goiters. Endocr Rev 1982;3:40–61
Peter HJ, Gerber H, Studer H, Smeds S. Pathogenesis of heterogeneity in human multinodular goiter. A study on growth and function of thyroid tissue transplanted onto nude mice. J Clin Invest 1985;76:1992–2002
Studer H, Peter HJ, Gerber H. Natural heterogeneity of thyroid cells: the basis for understanding thyroid function and nodular goiter growth. Endocr Rev 1989;10:125–135
Studer H, Peter HJ, Gerber H. Morphologic and functional changes in developing goiters. In: Hall R, Köbberling J, eds. Thyroid disorders associated with iodine deficiency and excess. New York: Raven Press; 1985; p.227–241
Brunn J, Block U, Ruf G, Bos I, Kunze WP, Scriba PC. Volumetric analysis of thyroid lobes by real-time ultrasound. Deut Med Wochenschr 1981;106:1338–1340
Mahlstedt J, Czirik J. TcTU—a A program for the IMAC processing system for 99mTc-thyroid uptake test in thyroid diagnostics. Nuc Compact 1981;12:37–40
Marinelli LD, Quinby EH, Hine GJ. Dosage determination with radioactive isotopes. Practical considerations in therapy and protection. Am J Roentgenol 1948;59:260–281
Dunkelmann S, Endlicher D, Prillwitz A, Rudolph F, Groth P, Schümichen C. Results of a TcTUs-optimized radioiodine therapy of multifocal and disseminated functional thyroid autonomy. Nuklearmedizin 1999;38:131–139
Meller J, Wisheu S, Munzel U, Behe M, Gratz S, Becker W. Radioiodine therapy for Plummer’s disease based on the thyroid uptake of technetium-99 m pertechnetate. Eur J Nucl Med 2000;27:1286–1291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinhardt, M.J., Biermann, K., Wissmeyer, M. et al. Dose selection for radioiodine therapy of borderline hyperthyroid patients according to thyroid uptake of 99mTc-pertechnetate: applicability to unifocal thyroid autonomy?. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33, 608–612 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-0051-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-0051-9